
Draw labelled diagram of Haber process for the manufacture of ammonia and write chemical equation?
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: Ammonia is manufactured by reacting nitrogen with hydrogen gas in presence of a catalyst. The nitrogen and hydrogen gas in a fixed ratio with catalysts are added into the reacting tank. The ammonia gas forms which converted into liquid and separated
Complete Step by step answer: The conversion of nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas into ammonia by using a metal catalyst is known as the Haber process.
In the Haber process, nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen gas in presence of a catalyst and at high temperature and pressure.
The chemical reaction is as follows:
\[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\,{\text{ + 3}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\,\mathop \rightleftarrows \limits^{{\text{Fe}}} {\text{2}}\,{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(g)}}\,{\text{ + }}\,{\text{heat}}\]
The reaction is exothermic because heat is released during the reaction.
Generally, the catalyst used in the Haber process is iron metal. Molybdenum catalysts are also used in the Haber process. Some promoter which increases the rate of reaction is also added. The promoters are calcium oxide, potassium oxide.
A labelled diagram of the Haber process for the manufacture of ammonia is shown as follows:
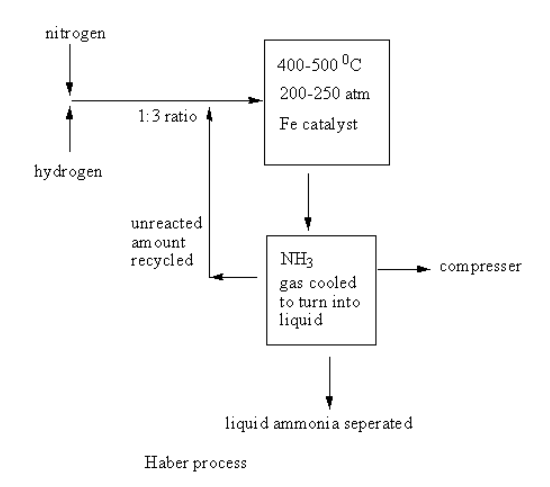
The nitrogen and hydrogen gases are taken into the reacting cylinder in ratio. The temperature and pressure are controlled and the iron catalyst is added. The reaction takes place and ammonia gas forms. This ammonia gas goes into a compressor where it gets cooled and converted into liquid. The liquid ammonia is separated.
Note: The formation of ammonia from the oxidation of nitrogen is known as the Haber process. Ostwald's process is associated with the Haber process. The formation of nitric acid by the catalytic oxidation of ammonia is known as the Ostwald process. In the first step, ammonia is converted into nitrogen oxide. When ammonia reacts with oxygen in presence of platinum catalyst it forms nitrogen oxide. In the second step, the nitrogen oxide gas converts into nitrogen dioxide, and this nitrogen dioxide gas reacts with water to form nitric acid.
Complete Step by step answer: The conversion of nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas into ammonia by using a metal catalyst is known as the Haber process.
In the Haber process, nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen gas in presence of a catalyst and at high temperature and pressure.
The chemical reaction is as follows:
\[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\,{\text{ + 3}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\,\mathop \rightleftarrows \limits^{{\text{Fe}}} {\text{2}}\,{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(g)}}\,{\text{ + }}\,{\text{heat}}\]
The reaction is exothermic because heat is released during the reaction.
Generally, the catalyst used in the Haber process is iron metal. Molybdenum catalysts are also used in the Haber process. Some promoter which increases the rate of reaction is also added. The promoters are calcium oxide, potassium oxide.
A labelled diagram of the Haber process for the manufacture of ammonia is shown as follows:

The nitrogen and hydrogen gases are taken into the reacting cylinder in ratio. The temperature and pressure are controlled and the iron catalyst is added. The reaction takes place and ammonia gas forms. This ammonia gas goes into a compressor where it gets cooled and converted into liquid. The liquid ammonia is separated.
Note: The formation of ammonia from the oxidation of nitrogen is known as the Haber process. Ostwald's process is associated with the Haber process. The formation of nitric acid by the catalytic oxidation of ammonia is known as the Ostwald process. In the first step, ammonia is converted into nitrogen oxide. When ammonia reacts with oxygen in presence of platinum catalyst it forms nitrogen oxide. In the second step, the nitrogen oxide gas converts into nitrogen dioxide, and this nitrogen dioxide gas reacts with water to form nitric acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




