
Draw diagrams of typical monocot and dicot leaves to show their venation pattern
Answer
513.9k+ views
Hint: The flowering plants have been divided into two major groups called: the Dicots and the Monocots. Dicots have two cotyledons and monocots and one single cotyledon. It is a classification of angiosperms.
Complete answer:
The plant’s on the basis of the number of cotyledons present are divided into monocot and dicot.
Major morphological differences between monocots and dicots-
A number of cotyledons: The number of cotyledons found in the embryo is the actual basis for distinguishing the two classes of angiosperms, and is the source of the names Monocotyledonae i.e one cotyledon and Dicotyledonae i.e two cotyledons. The cotyledons actually are the "seed leaves" produced by the embryo. They serve to provide nutrition. An example of monocot is maize, and dicot is the gram.
Pollen structure: The monocots had pollen with a single furrow or pore through the outer layer (monosulcate), but most dicots are descended from a plant that developed three furrows or pores in its pollen (triporate).
Leaf veins: In monocots, there are usually a number of major leaf veins which run parallel to the length of the leaf whereas, in dicots, there are usually numerous Auxillary veins that reticulate between the major ones.
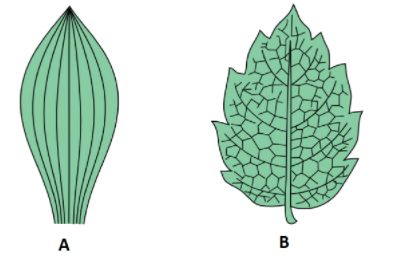
Thus, A- Monocot leaves(Parallel venation) B- Dicot leaves(Reticulate venation)
Note: Monocot plants mostly have fibrous root system. All the plants of the grass family belong to the monocot. Number of flower parts - If you count the number of petals, stamens, or other floral parts, in monocot flowers tend to have a number of parts that is divisible by three, usually three or six. Dicot flowers on the have parts in multiples of four or five (four, five, ten, etc.).
Complete answer:
The plant’s on the basis of the number of cotyledons present are divided into monocot and dicot.
Major morphological differences between monocots and dicots-
A number of cotyledons: The number of cotyledons found in the embryo is the actual basis for distinguishing the two classes of angiosperms, and is the source of the names Monocotyledonae i.e one cotyledon and Dicotyledonae i.e two cotyledons. The cotyledons actually are the "seed leaves" produced by the embryo. They serve to provide nutrition. An example of monocot is maize, and dicot is the gram.
Pollen structure: The monocots had pollen with a single furrow or pore through the outer layer (monosulcate), but most dicots are descended from a plant that developed three furrows or pores in its pollen (triporate).
Leaf veins: In monocots, there are usually a number of major leaf veins which run parallel to the length of the leaf whereas, in dicots, there are usually numerous Auxillary veins that reticulate between the major ones.

Thus, A- Monocot leaves(Parallel venation) B- Dicot leaves(Reticulate venation)
Note: Monocot plants mostly have fibrous root system. All the plants of the grass family belong to the monocot. Number of flower parts - If you count the number of petals, stamens, or other floral parts, in monocot flowers tend to have a number of parts that is divisible by three, usually three or six. Dicot flowers on the have parts in multiples of four or five (four, five, ten, etc.).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




