
Draw a well-labeled diagram of the nucleus
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: These are the cell organelle which is found in eukaryotic organisms that contain genetic material of cells. The main function is it regulates the activities of cells.
Complete answer:
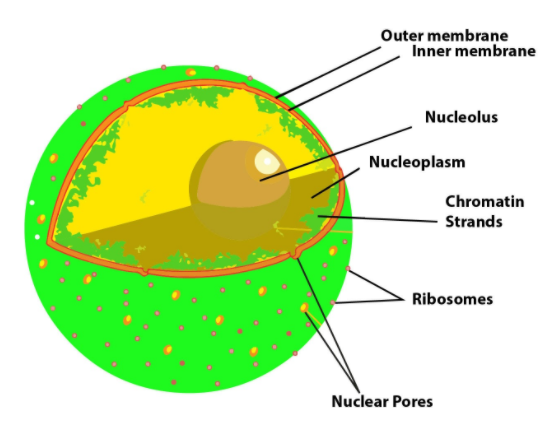
-It is a double membrane-bound organelle mainly found in eukaryotic cells.
-It contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction.
-It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is commonly the most prominent organelle in a cell accounting for about 10 percent of the cell’s volume.
-The nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell or the cytoplasm, by a nuclear membrane.
-As the nucleus regulates the integrity of genes and gene expression, it is also referred to as the control center of a cell.
-The structure of a nucleus encompasses the nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, chromosomes, and nucleolus.
-The nuclear membrane is a double-layered structure that encloses the contents of the nucleus. The outer layer of the membrane is connected to the endoplasmic reticulum.
-Nucleoplasm is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope. It supports the nucleus by helping to maintain its shape.
-Contained within the nucleus is a dense, membrane-less structure composed of RNA and proteins called the nucleolus.
-The nucleus is the organelle that houses chromosomes.
Note: The chromatin is further classified into heterochromatin and euchromatin based on the functions. The former type is a highly condensed, transcriptionally inactive form, mostly present adjacent to the nuclear membrane. On the other hand, euchromatin is a delicate, less condensed organization of chromatin, which is found abundantly in a transcribing cell.
Complete answer:

-It is a double membrane-bound organelle mainly found in eukaryotic cells.
-It contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction.
-It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is commonly the most prominent organelle in a cell accounting for about 10 percent of the cell’s volume.
-The nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell or the cytoplasm, by a nuclear membrane.
-As the nucleus regulates the integrity of genes and gene expression, it is also referred to as the control center of a cell.
-The structure of a nucleus encompasses the nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, chromosomes, and nucleolus.
-The nuclear membrane is a double-layered structure that encloses the contents of the nucleus. The outer layer of the membrane is connected to the endoplasmic reticulum.
-Nucleoplasm is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope. It supports the nucleus by helping to maintain its shape.
-Contained within the nucleus is a dense, membrane-less structure composed of RNA and proteins called the nucleolus.
-The nucleus is the organelle that houses chromosomes.
Note: The chromatin is further classified into heterochromatin and euchromatin based on the functions. The former type is a highly condensed, transcriptionally inactive form, mostly present adjacent to the nuclear membrane. On the other hand, euchromatin is a delicate, less condensed organization of chromatin, which is found abundantly in a transcribing cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




