
Draw a velocity-time graph for a uniform accelerated motion. What does its slope depict?
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: Use relation between acceleration, velocity and time to find the nature of the graph. The Velocity-time graph gives acceleration as slope. In non-uniform motion acceleration changes, eventually slope changes. The slope is either increasing or decreasing. While, in uniform motion, the acceleration remains constant, thus slope remains the same.
Complete solution:
The velocity-time graph for a uniform accelerated motion is shown below.
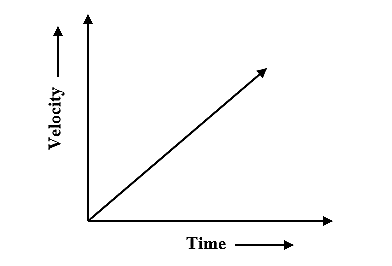
We know formula for acceleration is given by,
$a=\dfrac {v}{ t }$
where,
a: Acceleration
v: Velocity
t : Time
From the above equation, it can be understood that the slope calculated from the velocity-time graph gives acceleration. Thus, the velocity-time graph of a uniformly accelerated motion is a straight line graph inclining towards the time axis on the X-axis. If the body is moving with a positive constant acceleration then the graph slopes upward. In case, if the body is moving with negative constant acceleration then the graph slopes downward.
Additional Information:
If the acceleration of the body is zero then the slope of the graph will also be zero. Then, the graph will just be a straight horizontal line with zero slope. Such a motion is known as uniform motion with zero acceleration. The graph for zero acceleration is shown below.
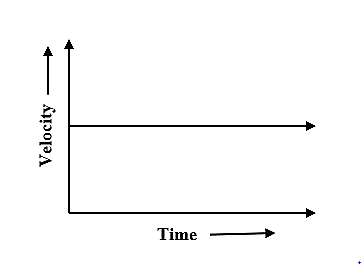
Note:
Students must not confuse between the nature of the graph for a uniform accelerated motion and non-uniform accelerated motion. The velocity-time graph for uniform accelerated motion is a straight line. Whereas, for non-uniform accelerated motion it gives a curved line. If we draw a distance versus time graph, it will show the same nature of graph for uniform motion and non-uniform motion as it is in velocity versus time graph.
Complete solution:
The velocity-time graph for a uniform accelerated motion is shown below.

We know formula for acceleration is given by,
$a=\dfrac {v}{ t }$
where,
a: Acceleration
v: Velocity
t : Time
From the above equation, it can be understood that the slope calculated from the velocity-time graph gives acceleration. Thus, the velocity-time graph of a uniformly accelerated motion is a straight line graph inclining towards the time axis on the X-axis. If the body is moving with a positive constant acceleration then the graph slopes upward. In case, if the body is moving with negative constant acceleration then the graph slopes downward.
Additional Information:
If the acceleration of the body is zero then the slope of the graph will also be zero. Then, the graph will just be a straight horizontal line with zero slope. Such a motion is known as uniform motion with zero acceleration. The graph for zero acceleration is shown below.

Note:
Students must not confuse between the nature of the graph for a uniform accelerated motion and non-uniform accelerated motion. The velocity-time graph for uniform accelerated motion is a straight line. Whereas, for non-uniform accelerated motion it gives a curved line. If we draw a distance versus time graph, it will show the same nature of graph for uniform motion and non-uniform motion as it is in velocity versus time graph.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




