
Draw a triangle of sides 5 cm and construct its incircle. Write the radius of the incircle.
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: In this particular question use the concept that if all the sides of a triangle are equal than it is an equilateral triangle and in an equilateral triangle all angles are equal to 60 degrees, and later on in the solution use that the tan is the ratio of perpendicular to base, so use these concepts to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given data:
A triangle of sides 5 cm.
As we all know that in a triangle there are 3 sides.
So it is given that the length of the sides is 5 cm.
Let us consider a triangle ABC, with AB = BC = CA = 5cm as shown in the below figure.

As we all know that if a triangle has all sides same then it is called an equilateral triangle.
And in an equilateral triangle all angles are equal.
In a triangle the sum of all angles is 180 degrees.
So let that measure of one angle be x degrees.
So, ${x^o} + {x^o} + {x^o} = {180^o}$
$ \Rightarrow 3{x^o} = {180^o}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^o} = {60^o}$
So in an equilateral triangle the measure of all the angles are equal to 60 degrees.
Now we have to construct its incircle
Steps of construction
$\left( i \right)$ Draw a triangle ABC with sides 5 cm as above.
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Now draw the bisector of any two angles, say angle B and angle C, let these bisectors intersect at point O, as shown in the below figure.
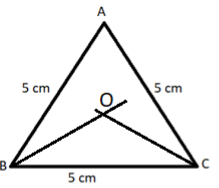
$\left( {iii} \right)$ Now draw a perpendicular from the intersection point O, of these two bisectors on line BC which cuts the line BC at point D, as shown in the below figure.
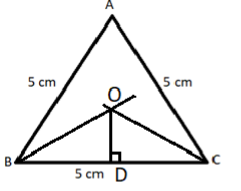
$\left( {iv} \right)$Now take a compass and in compass fill the length OD, with pointed end at O and pencil end at D and draw a circle which touches all the three sides as shown in the below figure.
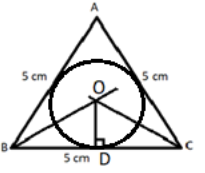
So this is the required incircle with center O.
Now we have to find out the radius of the incircle.
As shown in the above figure OD is the radius of the circle.
Now OB is a bisector of $\angle ABD$.
Therefore, $\angle OBD = \dfrac{{\angle ABD}}{2} = \dfrac{{{{60}^0}}}{2} = {30^0}$
And OD is perpendicular on BC, so BD = $\dfrac{{BC}}{2} = \dfrac{5}{2} = 2.5$ cm
Now in triangle OBD, tan x = (perpendicular/base).
Therefore, $\tan {30^o} = \dfrac{{OD}}{{BD}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan {30^o} = \dfrac{{OD}}{{2.5}}$
$ \Rightarrow OD = 2.5\tan {30^o}$
$ \Rightarrow OD = 2.5 \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = 1.44 \simeq 1.5$ cm
So this is the required radius of the incircle.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall that the bisector of any angle is divide the angle into two equal halves, and always recall the steps of construction which is stated above, these steps are the basis of the construction, without these steps we cannot draw the incircle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given data:
A triangle of sides 5 cm.
As we all know that in a triangle there are 3 sides.
So it is given that the length of the sides is 5 cm.
Let us consider a triangle ABC, with AB = BC = CA = 5cm as shown in the below figure.

As we all know that if a triangle has all sides same then it is called an equilateral triangle.
And in an equilateral triangle all angles are equal.
In a triangle the sum of all angles is 180 degrees.
So let that measure of one angle be x degrees.
So, ${x^o} + {x^o} + {x^o} = {180^o}$
$ \Rightarrow 3{x^o} = {180^o}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^o} = {60^o}$
So in an equilateral triangle the measure of all the angles are equal to 60 degrees.
Now we have to construct its incircle
Steps of construction
$\left( i \right)$ Draw a triangle ABC with sides 5 cm as above.
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Now draw the bisector of any two angles, say angle B and angle C, let these bisectors intersect at point O, as shown in the below figure.

$\left( {iii} \right)$ Now draw a perpendicular from the intersection point O, of these two bisectors on line BC which cuts the line BC at point D, as shown in the below figure.

$\left( {iv} \right)$Now take a compass and in compass fill the length OD, with pointed end at O and pencil end at D and draw a circle which touches all the three sides as shown in the below figure.

So this is the required incircle with center O.
Now we have to find out the radius of the incircle.
As shown in the above figure OD is the radius of the circle.
Now OB is a bisector of $\angle ABD$.
Therefore, $\angle OBD = \dfrac{{\angle ABD}}{2} = \dfrac{{{{60}^0}}}{2} = {30^0}$
And OD is perpendicular on BC, so BD = $\dfrac{{BC}}{2} = \dfrac{5}{2} = 2.5$ cm
Now in triangle OBD, tan x = (perpendicular/base).
Therefore, $\tan {30^o} = \dfrac{{OD}}{{BD}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan {30^o} = \dfrac{{OD}}{{2.5}}$
$ \Rightarrow OD = 2.5\tan {30^o}$
$ \Rightarrow OD = 2.5 \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = 1.44 \simeq 1.5$ cm
So this is the required radius of the incircle.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall that the bisector of any angle is divide the angle into two equal halves, and always recall the steps of construction which is stated above, these steps are the basis of the construction, without these steps we cannot draw the incircle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

The plural of Chief is Chieves A True B False class 7 english CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE





