
Draw a ray to illustrate how a ray of light incident obliquely on one face of a rectangular glass slab of uniform thickness emerges.
Answer
613.2k+ views
Hint: In this question consider a glass slab of uniform thickness say (d) and an incident light ray incident at an angle $x_i$ on it. This ray will be reflected as well as refracted from this glass slab interface as the refractive index of air is somewhat different from that of the glass slab. This will help approaching the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The rectangular glass slab having uniform thickness say (d) is shown above in the figure.
As we know that the refractive index of glass is higher than the air.
So whenever a light ray is passing through the surface of the glass slab it bends towards the normal as shown in the figure, because glass is denser medium than air.
Now as we know the surface of the glass is smooth so the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection = $x_i$, as shown in the figure.
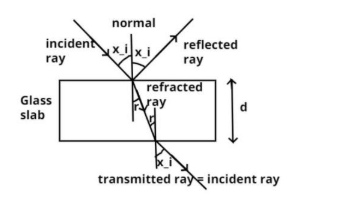
But the angle of refraction (r) is not the same to the angle of incidence.
Now when the ray of light travels inside the glass and reaches at the bottom surface of the glass slab it makes an angle with the normal equal to the angle of refraction (r) as shown in the figure.
Now when the ray of light passes out from the glass slab it bends away from the normal because at this time it travel into the less denser medium (i.e. from glass to the air) therefore it bends away from the normal and it makes an angle equal to the angle of the incidence with the normal as shown in the figure.
So this is the complete phenomenon of how a ray of light emerges when incident obliquely on one face of a rectangular glass slab of uniform thickness.
So this is the required answer.
Note: When a light ray travels from a medium of density or refractive index into another medium of different densities than the ray will be refracted. However if the ray travels in the same medium all throughout the journey then it is reflected. There are certain laws that are accompanied with reflection like, the angle of incidence will always be equal to angle of reflection. The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal ray will always be in the same plane.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The rectangular glass slab having uniform thickness say (d) is shown above in the figure.
As we know that the refractive index of glass is higher than the air.
So whenever a light ray is passing through the surface of the glass slab it bends towards the normal as shown in the figure, because glass is denser medium than air.
Now as we know the surface of the glass is smooth so the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection = $x_i$, as shown in the figure.

But the angle of refraction (r) is not the same to the angle of incidence.
Now when the ray of light travels inside the glass and reaches at the bottom surface of the glass slab it makes an angle with the normal equal to the angle of refraction (r) as shown in the figure.
Now when the ray of light passes out from the glass slab it bends away from the normal because at this time it travel into the less denser medium (i.e. from glass to the air) therefore it bends away from the normal and it makes an angle equal to the angle of the incidence with the normal as shown in the figure.
So this is the complete phenomenon of how a ray of light emerges when incident obliquely on one face of a rectangular glass slab of uniform thickness.
So this is the required answer.
Note: When a light ray travels from a medium of density or refractive index into another medium of different densities than the ray will be refracted. However if the ray travels in the same medium all throughout the journey then it is reflected. There are certain laws that are accompanied with reflection like, the angle of incidence will always be equal to angle of reflection. The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal ray will always be in the same plane.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




