
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Hyaline Cartilage.
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Cartilage is the kind of animal tissue found in areas like the nose, ears, and trachea of the physical body. A type of cartilage found on many joint surfaces; it contains no nerves or blood vessels, and its structure is comparatively simple.
Complete answer:
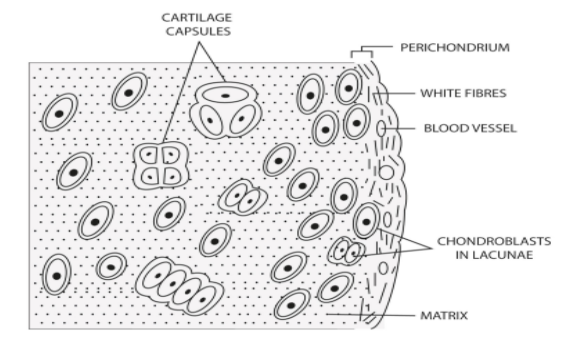
Additional Information:
-The cartilage is the tissue that is rigid and flexible than the bones and the muscles.
-The cartilage consists of various fibres including collagen, elastin, proteoglycans, and glycosaminoglycans.
-It is mostly found in the area around the ribcage, ear, nose, bronchi, etc.
-They sometimes hold body tubes due to the presence of collagen fibres.
-Cartilages are of three types: elastic cartilage, headline cartilage, and fibrocartilage.
-The cartilages vary depending upon the presence of collagen and proteoglycan.
-The blood vessels and nerves are not present inside the cartilage.
-By the process of diffusion through chondrocytes, nutrition is supplied to the body.
-It is mesodermal in origin which is derived from the mesoderm germ layer during embryogenesis.
-The cartilage shows very little repair capabilities.
-The cartilage cannot be observed simply by X-rays, it requires dye to stain then only it will appear on the X-ray.
Note: -The cartilage was first observed and discovered during the fourth century by Aristotle (384-322). The word cartilage was derived from the French and English word cartilage, meaning ‘cartilage’. In medical science, the word ‘chondro' is used to describe the cartilage. The cartilage is made up of chondroblasts cells and chondrocytes along with the matrix containing 10% aggrecan, 75% water, and a mixture of collagen and other substances.
-Bones such as ribs and cranial bones are protective structures for critical organs such as the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs. Bones are relatively inflexible than cartilage. Cartilages are also found in the covering of the ends of long bones in the synovial joints as articular cartilages. The smooth and slippery texture of the cartilage helps minimize friction in joints.
Complete answer:

Additional Information:
-The cartilage is the tissue that is rigid and flexible than the bones and the muscles.
-The cartilage consists of various fibres including collagen, elastin, proteoglycans, and glycosaminoglycans.
-It is mostly found in the area around the ribcage, ear, nose, bronchi, etc.
-They sometimes hold body tubes due to the presence of collagen fibres.
-Cartilages are of three types: elastic cartilage, headline cartilage, and fibrocartilage.
-The cartilages vary depending upon the presence of collagen and proteoglycan.
-The blood vessels and nerves are not present inside the cartilage.
-By the process of diffusion through chondrocytes, nutrition is supplied to the body.
-It is mesodermal in origin which is derived from the mesoderm germ layer during embryogenesis.
-The cartilage shows very little repair capabilities.
-The cartilage cannot be observed simply by X-rays, it requires dye to stain then only it will appear on the X-ray.
Note: -The cartilage was first observed and discovered during the fourth century by Aristotle (384-322). The word cartilage was derived from the French and English word cartilage, meaning ‘cartilage’. In medical science, the word ‘chondro' is used to describe the cartilage. The cartilage is made up of chondroblasts cells and chondrocytes along with the matrix containing 10% aggrecan, 75% water, and a mixture of collagen and other substances.
-Bones such as ribs and cranial bones are protective structures for critical organs such as the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs. Bones are relatively inflexible than cartilage. Cartilages are also found in the covering of the ends of long bones in the synovial joints as articular cartilages. The smooth and slippery texture of the cartilage helps minimize friction in joints.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




