
Draw a neat diagram of the AC dynamo and label the parts.
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: AC dynamo is also known as AC generator. AC dynamo works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
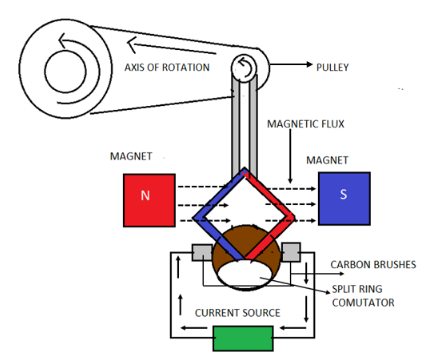
An AC dynamo has a rectangular rotating coil ABCD situated between two poles of a permanent magnet. A pulley is attached to the magnet. The magnet produces a magnetic flux near the rectangular coil. The inner parts of the two rings are insulated. The carbon brushes B1 and B2 are stationary and press separately on the rings R1and R2. These two rings are attached to an axle internally. This axle can be rotated mechanically from the outside so as to make the coil inside the magnetic field rotate. The outer parts of both brushes are connected to the galvanometer, so we can see the flow of electric current in the given circuit.
Additional Information: A dynamo is a generator that makes direct current with the help of a commutator. It consists of a rotating coil in between two permanent magnets. The commutator transforms alternating current to direct current by reversing the current direction in each and every cycle.
The kind of current that changes its course with changes in specific and similar time intervals is termed as alternating current or AC.
An AC dynamo or generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a coil placed in a magnetic field produces an electric current. A dynamo is generally used for low power requiring tasks like charging batteries of vehicles and other domestic uses.
Note: Make sure to label the poles of the permanent magnets properly. Changing the position of the north and south poles will change the direction of the magnetic field as well.
Complete step-by-step answer:

An AC dynamo has a rectangular rotating coil ABCD situated between two poles of a permanent magnet. A pulley is attached to the magnet. The magnet produces a magnetic flux near the rectangular coil. The inner parts of the two rings are insulated. The carbon brushes B1 and B2 are stationary and press separately on the rings R1and R2. These two rings are attached to an axle internally. This axle can be rotated mechanically from the outside so as to make the coil inside the magnetic field rotate. The outer parts of both brushes are connected to the galvanometer, so we can see the flow of electric current in the given circuit.
Additional Information: A dynamo is a generator that makes direct current with the help of a commutator. It consists of a rotating coil in between two permanent magnets. The commutator transforms alternating current to direct current by reversing the current direction in each and every cycle.
The kind of current that changes its course with changes in specific and similar time intervals is termed as alternating current or AC.
An AC dynamo or generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a coil placed in a magnetic field produces an electric current. A dynamo is generally used for low power requiring tasks like charging batteries of vehicles and other domestic uses.
Note: Make sure to label the poles of the permanent magnets properly. Changing the position of the north and south poles will change the direction of the magnetic field as well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




