
Draw a neat diagram of human respiratory system and label its following parts: Rings of cartilage, lung, bronchi, and alveolar sac.
Answer
531.7k+ views
Hint: Human respiratory system consists of series of organs that are involved in taking in oxygen and throwing put carbon dioxide. The respiratory system is lined with a mucous membrane which secretes mucus. The mucus collects smaller particles, such as pollen or smoke. Hairlike structures called cilia line the mucous membrane and move the particles stuck in the mucous membrane out of the nose.
Complete answer:
All the essential parts of human respiratory system are well-marked in the diagram given below:
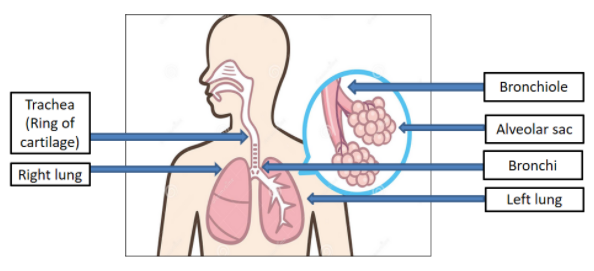
The lungs are a pair of spongy, air-filled organs found on either side of the chest (thorax). Humans have two lungs, a right, and a left lung. They are found in the chest thoracic cavity. The right lung is larger than the left, and has room in the chest with the heart.
There are tracheal loops in the trachea or windpipe, also known as ring of cartilages. Cartilage is a solid, but flexible tissue. Tracheal cartilages help to stabilize the trachea while also allowing it to rotate and flex during breathing. The trachea starts under the larynx and continues below the breastbone (sternum). It then splits into two smaller bronchial tubes: one bronchus per lung.
The bronchial tubes again break up to bring air into each lung's lobes. The right lung has three lobes, while the left lung only has two lobes that can support the heart.
Alveoli are small pockets of air in the lungs that take up the oxygen and keep your body moving. Alveoli are the workhorses of the respiratory system, but it's microscopic. The alveoli at the end of bronchial tubes are about four hundred and eighty million. The alveolar walls are extremely thin and consist of a single layer of tissues called epithelial cells and small blood vessels known as pulmonary capillaries. Blood is drained by oxygen and carbon dioxide in the capillary structures. The blood that is oxygenated then enters the venous tract. This vein is rich in oxygen and pumps the blood to the left part of the heart. The carbon dioxide of the blood that is left in the alveoli travels into our exhaled air and expels it.
Note: The human gas-exchange organ, the lung, is situated in the thorax, where its delicate tissues are covered by the bone and muscular thoracic cage. The lung supplies the tissues of the human body with a steady supply of oxygen and extracts the blood from the gaseous waste product, carbon dioxide. Atmospheric air is pumped in and out continuously through a pipe system called a conductive airway, which links the gas-exchange area to the outside of the body. Airways can be divided into upper and lower airway systems.
Complete answer:
All the essential parts of human respiratory system are well-marked in the diagram given below:

The lungs are a pair of spongy, air-filled organs found on either side of the chest (thorax). Humans have two lungs, a right, and a left lung. They are found in the chest thoracic cavity. The right lung is larger than the left, and has room in the chest with the heart.
There are tracheal loops in the trachea or windpipe, also known as ring of cartilages. Cartilage is a solid, but flexible tissue. Tracheal cartilages help to stabilize the trachea while also allowing it to rotate and flex during breathing. The trachea starts under the larynx and continues below the breastbone (sternum). It then splits into two smaller bronchial tubes: one bronchus per lung.
The bronchial tubes again break up to bring air into each lung's lobes. The right lung has three lobes, while the left lung only has two lobes that can support the heart.
Alveoli are small pockets of air in the lungs that take up the oxygen and keep your body moving. Alveoli are the workhorses of the respiratory system, but it's microscopic. The alveoli at the end of bronchial tubes are about four hundred and eighty million. The alveolar walls are extremely thin and consist of a single layer of tissues called epithelial cells and small blood vessels known as pulmonary capillaries. Blood is drained by oxygen and carbon dioxide in the capillary structures. The blood that is oxygenated then enters the venous tract. This vein is rich in oxygen and pumps the blood to the left part of the heart. The carbon dioxide of the blood that is left in the alveoli travels into our exhaled air and expels it.
Note: The human gas-exchange organ, the lung, is situated in the thorax, where its delicate tissues are covered by the bone and muscular thoracic cage. The lung supplies the tissues of the human body with a steady supply of oxygen and extracts the blood from the gaseous waste product, carbon dioxide. Atmospheric air is pumped in and out continuously through a pipe system called a conductive airway, which links the gas-exchange area to the outside of the body. Airways can be divided into upper and lower airway systems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




