
Draw a labelled diagram of the mature embryo sac of angiosperms.
Answer
533.2k+ views
Hint: Gametophyte of the angiosperms is also called embryo sac, usually it is a tiny cell and it contains a few nuclei and cytoplasm, which are again separated by the septa, embryo sac is mainly useful for the sexual reproduction in plants.
Complete answer:
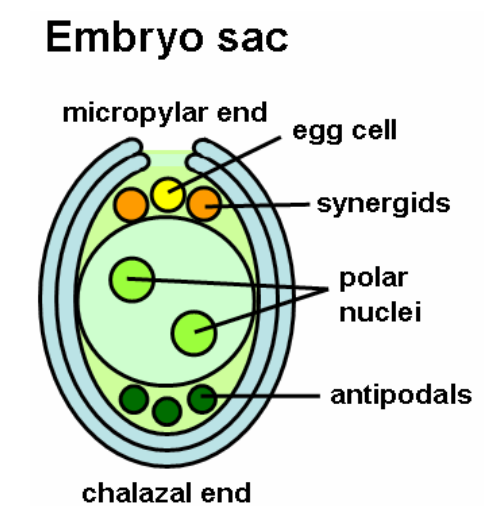
- In the plants which contain seed, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to female reproductive parts.
- Ovule mainly contains the three parts, where the first layer or part is called as integument
- The next one is the nucellus, this is considered a remnant of the megasporangium
- The last one is female gametophyte, it is usually haploid in nature, it is formed from the megaspore, and it is present in the center of the ovule
- This female gametophyte is considered as embryo sac in the angiosperms
- This megagametophyte purpose fully produces the egg cell for the fertilization.
> Structure of embryo sac:
- It consists of total six haploid cells, which does have any cell wall
- It consists of two haploid nucleus
- Embryo sac has two ends such as micropylar end and chalaza end
- Egg is present at the micropylar end
> Formation of embryo sac:
- It consists of two stages
- In first stage, meiosis of megaspore occurs and form the tetrad of haploid cells
- Among these, three cells disintegrate and one sustains and finally develops into an embryo sac
- First stage is named as megasporogenesis
- In the second stage mega gametogenesis occurs, resulting in the formation of 8 nucleate and 7 celled gametophytes.
- The polar nuclei, which moves to the center and forms the single diploid nuclei, it in turn combines with sperm and generates the triploid endosperm.
Note: After the fusion and the formation of triploid endosperm, the three nuclei which remain the antipodal cells, out of three, two converts to synergid cells, and other degenerates by itself
Complete answer:

- In the plants which contain seed, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to female reproductive parts.
- Ovule mainly contains the three parts, where the first layer or part is called as integument
- The next one is the nucellus, this is considered a remnant of the megasporangium
- The last one is female gametophyte, it is usually haploid in nature, it is formed from the megaspore, and it is present in the center of the ovule
- This female gametophyte is considered as embryo sac in the angiosperms
- This megagametophyte purpose fully produces the egg cell for the fertilization.
> Structure of embryo sac:
- It consists of total six haploid cells, which does have any cell wall
- It consists of two haploid nucleus
- Embryo sac has two ends such as micropylar end and chalaza end
- Egg is present at the micropylar end
> Formation of embryo sac:
- It consists of two stages
- In first stage, meiosis of megaspore occurs and form the tetrad of haploid cells
- Among these, three cells disintegrate and one sustains and finally develops into an embryo sac
- First stage is named as megasporogenesis
- In the second stage mega gametogenesis occurs, resulting in the formation of 8 nucleate and 7 celled gametophytes.
- The polar nuclei, which moves to the center and forms the single diploid nuclei, it in turn combines with sperm and generates the triploid endosperm.
Note: After the fusion and the formation of triploid endosperm, the three nuclei which remain the antipodal cells, out of three, two converts to synergid cells, and other degenerates by itself
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




