
Draw a labelled diagram of an electrolytic cell for the extraction of aluminium and the overall reaction taking place in it.
Answer
549.3k+ views
Hint: Aluminum is the most abundant (found in huge amounts) metal on the Earth's crust. It is costly, generally due to the measure of electricity needed in the extraction interaction.
Aluminum metal is called bauxite. The bauxite is decontaminated to create aluminum oxide, a white powder structure in which aluminum can be removed.
Complete step by step answer:
The diagram of the electrolytic cell:
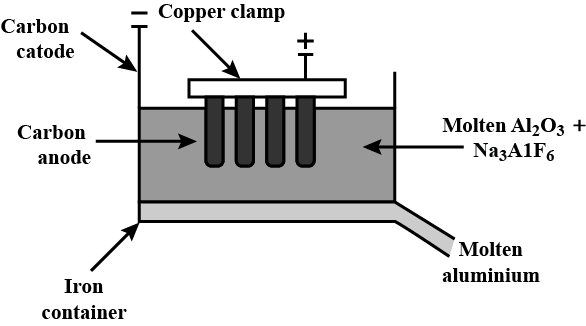
All the reactions taking place in the electrolytic cell is shown below:
Oxidation at anode:
\[6{O^{2 - }} - 12{e^ - } \to 3{O_2}\]
Reduction at anode:
\[4A{l^{3 + }} + 12{e^ - } \to 4Al\]
Overall reaction:
\[2A{l_2}{O_3} \to 4Al + 3{O_2}\]
Following two concepts are there for the reaction taking place during electrolysis:
According to the first theory which is most popular, ionization of alumina occurs firstly:
At cathode:
\[A{l_2}{O_3}(molten)\xrightarrow{{electrolysis}}4Al + 3{O_2}\]
\[A{l^{3 + }} + 3{e^ - } \to Al(l)\]
At anode:
{\[{O^{2 - }} \to O + 2{e^ - }\]
\[O + O \to {O_2}\]
\[4C + 3{O_2} \to 2CO + 2C{O_2}\]}
\[2C + {O_2} \to 2CO\]
\[2CO + {O_2} \to 2C{O_2}\]
Hence, corrosion of graphite rods (anode) occurs and they have to be replaced periodically. For one kg of aluminium produced about \[0.5\] kg of the anode (graphite) is consumed.
2. According to the second concept, ionization of 'Cryolite' occurs firstly on passing electric current.
\[N{a_3}Al{F_6}(molten. cryolite)\overset {electrolysis} \leftrightarrows 3NaF + Al{F_3}\]
\[Al{F_3}\overset {electrolysis} \leftrightarrows A{l^{3 + }}3{F^ - }\]
At cathode: \[A{l^{3 + }} + 3{e^ - } \to Al(l)\]
At anode: \[{F^ - } \to F + {e^ - }\]
\[3C + 2A{l_2}{O_3} \to 4Al + 3C{O_2}\]
At anode, \[A{l_2}{O_3}\] is changed into \[Al{F_3}\] and the process of electrolysis continuously goes on when \[A{l_2}{O_3}\] is again ionised.
The whole reaction may be written in the following way:
\[2A{l_2}{O_3} + {\text{ }}3C{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}4Al{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}3CO\]
Note: Molten aluminium thus obtained is collected at the bottom of the cell which is taken out with the help of tap. The aluminium metal obtained by this method is about \[99.5\% \] pure. The complete process is known as electrometallurgy.
Aluminum metal is called bauxite. The bauxite is decontaminated to create aluminum oxide, a white powder structure in which aluminum can be removed.
Complete step by step answer:
The diagram of the electrolytic cell:

All the reactions taking place in the electrolytic cell is shown below:
Oxidation at anode:
\[6{O^{2 - }} - 12{e^ - } \to 3{O_2}\]
Reduction at anode:
\[4A{l^{3 + }} + 12{e^ - } \to 4Al\]
Overall reaction:
\[2A{l_2}{O_3} \to 4Al + 3{O_2}\]
Following two concepts are there for the reaction taking place during electrolysis:
According to the first theory which is most popular, ionization of alumina occurs firstly:
At cathode:
\[A{l_2}{O_3}(molten)\xrightarrow{{electrolysis}}4Al + 3{O_2}\]
\[A{l^{3 + }} + 3{e^ - } \to Al(l)\]
At anode:
{\[{O^{2 - }} \to O + 2{e^ - }\]
\[O + O \to {O_2}\]
\[4C + 3{O_2} \to 2CO + 2C{O_2}\]}
\[2C + {O_2} \to 2CO\]
\[2CO + {O_2} \to 2C{O_2}\]
Hence, corrosion of graphite rods (anode) occurs and they have to be replaced periodically. For one kg of aluminium produced about \[0.5\] kg of the anode (graphite) is consumed.
2. According to the second concept, ionization of 'Cryolite' occurs firstly on passing electric current.
\[N{a_3}Al{F_6}(molten. cryolite)\overset {electrolysis} \leftrightarrows 3NaF + Al{F_3}\]
\[Al{F_3}\overset {electrolysis} \leftrightarrows A{l^{3 + }}3{F^ - }\]
At cathode: \[A{l^{3 + }} + 3{e^ - } \to Al(l)\]
At anode: \[{F^ - } \to F + {e^ - }\]
\[3C + 2A{l_2}{O_3} \to 4Al + 3C{O_2}\]
At anode, \[A{l_2}{O_3}\] is changed into \[Al{F_3}\] and the process of electrolysis continuously goes on when \[A{l_2}{O_3}\] is again ionised.
The whole reaction may be written in the following way:
\[2A{l_2}{O_3} + {\text{ }}3C{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}4Al{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}3CO\]
Note: Molten aluminium thus obtained is collected at the bottom of the cell which is taken out with the help of tap. The aluminium metal obtained by this method is about \[99.5\% \] pure. The complete process is known as electrometallurgy.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




