
Draw a graph showing the variation of potential energy and kinetic energy with respect to height of a free fall under gravitational force.
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint:We are asked to draw a graph of kinetic energy and potential energy with respect to height. Recall the formula to find the potential energy of a body falling from a height. And apply the law of conservation of energy to find the value of kinetic energy. Use these values to draw the required graph.
Complete answer:
We are asked to draw a graph showing the variation of potential energy and kinetic energy with respect to height of a free fall under gravitational force.Let us assume a body of mass \[m\] is falling from a height \[h\] under gravitational force. The potential energy of a body falling from a height \[h\] is given as,
\[P.E = mgh\]
where \[m\] is the mass of the body and \[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity.
From conservation of energy we have total energy as,
\[E = K.E + P.E\] (i)
where \[K.E\] is the kinetic energy and \[P.E\] is the potential energy.
Putting the value of \[P.E\] in equation (i) we get,
\[E = K.E + mgh\]
\[ \Rightarrow K.E = E - mgh\]
So, we have potential energy as \[P.E = mgh\], kinetic energy as \[K.E = E - mgh\] and total energy as \[E = K.E + P.E\].From these equations, we observe that as height decreases potential energy also decreases while the kinetic energy increases with decrease in height and the total energy remains constant.The plot of kinetic and potential energy with respect to height will be,
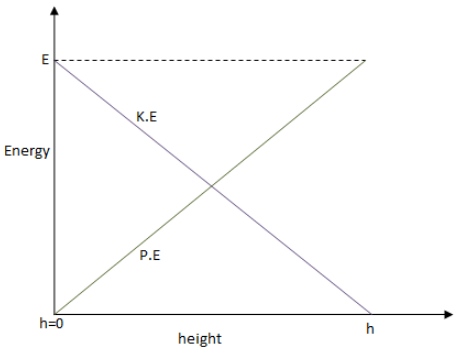
Note: Potential energy of a body is the energy stored in an object due to its position while kinetic energy is the energy acquired by an object due to its motion. Also, remember the total energy is always conserved and as potential energy of an object decreases the kinetic energy of the object decreases.
Complete answer:
We are asked to draw a graph showing the variation of potential energy and kinetic energy with respect to height of a free fall under gravitational force.Let us assume a body of mass \[m\] is falling from a height \[h\] under gravitational force. The potential energy of a body falling from a height \[h\] is given as,
\[P.E = mgh\]
where \[m\] is the mass of the body and \[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity.
From conservation of energy we have total energy as,
\[E = K.E + P.E\] (i)
where \[K.E\] is the kinetic energy and \[P.E\] is the potential energy.
Putting the value of \[P.E\] in equation (i) we get,
\[E = K.E + mgh\]
\[ \Rightarrow K.E = E - mgh\]
So, we have potential energy as \[P.E = mgh\], kinetic energy as \[K.E = E - mgh\] and total energy as \[E = K.E + P.E\].From these equations, we observe that as height decreases potential energy also decreases while the kinetic energy increases with decrease in height and the total energy remains constant.The plot of kinetic and potential energy with respect to height will be,

Note: Potential energy of a body is the energy stored in an object due to its position while kinetic energy is the energy acquired by an object due to its motion. Also, remember the total energy is always conserved and as potential energy of an object decreases the kinetic energy of the object decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




