
Draw a frequency polygon of the following data:
C 10-19 20-29 30-39 40-49 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-90 f 3 7 5 11 6 8 4 5
| C | 10-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70-79 | 80-90 |
| f | 3 | 7 | 5 | 11 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 5 |
Answer
538.5k+ views
Hint: We first find the class intervals of equal width and the class marks for the given data series. We plot the class marks and the frequencies along the horizontal and vertical axes respectively to find the frequency polygon.
Complete step-by-step solution:
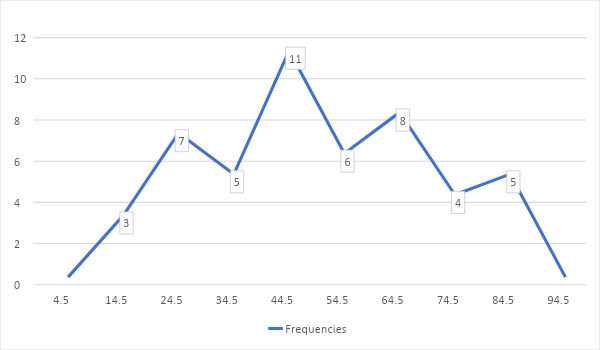
A frequency polygon is to exhibit the frequency distribution of a continuous variable. Two mutually perpendicular axes are taken for the class marks and the frequencies. They are plotted along the horizontal and vertical axes respectively.
We find the class intervals of equal width and the class marks for the given set of class limits of the continuous data.
Now we draw the frequency polygon based on the frequencies and the class-marks. To get a closed polygon, we take two additional classes, one at each end which have zero frequencies.
Note: We have to be careful about the class intervals being of equal width. The changes of axes for different points are also allowed. So, we have to find the variables for the two series to place points.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A frequency polygon is to exhibit the frequency distribution of a continuous variable. Two mutually perpendicular axes are taken for the class marks and the frequencies. They are plotted along the horizontal and vertical axes respectively.
We find the class intervals of equal width and the class marks for the given set of class limits of the continuous data.
| Class-limits | Class-intervals | Class-marks | Frequencies |
| 10-19 | 9.5-19.5 | 14.5 | 3 |
| 20-29 | 19.5-29.5 | 24.5 | 7 |
| 30-39 | 29.5-39.5 | 34.5 | 5 |
| 40-49 | 39.5-49.5 | 44.5 | 11 |
| 50-59 | 49.5-59.5 | 54.5 | 6 |
| 60-69 | 59.5-69.5 | 64.5 | 8 |
| 70-79 | 69.5-79.5 | 74.5 | 4 |
| 80-90 | 79.5-89.5 | 84.5 | 5 |
Now we draw the frequency polygon based on the frequencies and the class-marks. To get a closed polygon, we take two additional classes, one at each end which have zero frequencies.

Note: We have to be careful about the class intervals being of equal width. The changes of axes for different points are also allowed. So, we have to find the variables for the two series to place points.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




