
Draw a diagram to show the effect on the needle of a magnetic compass on bringing a bar magnet near it. Also draw a diagram to show the effects when the other end of the bar magnet is brought near to it.

Answer
514.2k+ views
Hint: A compass has a small magnet; the red tip is the north pole of that small magnet, which shows the north direction of earth or simply points towards the magnetic north pole of earth. So basically the magnetic north pole of earth is actually the south pole of the big magnet inside earth.
Complete answer:
Magnetism is one of the four fundamental forces in nature, the other three being the Gravitational force, the weak nuclear force and the strong nuclear force. Magnetism is basically a force of attraction or repulsion between two magnetic substances. All magnets have a region where they show the phenomenon of magnetism that is called the magnetic field of that magnet. There are two poles of every magnet, North and South.
Opposite poles of a magnet attract each other and the same poles repel. The North Pole of one magnet attracts the South Pole while repels the North Pole of another magnet. This simply means that opposite poles attract each other while the similar poles repel each other.Earth is also a big magnet in itself. Scientists believe that the movement of molten magma is the reason behind it. Therefore earth also has magnetic poles, North and South.
But if a bar magnet is brought near to the magnetic compass, it will point to the direction depending on which of the poles of the bar magnet is near to the compass. For example if the north pole of the bar magnet is brought near to the compass, then the red tip of the compass will move away from the bar magnet; but if the south pole is brought up, then the red tip or the north tip of the magnetic compass will point towards the bar magnet.
Diagrams showing the deflections in the needle of magnetic compass when a bar magnet is brought near to it:
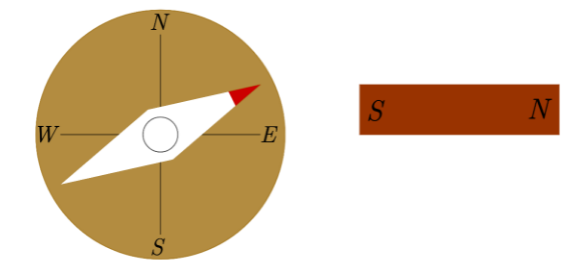
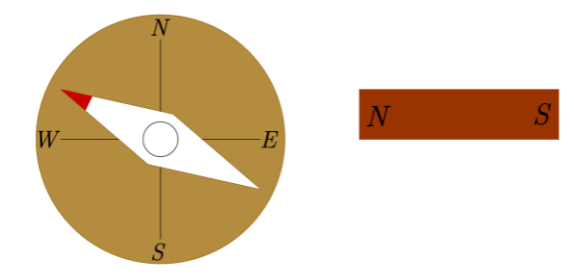
Note: The magnetic poles of earth are slightly at a small angular distance from the real poles. The field strength of Earth’s magnet is very weak, that's why we use the light weight needles in magnetic compasses which are mounted on frictionless bearings.
Complete answer:
Magnetism is one of the four fundamental forces in nature, the other three being the Gravitational force, the weak nuclear force and the strong nuclear force. Magnetism is basically a force of attraction or repulsion between two magnetic substances. All magnets have a region where they show the phenomenon of magnetism that is called the magnetic field of that magnet. There are two poles of every magnet, North and South.
Opposite poles of a magnet attract each other and the same poles repel. The North Pole of one magnet attracts the South Pole while repels the North Pole of another magnet. This simply means that opposite poles attract each other while the similar poles repel each other.Earth is also a big magnet in itself. Scientists believe that the movement of molten magma is the reason behind it. Therefore earth also has magnetic poles, North and South.
But if a bar magnet is brought near to the magnetic compass, it will point to the direction depending on which of the poles of the bar magnet is near to the compass. For example if the north pole of the bar magnet is brought near to the compass, then the red tip of the compass will move away from the bar magnet; but if the south pole is brought up, then the red tip or the north tip of the magnetic compass will point towards the bar magnet.
Diagrams showing the deflections in the needle of magnetic compass when a bar magnet is brought near to it:


Note: The magnetic poles of earth are slightly at a small angular distance from the real poles. The field strength of Earth’s magnet is very weak, that's why we use the light weight needles in magnetic compasses which are mounted on frictionless bearings.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




