
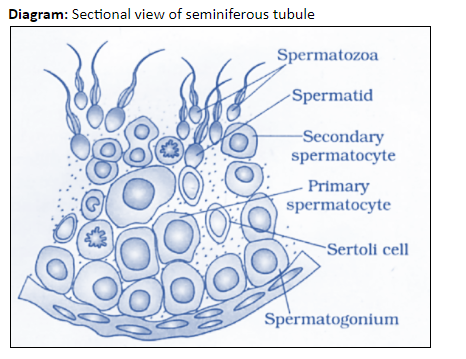
Draw a diagram of the sectional view of human seminiferous tubules and label its parts.
Answer
603.3k+ views
Hint: Seminiferous tubules are the highly coiled structure found in testicular lobules. Enclosed in a thick basal lamina, seminiferous tubule is surrounded by a few layers of smooth muscle cells known as myoid cells. It is lined inside by germinal epithelium and contains two types of cells: Sertoli cells and spermatogonia.
Complete answer:
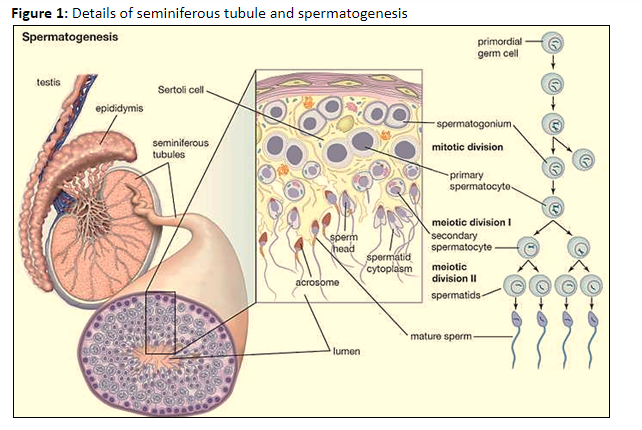
The seminiferous tubule is a site of sperm production, as it contains tightly packed cells (spermatogonia) that can undergo spermatogenesis.
The seminiferous tubule is made of three types of cells, an outer epithelial covering of delicate connective tissue of epithelial cells. This epithelial covering encloses two types of cell:
Sertoli cells that extend from the epithelial covering to the lumen of the tubule. These Sertoli cells regulate the development of cells undergoing spermatogenesis, provide support, and nourishment to spermatogonia cells.
Spermatogonia cells form the innermost layer of the tubule, with a lumen in the center. These spermatogonium (single spermatogonia cells) are the germ cells that undergo cell division to produce spermatids.
The ends of the seminiferous tubule are connected to the central region of the testis to form a network of small ductules (rete testis).
Additional Information:
1. Seminiferous tubule on the outside is surrounded by small blood vessels and the Leydig cells that are involved in the secretion of androgen and testosterone.
2. Seminiferous tubules have tightly packed Sertoli cells that help in nourishment of germ cells, phagocytize defective sperm, secrete inhibin hormone, and provide support to spermatogonia.
3. Another type of cell packed in a seminiferous tubule is the Spermatogonia cells, which are the male germ cells that undergo a series of meiotic and mitotic divisions to form spermatozoa.
Note: The sectional view of the seminiferous tubule gives the complete details of the tubule structure when seen from the top. It is made up of three types of cells: the long pseudostratified epithelial cells as the outer lining enclosing the large cuboidal Sertoli cells and polyhedral shaped spermatogonia cells.
Complete answer:
The seminiferous tubule is a site of sperm production, as it contains tightly packed cells (spermatogonia) that can undergo spermatogenesis.
The seminiferous tubule is made of three types of cells, an outer epithelial covering of delicate connective tissue of epithelial cells. This epithelial covering encloses two types of cell:
Sertoli cells that extend from the epithelial covering to the lumen of the tubule. These Sertoli cells regulate the development of cells undergoing spermatogenesis, provide support, and nourishment to spermatogonia cells.
Spermatogonia cells form the innermost layer of the tubule, with a lumen in the center. These spermatogonium (single spermatogonia cells) are the germ cells that undergo cell division to produce spermatids.
The ends of the seminiferous tubule are connected to the central region of the testis to form a network of small ductules (rete testis).

Additional Information:
1. Seminiferous tubule on the outside is surrounded by small blood vessels and the Leydig cells that are involved in the secretion of androgen and testosterone.
2. Seminiferous tubules have tightly packed Sertoli cells that help in nourishment of germ cells, phagocytize defective sperm, secrete inhibin hormone, and provide support to spermatogonia.
3. Another type of cell packed in a seminiferous tubule is the Spermatogonia cells, which are the male germ cells that undergo a series of meiotic and mitotic divisions to form spermatozoa.

Note: The sectional view of the seminiferous tubule gives the complete details of the tubule structure when seen from the top. It is made up of three types of cells: the long pseudostratified epithelial cells as the outer lining enclosing the large cuboidal Sertoli cells and polyhedral shaped spermatogonia cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE

Why is solder used for welding electrical wires ABecause class 11 chemistry CBSE




