
Draw a diagram of bubble plate type fractionating columns. When do we require such a type of column for separating two liquids? Explain the principle involved in the separation of components of a mixture of liquids by using fractionating columns. What industrial applications does this process have?
Answer
516k+ views
Hint :Organic liquids which have a small difference in boiling points which cannot be separated using simple distillation are separated and purified using fractional distillation.There are a variety of Fractional distillation columns like Younger’s pear shaped column,Hemple’s column and bubble plate column.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
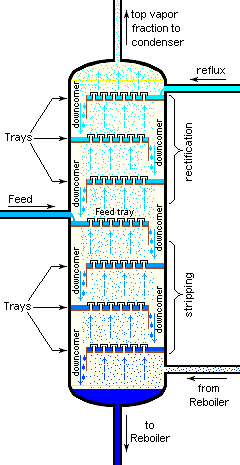
Fractional distillation is used when organic liquids need to be separated from non-volatile impurities or when two or more volatile liquids need to be separated from a liquid mixture which have boiling points close to each other . In this process, the distillate is collected in fractions under different temperatures hence it is known as fractional distillation.Fractional distillation helps in obtaining the constituents in their pure form.
Fractional distillation comes into picture when the difference in boiling points of two miscible liquids in an organic solution is less than $30K$ .In such a scenario the use of simple distillation would be futile.The fractional distillation column consists of a series of obstructions between the flask and condenser.As the vapours of the liquid rise in the column they come in contact with the obstructions.The vapours of liquid with lower boiling point continue to rise however the liquid with higher boiling point get condensed in the column itself.The liquid which gets condensed trickles back down into the flask.In order to purify the fractions obtained the process of distillation will be carried out repeatedly.In the petroleum industry this process is used for the distillation of petrol,crude oil.The chemical industry uses this process for separation of acetone and benzene.
Note :
It’s worth noting that liquids forming constant boiling point(azeotropic mixture) cannot be separated with this process.Fractional distillation works on the principle that the liquid which is more volatile distils first leaving behind the less volatile liquid behind in the distillation flask.
Complete Step By Step Answer:

Fractional distillation is used when organic liquids need to be separated from non-volatile impurities or when two or more volatile liquids need to be separated from a liquid mixture which have boiling points close to each other . In this process, the distillate is collected in fractions under different temperatures hence it is known as fractional distillation.Fractional distillation helps in obtaining the constituents in their pure form.
Fractional distillation comes into picture when the difference in boiling points of two miscible liquids in an organic solution is less than $30K$ .In such a scenario the use of simple distillation would be futile.The fractional distillation column consists of a series of obstructions between the flask and condenser.As the vapours of the liquid rise in the column they come in contact with the obstructions.The vapours of liquid with lower boiling point continue to rise however the liquid with higher boiling point get condensed in the column itself.The liquid which gets condensed trickles back down into the flask.In order to purify the fractions obtained the process of distillation will be carried out repeatedly.In the petroleum industry this process is used for the distillation of petrol,crude oil.The chemical industry uses this process for separation of acetone and benzene.
Note :
It’s worth noting that liquids forming constant boiling point(azeotropic mixture) cannot be separated with this process.Fractional distillation works on the principle that the liquid which is more volatile distils first leaving behind the less volatile liquid behind in the distillation flask.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




