
Draw a circuit diagram of a P-N-P transistor to obtain characteristics curves in common base configuration. Establish the relations between current amplification factors in a transistor in common base and common emitter configuration.
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint:
First, we draw a diagram of a N-P-N transistor with a common base between emitter and collector. Then describe the input and output characteristics with the help of graphs. Generate the relationship between current amplification factor in common base and common emitter position.
Complete step by step solution:
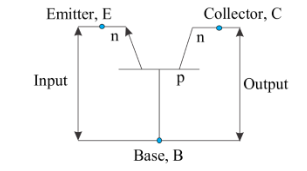
In N-P-N transistors the base terminal is common between the input and the output terminals of the transistor. Here the emitter works as the input terminal, collector as the output terminal.
Input Characteristics:
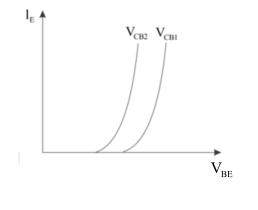
The input characteristics of the transistor is obtained from the input current $({I_E})$ and input voltage $({V_{BE}})$.Here in this figure the output voltage $({V_{BE}})$ is kept constant and in this configuration the input voltage $({V_{BE}})$ is varied gradually and simultaneously the input current $({I_E})$ is noted down and we get this type of characteristics curve.
 Input Characteristics curve
Input Characteristics curve
Output Characteristics:
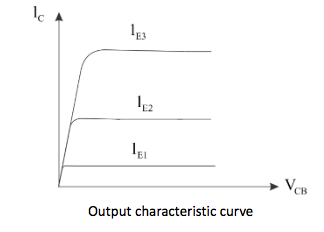
In the output characteristics the input current $({I_E})$ is kept constant and then the output voltage $({V_{CB}})$ is increased gradually. Thus for that variation the output current ${I_C}$ is recorded and this curve is obtained.
Output characteristic curve
The current amplification factor of a transistor in common base configuration is the ratio of output current $({I_C})$ to the input current $({I_E})$. It is denoted by $\alpha $.
$\alpha = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_E}}}$.
In common emitter configuration the input current is the base current $({I_B})$ and output current is collector current$({I_C})$.
So the current amplification factor in common emitter configuration is $\beta = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_B}}}$.
We know that ${I_E} = {I_C} + {I_B}$
So, $\beta = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_E} - {I_C}}}$
Dividing by ${I_E}$ We get
$
\beta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_E}}}}}{{1 - \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_E}}}}} \\
= > \beta = \dfrac{\alpha }{{1 - \alpha }} \\
$
This is the relationship between $\alpha $ and $\beta $.
NoteThe significance of the relation between current amplification factors in a transistor in common base and common emitter configuration indicates that, when $\alpha $ reaches unity, then the value of $\beta $ reaches to infinity. This conclusion shows that the current gain in a common emitter configuration is very high.
First, we draw a diagram of a N-P-N transistor with a common base between emitter and collector. Then describe the input and output characteristics with the help of graphs. Generate the relationship between current amplification factor in common base and common emitter position.
Complete step by step solution:
In N-P-N transistors the base terminal is common between the input and the output terminals of the transistor. Here the emitter works as the input terminal, collector as the output terminal.

Input Characteristics:
The input characteristics of the transistor is obtained from the input current $({I_E})$ and input voltage $({V_{BE}})$.Here in this figure the output voltage $({V_{BE}})$ is kept constant and in this configuration the input voltage $({V_{BE}})$ is varied gradually and simultaneously the input current $({I_E})$ is noted down and we get this type of characteristics curve.

Output Characteristics:
In the output characteristics the input current $({I_E})$ is kept constant and then the output voltage $({V_{CB}})$ is increased gradually. Thus for that variation the output current ${I_C}$ is recorded and this curve is obtained.

Output characteristic curve
The current amplification factor of a transistor in common base configuration is the ratio of output current $({I_C})$ to the input current $({I_E})$. It is denoted by $\alpha $.
$\alpha = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_E}}}$.
In common emitter configuration the input current is the base current $({I_B})$ and output current is collector current$({I_C})$.
So the current amplification factor in common emitter configuration is $\beta = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_B}}}$.
We know that ${I_E} = {I_C} + {I_B}$
So, $\beta = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_E} - {I_C}}}$
Dividing by ${I_E}$ We get
$
\beta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_E}}}}}{{1 - \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_E}}}}} \\
= > \beta = \dfrac{\alpha }{{1 - \alpha }} \\
$
This is the relationship between $\alpha $ and $\beta $.
NoteThe significance of the relation between current amplification factors in a transistor in common base and common emitter configuration indicates that, when $\alpha $ reaches unity, then the value of $\beta $ reaches to infinity. This conclusion shows that the current gain in a common emitter configuration is very high.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




