
How do you draw $45{}^\circ $ and $-45{}^\circ $ in standard position and then show that $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos \left( 45{}^\circ \right)?$
Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: We know that the initial side of the angle lies along the $x-$axis. When we draw a positive angle, we will start the rotation from the positive $x-$axis in the counterclockwise direction. When we draw a negative angle, we will start the rotation from the negative $x-$axis in the clockwise direction.
Complete step by step answer:
We are asked to draw the angle $45{}^\circ $ and $-45{}^\circ $ in the standard position.
As we can see, we need to draw a positive angle and a negative angle.
Let us consider the initial sides of the angles. We will locate the initial side along the $x-$axis.
When we draw a positive angle, we will start the rotation from the positive $x-$axis in the counterclockwise direction and when we draw a negative angle, we will start the rotation from the negative $x-$axis.
So, a graph containing $45{}^\circ $ and $-45{}^\circ $ angles in the standard position is given below:
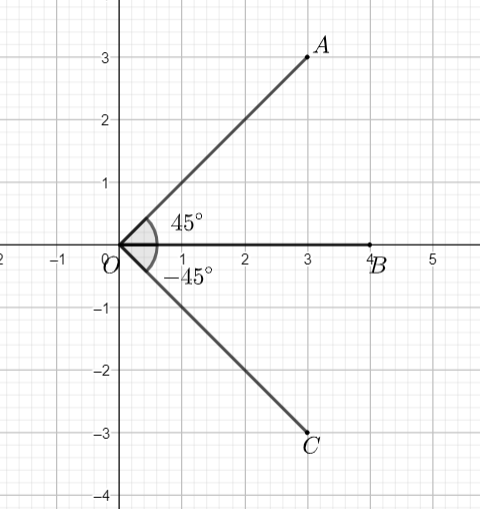
And now, we need to prove that $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos 45{}^\circ .$
We know that the Cosine function is an even function.
We have learnt that all even functions satisfy the property given by: $f\left( -x \right)=f\left( x \right).$
Therefore, the Cosine function satisfies the property: $\cos \left( -x \right)=\cos \left( x \right).$
Hence, we have proved that $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos 45{}^\circ .$
Note: We know that $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos \left( 0{}^\circ -45{}^\circ \right).$ We will use the identity $\cos \left( x-y \right)=\cos x\cos y+\sin x\sin y.$ Then we will get $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos \left( 0{}^\circ -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos 0{}^\circ \cos 45{}^\circ +\sin 0{}^\circ \sin 45{}^\circ .$ Also, we know that $\cos 0{}^\circ =1, \cos 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}, \sin 0{}^\circ =0$ and $\sin 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}.$ Now, we will get $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos 0{}^\circ \cos 45{}^\circ +\sin 0{}^\circ \sin 45{}^\circ =1\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}+0=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\cos 45{}^\circ .$ Remember that the Sine function is an odd function. So, it satisfies the property given by $f\left( -x \right)=-f\left( x \right).$
Complete step by step answer:
We are asked to draw the angle $45{}^\circ $ and $-45{}^\circ $ in the standard position.
As we can see, we need to draw a positive angle and a negative angle.
Let us consider the initial sides of the angles. We will locate the initial side along the $x-$axis.
When we draw a positive angle, we will start the rotation from the positive $x-$axis in the counterclockwise direction and when we draw a negative angle, we will start the rotation from the negative $x-$axis.
So, a graph containing $45{}^\circ $ and $-45{}^\circ $ angles in the standard position is given below:

And now, we need to prove that $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos 45{}^\circ .$
We know that the Cosine function is an even function.
We have learnt that all even functions satisfy the property given by: $f\left( -x \right)=f\left( x \right).$
Therefore, the Cosine function satisfies the property: $\cos \left( -x \right)=\cos \left( x \right).$
Hence, we have proved that $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos 45{}^\circ .$
Note: We know that $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos \left( 0{}^\circ -45{}^\circ \right).$ We will use the identity $\cos \left( x-y \right)=\cos x\cos y+\sin x\sin y.$ Then we will get $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos \left( 0{}^\circ -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos 0{}^\circ \cos 45{}^\circ +\sin 0{}^\circ \sin 45{}^\circ .$ Also, we know that $\cos 0{}^\circ =1, \cos 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}, \sin 0{}^\circ =0$ and $\sin 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}.$ Now, we will get $\cos \left( -45{}^\circ \right)=\cos 0{}^\circ \cos 45{}^\circ +\sin 0{}^\circ \sin 45{}^\circ =1\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}+0=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\cos 45{}^\circ .$ Remember that the Sine function is an odd function. So, it satisfies the property given by $f\left( -x \right)=-f\left( x \right).$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




