
What is the domain and range of \[y=\tan x\]?
Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint: In this problem, we have to find the domain and range of the given function \[y=\tan x\]. We know that the domain of the function \[y=\tan x\] is all real numbers except the values where \[\cos x\] is equal to zero, i.e. the values \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\pi n\] for all integers n. The range of the tangent function is all real numbers. We can draw the graph for the given function and write the domain and the range.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have to find the domain and the range of the given function \[y=\tan x\].
We know that the domain of the function \[y=\tan x\] is all real numbers except the values where \[\cos x\] is equal to zero, i.e. the values \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\pi n\] for all integers n as we know that \[\tan x=\dfrac{\sin x}{\cos x}\] which is not defined when denominator is 0.
The range of the tangent function is all real numbers.
If we plug \[y=\tan x\] in a graphing calculator, we can see that the ends of each section continue on infinitely along the y-axis.
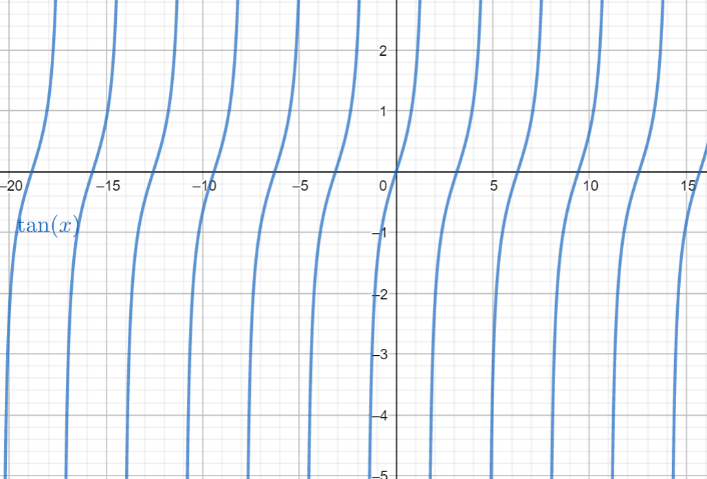
Therefore, the domain of the given function \[y=\tan x\] is \[\left( \theta \ne k\dfrac{\pi }{2},\text{ where k is an integer} \right)\].
The range is \[\left( -\infty ,\infty \right)\].
Note: We should always remember that the function \[y=\tan x\] is all real numbers except the values where \[\cos x\] is equal to zero, i.e. the values \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\pi n\] for all integers n as we know that \[\tan x=\dfrac{\sin x}{\cos x}\] which is not defined when denominator is 0. The range of the tangent function is all real numbers.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have to find the domain and the range of the given function \[y=\tan x\].
We know that the domain of the function \[y=\tan x\] is all real numbers except the values where \[\cos x\] is equal to zero, i.e. the values \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\pi n\] for all integers n as we know that \[\tan x=\dfrac{\sin x}{\cos x}\] which is not defined when denominator is 0.
The range of the tangent function is all real numbers.
If we plug \[y=\tan x\] in a graphing calculator, we can see that the ends of each section continue on infinitely along the y-axis.

Therefore, the domain of the given function \[y=\tan x\] is \[\left( \theta \ne k\dfrac{\pi }{2},\text{ where k is an integer} \right)\].
The range is \[\left( -\infty ,\infty \right)\].
Note: We should always remember that the function \[y=\tan x\] is all real numbers except the values where \[\cos x\] is equal to zero, i.e. the values \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\pi n\] for all integers n as we know that \[\tan x=\dfrac{\sin x}{\cos x}\] which is not defined when denominator is 0. The range of the tangent function is all real numbers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




