
What is the domain and range of a sine graph?
Answer
540k+ views
Hint: The domain of a function $f\left( x \right)$ is defined as the complete set of the values of the argument x for which the function is defined. And the range is the complete set of values which the function gives after substituting the values of the argument from the domain set. Therefore, for determining the domain of the sine graph, we need to observe the values on the x-axis on which it is well defined. And for determining the range, we need to observe the values on the y-axis which are obtained from the graph.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, we need to determine the domain and the range of the sine function. Therefore, we consider the graph of the sine function as shown below.
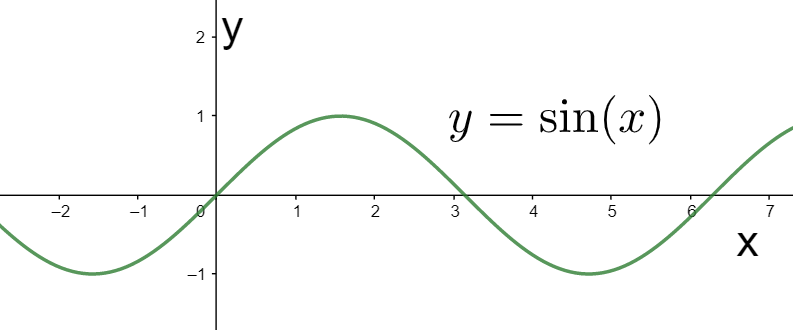
We know that the domain is defined as the complete set of the values of the argument x for which the function is defined. Therefore, we have to observe the values on the x-axis for which the function is defined. In the above graph, we can see that it is defined for the complete x-axis. Therefore, the domain of the sine function is the complete set of real numbers $R$.
We also know that the range is the complete set of values which the function gives after substituting the values of the argument from the domain set. Therefore, we must observe the values on the y-axis which are obtained by the graph of the function. In the above graph, we can observe that the values obtained range from $-1$ to $1$. Therefore, the range of the sine function is represented by the interval \[\left[ -1,1 \right]\].
Hence, we have determined the domain and the range of the sine graph.
Note: Do not make the mistake of writing the range of the sine graph to be equal to the real set $R$ just because it does not have breaks. It holds true for checking the domain, but not for range. For the range of a continuous function, we need to first observe whether its graph is bounded or not.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, we need to determine the domain and the range of the sine function. Therefore, we consider the graph of the sine function as shown below.

We know that the domain is defined as the complete set of the values of the argument x for which the function is defined. Therefore, we have to observe the values on the x-axis for which the function is defined. In the above graph, we can see that it is defined for the complete x-axis. Therefore, the domain of the sine function is the complete set of real numbers $R$.
We also know that the range is the complete set of values which the function gives after substituting the values of the argument from the domain set. Therefore, we must observe the values on the y-axis which are obtained by the graph of the function. In the above graph, we can observe that the values obtained range from $-1$ to $1$. Therefore, the range of the sine function is represented by the interval \[\left[ -1,1 \right]\].
Hence, we have determined the domain and the range of the sine graph.
Note: Do not make the mistake of writing the range of the sine graph to be equal to the real set $R$ just because it does not have breaks. It holds true for checking the domain, but not for range. For the range of a continuous function, we need to first observe whether its graph is bounded or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




