
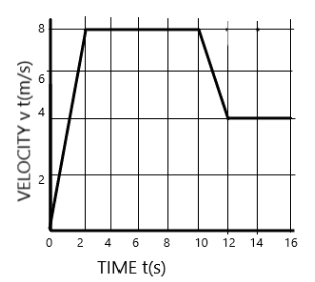
How far does the runner whose time-velocity graph is shown in the figure travel in 16 seconds

Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: Area under the curve of a velocity - time graph (or time – velocity graph) is equal to the displacement covered. Split the velocity time graphs into simple shapes and calculate each of their areas, then add them together.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
$ {A_t} = \dfrac{1}{2}bh $ where $ {A_t} $ is the area of a triangle, $ b $ is the base of the triangle, and $ h $ is the height of the triangle.
$ {A_r} = lb $ where $ {A_r} $ is the area of a rectangle, $ l $ is the length of the rectangle, and $ b $ is the breath of the rectangle.
Complete Step-by-Step solution
Generally, when a velocity time graph of an object is known, the area under the curve is the displacement of the object. Hence, to find how far the runner went, we shall calculate the area under each curve of the graph shown.
So be simpler, we split it into simple shapes. The first one being the triangle. The area under the triangle ABC is
$ {A_t} = \dfrac{1}{2}2\left( 8 \right) $ since $ {A_t} = \dfrac{1}{2}bh $ where $ {A_t} $ is the area of a triangle, $ b $ is the base of the triangle, and $ h $ is the height of the triangle
$ {A_{ABC}} = 8m $
For the rectangle / square CBDE we have
$ {A_{CBDE}} = \left( {10 - 2} \right)\left( 8 \right) $ since $ {A_r} = lb $ where $ {A_r} $ is the area of a rectangle, $ l $ is the length of the rectangle, and $ b $ is the breath of the rectangle.
Then the triangle, DFG is
$ {A_{DFG}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {12 - 10} \right)\left( {8 - 4} \right) = 4{m^2} $
Rectangle EFGH,
$ {A_{EFGH}} = \left( {12 - 10} \right)\left( 4 \right) = 8{m^2} $
Rectangle GHIJ
$ {A_{GHIJ}} = \left( {16 - 12} \right)\left( 4 \right) = 16{m^2} $
To the total area under the curve is
$ A = 8 + 4 + 8 + 16 = 36m $
Hence, the total displacement covered is 36 m.
Note
Although, it didn’t apply in this case, note that, the velocity time graphs shows gives total displacement, and hence when the velocity is negative, for total displacement, the area under (actually, it would be above the curve now) would be subtracted and not added.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
$ {A_t} = \dfrac{1}{2}bh $ where $ {A_t} $ is the area of a triangle, $ b $ is the base of the triangle, and $ h $ is the height of the triangle.
$ {A_r} = lb $ where $ {A_r} $ is the area of a rectangle, $ l $ is the length of the rectangle, and $ b $ is the breath of the rectangle.
Complete Step-by-Step solution
Generally, when a velocity time graph of an object is known, the area under the curve is the displacement of the object. Hence, to find how far the runner went, we shall calculate the area under each curve of the graph shown.
So be simpler, we split it into simple shapes. The first one being the triangle. The area under the triangle ABC is
$ {A_t} = \dfrac{1}{2}2\left( 8 \right) $ since $ {A_t} = \dfrac{1}{2}bh $ where $ {A_t} $ is the area of a triangle, $ b $ is the base of the triangle, and $ h $ is the height of the triangle
$ {A_{ABC}} = 8m $
For the rectangle / square CBDE we have
$ {A_{CBDE}} = \left( {10 - 2} \right)\left( 8 \right) $ since $ {A_r} = lb $ where $ {A_r} $ is the area of a rectangle, $ l $ is the length of the rectangle, and $ b $ is the breath of the rectangle.
Then the triangle, DFG is
$ {A_{DFG}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {12 - 10} \right)\left( {8 - 4} \right) = 4{m^2} $
Rectangle EFGH,
$ {A_{EFGH}} = \left( {12 - 10} \right)\left( 4 \right) = 8{m^2} $
Rectangle GHIJ
$ {A_{GHIJ}} = \left( {16 - 12} \right)\left( 4 \right) = 16{m^2} $
To the total area under the curve is
$ A = 8 + 4 + 8 + 16 = 36m $
Hence, the total displacement covered is 36 m.
Note
Although, it didn’t apply in this case, note that, the velocity time graphs shows gives total displacement, and hence when the velocity is negative, for total displacement, the area under (actually, it would be above the curve now) would be subtracted and not added.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




