
What does the Golgi apparatus do in a plant cell?
Answer
500.1k+ views
Hint: A Golgi body, also known as a Golgi apparatus, is a cell organelle that assists in the processing and packaging of proteins and lipid molecules, particularly those destined for cell export. The Golgi body is a series of stacked membranes named after its discoverer, Camillo Golgi.
Complete answer:
The Golgi apparatus in plants is not only important for protein glycosylation and sorting, but it is also a major biosynthetic organelle that produces large amounts of cell wall polysaccharides. The Golgi apparatus is organized as numerous individual stacks of cisternae that are dispersed throughout the cell to reflect this.
Proteins and lipids are collected, modified, packaged, and distributed by the Golgi apparatus. It's also known as the cell's shipping and receiving department. It resembles a stack of bowls, each with secretory vesicles on the rims.
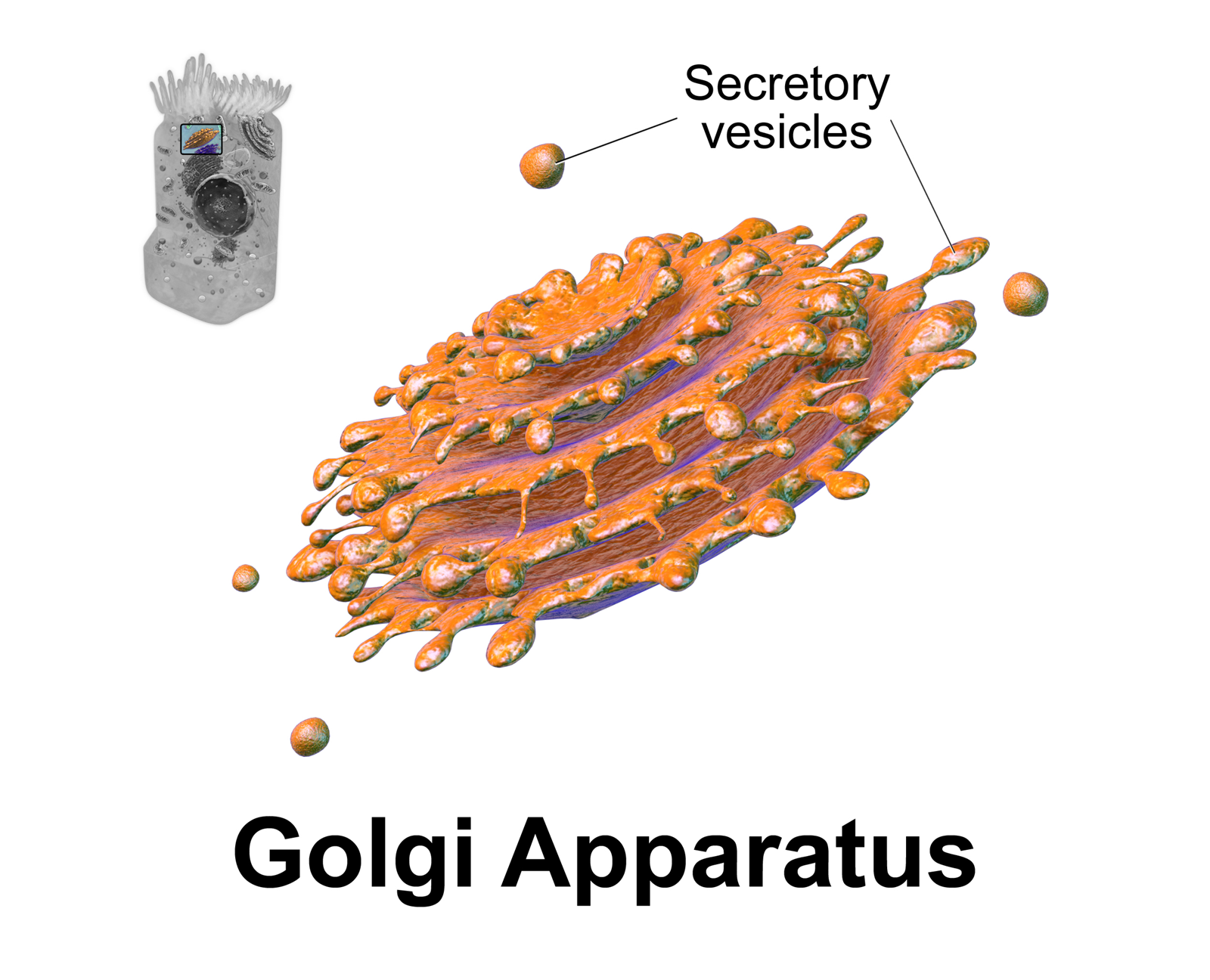
The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins and lipids into secretory vesicles, which are small, spherically shaped sacs that bud from the apparatus's ends. These vesicles frequently migrate to the plasma membrane and merge with it, releasing their contents outside of the cell. The Golgi apparatus is found in greater numbers and is more developed in cells that secrete protein, such as the cells of the salivary glands or the pancreas.
During cytokinesis in higher plants, vesicles from the Golgi apparatus are involved in forming the cell plate, which is where the new cell walls are manufactured. In-plant cells, the Golgi apparatus can devote up to 80% of its biochemical activity to producing chemicals like pectin and polysaccharides, which are used to make cell walls.
Thus, A Golgi body, also known as a Golgi apparatus, is a cell organelle that assists in the processing and packaging of proteins and lipid molecules, particularly those destined for cell export.
Note:
Multiple Golgi apparatuses are found throughout the cytoplasm of yeast (as observed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae). Golgi stacks do not form Golgi ribbons in plants because they are not concentrated in the centrosomal region. Actin cables, not microtubules, are responsible for the organization of the plant Golgi. The proximity of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) exit sites is a common feature of Golgi.
Complete answer:
The Golgi apparatus in plants is not only important for protein glycosylation and sorting, but it is also a major biosynthetic organelle that produces large amounts of cell wall polysaccharides. The Golgi apparatus is organized as numerous individual stacks of cisternae that are dispersed throughout the cell to reflect this.
Proteins and lipids are collected, modified, packaged, and distributed by the Golgi apparatus. It's also known as the cell's shipping and receiving department. It resembles a stack of bowls, each with secretory vesicles on the rims.

The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins and lipids into secretory vesicles, which are small, spherically shaped sacs that bud from the apparatus's ends. These vesicles frequently migrate to the plasma membrane and merge with it, releasing their contents outside of the cell. The Golgi apparatus is found in greater numbers and is more developed in cells that secrete protein, such as the cells of the salivary glands or the pancreas.
During cytokinesis in higher plants, vesicles from the Golgi apparatus are involved in forming the cell plate, which is where the new cell walls are manufactured. In-plant cells, the Golgi apparatus can devote up to 80% of its biochemical activity to producing chemicals like pectin and polysaccharides, which are used to make cell walls.
Thus, A Golgi body, also known as a Golgi apparatus, is a cell organelle that assists in the processing and packaging of proteins and lipid molecules, particularly those destined for cell export.
Note:
Multiple Golgi apparatuses are found throughout the cytoplasm of yeast (as observed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae). Golgi stacks do not form Golgi ribbons in plants because they are not concentrated in the centrosomal region. Actin cables, not microtubules, are responsible for the organization of the plant Golgi. The proximity of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) exit sites is a common feature of Golgi.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




