
How does the angular separation between fringes in a single slit diffraction experiment change when the distance of separation between the slit and screen is doubled?
Answer
609k+ views
Hint: In this question, we first draw the two ray diagram of the single-slit experiment then write the path difference expression that is \[\Delta L = \dfrac{a}{2}\sin \theta \]. We can see that the path difference is dependent on the angle term $\sin \theta $ due to this when we double the distance between the slit and screen we get that the distance between fringes is also double.
Complete step-by-step solution -
In the single-slit diffraction experiment, we can observe the diffraction of light or bending phenomenon of light and because of this light ray from a coherent source interferes with another ray from the same source. Due to this interference, we can see a unique pattern on the screen known as the diffraction pattern. Diffraction is visible when the size of the source or the size of the slit behind which source is present is comparable to the wavelength of light. The two ray diagram for single slit diffraction is shown below.
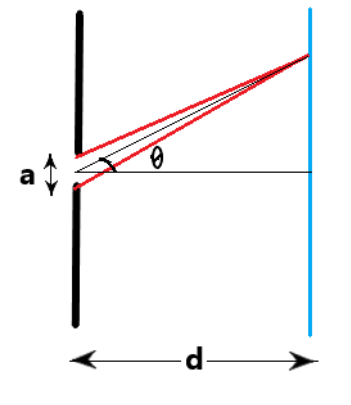
The path difference formula derived from for the single slit experiment is given as
\[\Delta L = \dfrac{a}{2}\sin \theta \]
To get a dark fringe, the path difference should be an odd integral multiple of λ/2. Where λ is the wavelength of the light to produce destructive interference
Now if we double the distance between the slit and the screen that is 2d the angular distance between fringes will also get doubled because the equation that we saw above that describes the fringe pattern contains angle terms that is $\sin \theta $ which depends on the distance between the slit and the screen. Doubling the distance will also cause the brightness of the fringe to reduce by four times.
Note: For these types of questions we need to know about singles slit diffraction experiment and young’s double-slit experiment. We also need to know the condition for path difference and how it varies with the distance between the slit and screen or with the size of the slits.
Complete step-by-step solution -
In the single-slit diffraction experiment, we can observe the diffraction of light or bending phenomenon of light and because of this light ray from a coherent source interferes with another ray from the same source. Due to this interference, we can see a unique pattern on the screen known as the diffraction pattern. Diffraction is visible when the size of the source or the size of the slit behind which source is present is comparable to the wavelength of light. The two ray diagram for single slit diffraction is shown below.

The path difference formula derived from for the single slit experiment is given as
\[\Delta L = \dfrac{a}{2}\sin \theta \]
To get a dark fringe, the path difference should be an odd integral multiple of λ/2. Where λ is the wavelength of the light to produce destructive interference
Now if we double the distance between the slit and the screen that is 2d the angular distance between fringes will also get doubled because the equation that we saw above that describes the fringe pattern contains angle terms that is $\sin \theta $ which depends on the distance between the slit and the screen. Doubling the distance will also cause the brightness of the fringe to reduce by four times.
Note: For these types of questions we need to know about singles slit diffraction experiment and young’s double-slit experiment. We also need to know the condition for path difference and how it varies with the distance between the slit and screen or with the size of the slits.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




