
How does Resonance affect stability?
Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint: Resonance is a term used to describe delocalized electrons within molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed using a single Lewis formula. Several resonance structures represent a molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons.
Complete answer:
If a molecule has multiple resonance structures, it is thought to be more stable than molecules with a single resonance structure. The reason for this is that because the resonance allows for delocalization, the molecule's overall energy is reduced because its electrons occupy a large volume.
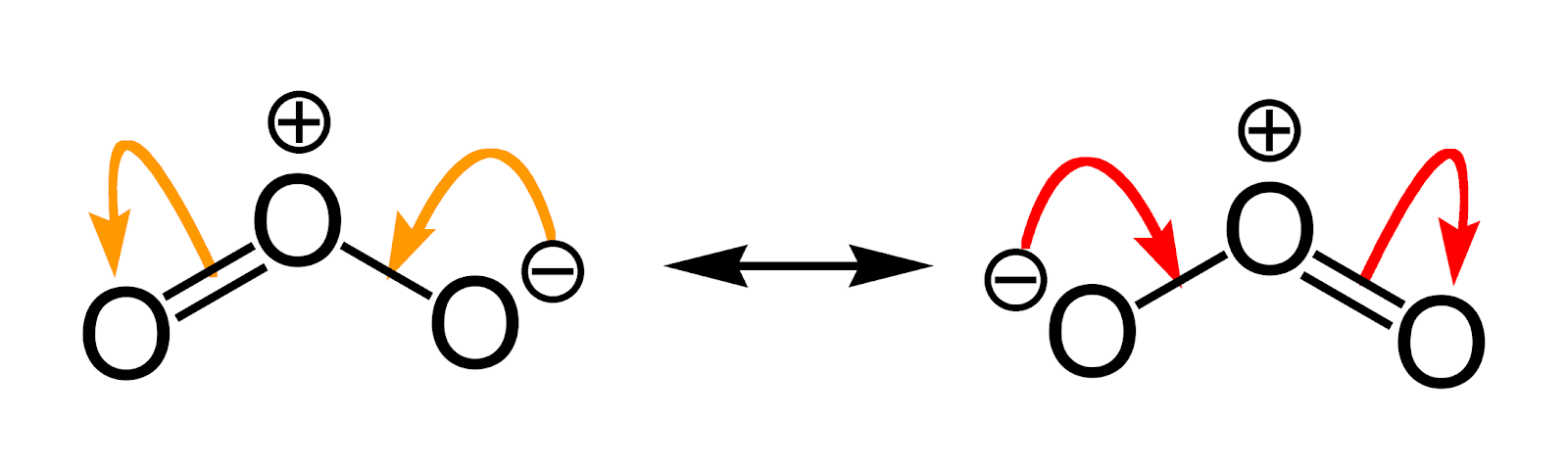
The Lewis skeleton's nuclear skeleton, the electron locations differ, but the structure of these resonance structures remains the same. Such is the case with ozone () an oxygen allotrope with a V-shaped structure and a 117.5° O–O–O angle.
Resonance structures are equivalent Lewis dot structures, such as those found in ozone. In the various resonance structures of a compound, the atoms are in the same place, but the electrons are in different places. Double-headed arrows connect a compound's various resonance structures:
Note:
While each resonance structure contributes to the molecule's total electronic structure, their contributions may not be equal. One mechanism for determining the viability of a resonance structure and its relative magnitude among other structures is to assign formal charges to atoms in the molecules. In a covalent species, the formal charge on an atom is the net charge the atom would have if the electrons in all of the atom's bonds were equally shared.
Complete answer:
If a molecule has multiple resonance structures, it is thought to be more stable than molecules with a single resonance structure. The reason for this is that because the resonance allows for delocalization, the molecule's overall energy is reduced because its electrons occupy a large volume.
The Lewis skeleton's nuclear skeleton, the electron locations differ, but the structure of these resonance structures remains the same. Such is the case with ozone () an oxygen allotrope with a V-shaped structure and a 117.5° O–O–O angle.
Resonance structures are equivalent Lewis dot structures, such as those found in ozone. In the various resonance structures of a compound, the atoms are in the same place, but the electrons are in different places. Double-headed arrows connect a compound's various resonance structures:

Note:
While each resonance structure contributes to the molecule's total electronic structure, their contributions may not be equal. One mechanism for determining the viability of a resonance structure and its relative magnitude among other structures is to assign formal charges to atoms in the molecules. In a covalent species, the formal charge on an atom is the net charge the atom would have if the electrons in all of the atom's bonds were equally shared.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




