
Does \[LiAl{H_4}\] reduce Amides?
Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: \[LiAl{H_4}\] is a very strong reducing agent. It reduces aldehydes, amides, ketones, esters, carboxylic acid and even carboxylate salts to alcohols.
Amide is a functional group that contains both nitrogen and carboxyl groups in it. It is usually represented as below:
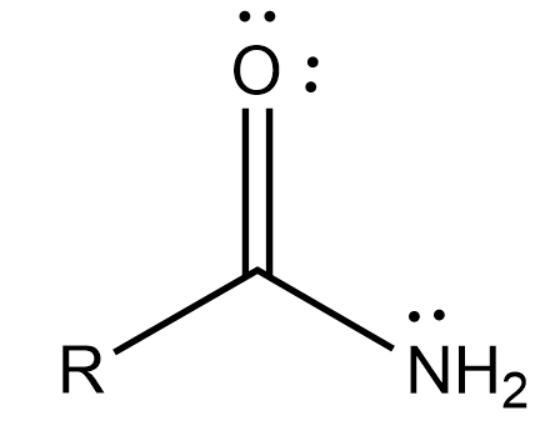
\[LiAl{H_4}\] will reduce Amides to Amines and this means that the oxygen that was present in the amide is removed from the molecule after the reaction completes.
Complete answer:
Let’s see how the reaction occurs when amide is treated with \[LiAl{H_4}\]
First there is a nucleophilic attack by one of the hydrides of \[LiAl{H_4}\] . Because the carbonyl group is highly polar the oxygen becomes negative and thus \[Al\] having negatively charge can now attack the positively charged carbonyl carbon and thus the following step occurs
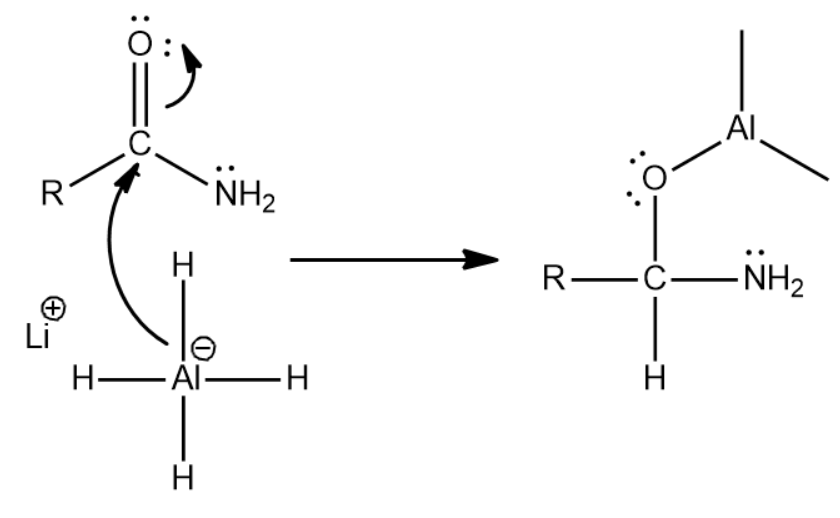
Now since there is an oxygen that can act as a leaving group we will get the following reaction which leads to the formation of an iminium ion
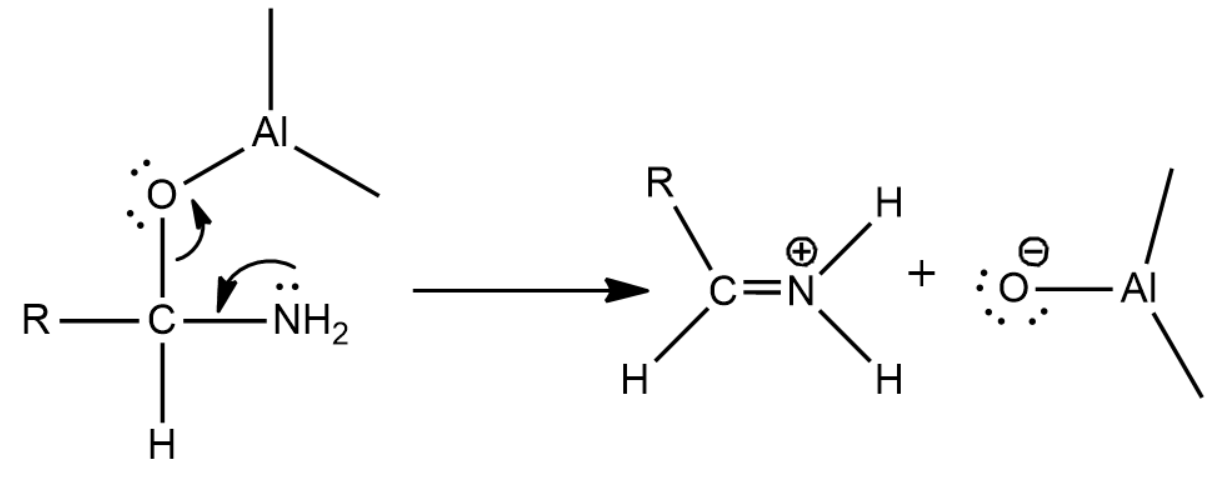
Now there is a nucleophilic attack by the hydride of \[LiAl{H_4}\] causing for the formation of the final product, amine
That is given by the following reaction:
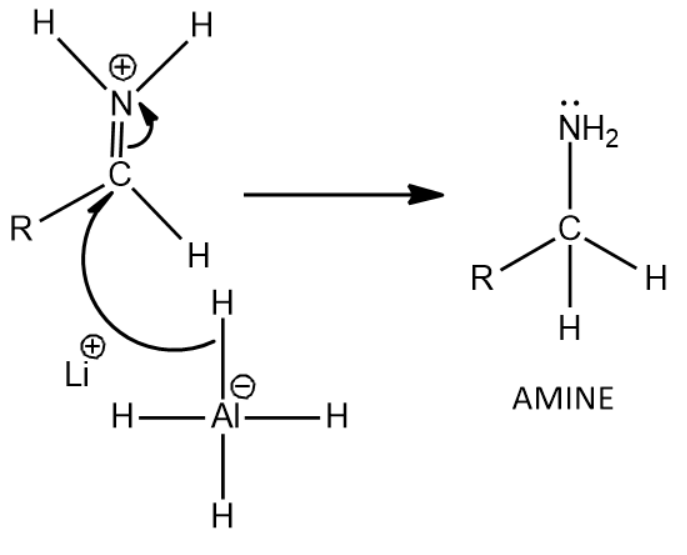
Thus we get Amine as the product when amides are treated with \[LiAl{H_4}\] which is a strong reducing agent.
Thus we can write the general form of the reaction as:

Note:
\[NaB{H_4}\] is also a reducing agent but it is very less reactive than \[LiAl{H_4}\]. \[NaB{H_4}\] can reduce aldehydes, ketones and acid chlorides but cannot reduce amides or esters.
Amides can be converted to \[{1^o},{\text{ }}{2^o}{\text{ or }}{3^o}\]amine just by using \[LiAl{H_4}\]. For doing this we have to select the suitable amides to begin the reaction with.
The purpose of using \[{H_2}O\] at the end is for a bit of workup. It neutralizes strongly basic reagents at the end of the reaction thus helping in the rate of the reaction.
Amide is a functional group that contains both nitrogen and carboxyl groups in it. It is usually represented as below:

\[LiAl{H_4}\] will reduce Amides to Amines and this means that the oxygen that was present in the amide is removed from the molecule after the reaction completes.
Complete answer:
Let’s see how the reaction occurs when amide is treated with \[LiAl{H_4}\]
First there is a nucleophilic attack by one of the hydrides of \[LiAl{H_4}\] . Because the carbonyl group is highly polar the oxygen becomes negative and thus \[Al\] having negatively charge can now attack the positively charged carbonyl carbon and thus the following step occurs

Now since there is an oxygen that can act as a leaving group we will get the following reaction which leads to the formation of an iminium ion

Now there is a nucleophilic attack by the hydride of \[LiAl{H_4}\] causing for the formation of the final product, amine
That is given by the following reaction:

Thus we get Amine as the product when amides are treated with \[LiAl{H_4}\] which is a strong reducing agent.
Thus we can write the general form of the reaction as:

Note:
\[NaB{H_4}\] is also a reducing agent but it is very less reactive than \[LiAl{H_4}\]. \[NaB{H_4}\] can reduce aldehydes, ketones and acid chlorides but cannot reduce amides or esters.
Amides can be converted to \[{1^o},{\text{ }}{2^o}{\text{ or }}{3^o}\]amine just by using \[LiAl{H_4}\]. For doing this we have to select the suitable amides to begin the reaction with.
The purpose of using \[{H_2}O\] at the end is for a bit of workup. It neutralizes strongly basic reagents at the end of the reaction thus helping in the rate of the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




