
How does frequency affect the sound?
Answer
512.7k+ views
Hint: The higher the pitch of the sound we hear, the higher the frequency waves oscillate. As you can see, sound frequency is governed by how sound waves oscillate as they travel to our ears, compressing and stretching the medium, which in most cases is air.
Complete step-by-step solution:
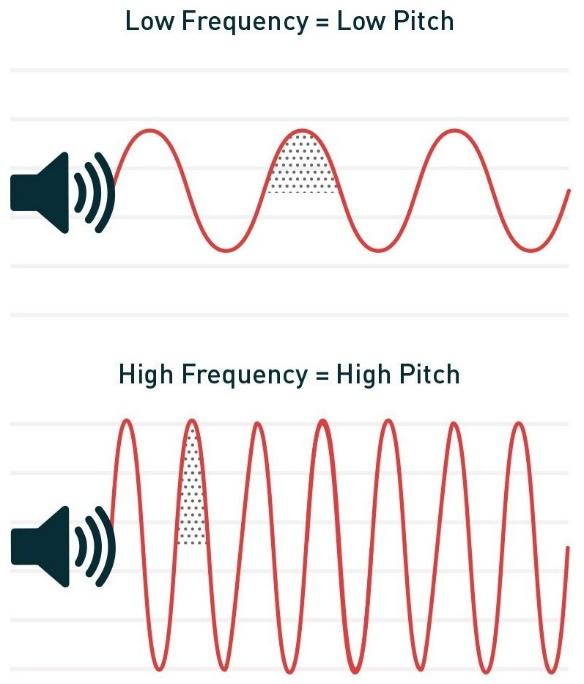
A frequency sensation is generally referred to as a sound's pitch. A high-frequency sound wave corresponds to a high pitch sound, whereas a low-frequency sound wave corresponds to a low pitch sound. Many people, especially those who have musically trained, are capable of discerning a frequency difference of as little as \[2\] Hz between two different sounds.
A frequency is the number of times sound waves pass through a given spot in a second. The pitch of a sound is how high or low we perceive it to be. The pitch is higher when the frequency is higher. Frequency is measured in hertz. GHz, or gigahertz, is another unit of measurement for frequencies. We can hear frequencies as high as \[20,000\] hertz. To summarise, the higher the pitch, the higher the frequency. The pitch decreases as the frequency decreases.
The pitch of the sound we hear will increase as the frequency of the waves increases. When the pitch of a sound is high, it is said to be shrill, and when the pitch is low, it is said to be flat. Whistles, school bells, and other high-frequency or high-pitch noises are examples. Thunder, man's voice, and other low frequency or low pitch sounds are examples.
Additional information:
Human (and another animal) ears are sensitive detectors capable of sensing air pressure variations that impact the eardrum. Later in this course, the physics of the ear's detection abilities will be examined. For the time being, it is adequate to state that the human ear can perceive sound waves with frequencies ranging from around \[20\] Hz to \[20,000\] Hz. Infrasound is any sound with a frequency below the audible range of hearing (less than \[20\] Hz), while ultrasound is any sound with a frequency above the audible range of hearing (greater than \[20,000\] Hz).
Note:
Sounds with a Low Frequency: Low-frequency noises, often known as infrasound, are sound waves that have a frequency lower than the lower limit of audibility (which is generally at about \[20\] Hz). Low-frequency noises are those with a frequency of less than \[500\] hertz.
Severe weather, waves, avalanches, earthquakes, whales, elephants, hippos, and giraffes are all examples of low-frequency sounds.
Sounds with a High Frequency: A high-frequency sound is defined as one that has a frequency of \[2000\] Hz or above. Whistles, mosquitoes, computers, screams, squeaks, glass shattering, and nails on a chalkboard are just a few examples.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A frequency sensation is generally referred to as a sound's pitch. A high-frequency sound wave corresponds to a high pitch sound, whereas a low-frequency sound wave corresponds to a low pitch sound. Many people, especially those who have musically trained, are capable of discerning a frequency difference of as little as \[2\] Hz between two different sounds.
A frequency is the number of times sound waves pass through a given spot in a second. The pitch of a sound is how high or low we perceive it to be. The pitch is higher when the frequency is higher. Frequency is measured in hertz. GHz, or gigahertz, is another unit of measurement for frequencies. We can hear frequencies as high as \[20,000\] hertz. To summarise, the higher the pitch, the higher the frequency. The pitch decreases as the frequency decreases.
The pitch of the sound we hear will increase as the frequency of the waves increases. When the pitch of a sound is high, it is said to be shrill, and when the pitch is low, it is said to be flat. Whistles, school bells, and other high-frequency or high-pitch noises are examples. Thunder, man's voice, and other low frequency or low pitch sounds are examples.

Additional information:
Human (and another animal) ears are sensitive detectors capable of sensing air pressure variations that impact the eardrum. Later in this course, the physics of the ear's detection abilities will be examined. For the time being, it is adequate to state that the human ear can perceive sound waves with frequencies ranging from around \[20\] Hz to \[20,000\] Hz. Infrasound is any sound with a frequency below the audible range of hearing (less than \[20\] Hz), while ultrasound is any sound with a frequency above the audible range of hearing (greater than \[20,000\] Hz).
Note:
Sounds with a Low Frequency: Low-frequency noises, often known as infrasound, are sound waves that have a frequency lower than the lower limit of audibility (which is generally at about \[20\] Hz). Low-frequency noises are those with a frequency of less than \[500\] hertz.
Severe weather, waves, avalanches, earthquakes, whales, elephants, hippos, and giraffes are all examples of low-frequency sounds.
Sounds with a High Frequency: A high-frequency sound is defined as one that has a frequency of \[2000\] Hz or above. Whistles, mosquitoes, computers, screams, squeaks, glass shattering, and nails on a chalkboard are just a few examples.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




