
How does electricity and magnetism work together?
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: In order to understand the relationship with which electricity and magnetism work together, it is important to understand two concepts: electromagnet and electromagnetic induction. These two phenomena describe in detail, the working relationship between electricity and magnetism.
Complete answer:
i) Electromagnet:
To put it effectively, we can define electromagnet as a device that converts electrical energy to magnetic energy. Think of an electromagnet as a device whose input is electric current and the output is magnetic field.
The electromagnets are available in several forms; however, the most common forms of electromagnets are: Solenoid and Toroid
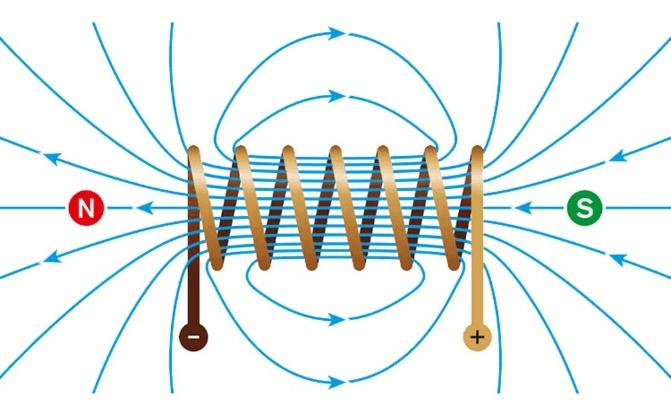

When electric current is passed through the wire, the coils behave like a magnetic forming its own North and South poles.
The magnetic field is defined as a vector field quantity that describes the magnetic influence on a unit electric charge moving perpendicular to it. The SI unit for magnetic field is tesla (T).
Now, we will consider an electromagnet in the form of a solenoid.
ii) Electromagnetic induction:
The theory of electromagnetic induction is given by the Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
It states that the voltage induced is directly proportional to rate of change of magnetic flux. The expression is given by –
The emf induced,
$E = - N\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$
where, N= number of turns of the coil, $\phi $= Magnetic flux.
Magnetic flux,
$\phi = BA\cos \theta $,
Where, B= External magnetic field, $\theta $=Angle between the coil and the magnetic field, and A=Area of the coil.
Thus, these phenomena, successfully, help us understand how electricity and magnetism work together.
Note: Another classic example of the relationship between electricity and magnetism is given by the Maxwell equations, which are a set of 4 partial differential equations that form the fundamental principle of the field of electromagnetism.
Complete answer:
i) Electromagnet:
To put it effectively, we can define electromagnet as a device that converts electrical energy to magnetic energy. Think of an electromagnet as a device whose input is electric current and the output is magnetic field.
The electromagnets are available in several forms; however, the most common forms of electromagnets are: Solenoid and Toroid


When electric current is passed through the wire, the coils behave like a magnetic forming its own North and South poles.
The magnetic field is defined as a vector field quantity that describes the magnetic influence on a unit electric charge moving perpendicular to it. The SI unit for magnetic field is tesla (T).
Now, we will consider an electromagnet in the form of a solenoid.
ii) Electromagnetic induction:
The theory of electromagnetic induction is given by the Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
It states that the voltage induced is directly proportional to rate of change of magnetic flux. The expression is given by –
The emf induced,
$E = - N\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$
where, N= number of turns of the coil, $\phi $= Magnetic flux.
Magnetic flux,
$\phi = BA\cos \theta $,
Where, B= External magnetic field, $\theta $=Angle between the coil and the magnetic field, and A=Area of the coil.
Thus, these phenomena, successfully, help us understand how electricity and magnetism work together.
Note: Another classic example of the relationship between electricity and magnetism is given by the Maxwell equations, which are a set of 4 partial differential equations that form the fundamental principle of the field of electromagnetism.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




