
How does a positive slope differ from a negative slope?
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: We first try to describe the relation between the slope of a curve and the characteristics of it being increasing, decreasing. We find the differentiation of the curve for $y=f\left( x \right)$. Depending on the value of slope we get the characteristics of the function.
Complete step by step answer:
We first try to find the general term of a function where $y=f\left( x \right)$. We express the terms as ${{t}_{n}}$, the ${{n}^{th}}$ term of the series.
We take differentiation of the function and find the slope of the function.
So, $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)$ is the slope of the function.
Now, if the slope at any fixed point is negative which means $\dfrac{df}{dx}<0$ then the function is decreasing and if $\dfrac{df}{dx}>0$ then the function is increasing.
If the changes for the whole curve happens very rapidly then the function is not monotone.
Lets’ take as an example where $f\left( x \right)=2x$.
We find the slope of the function by taking $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)$.
So, $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=2$ as \[\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n{{x}^{n-1}}\].
Now for any value of $x$, the value of $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=2>0$.
The function is monotonically increasing the whole function.
If we change the function from $f\left( x \right)=2x$ to $f\left( x \right)=-2x$, the function becomes monotonically decreasing as $\dfrac{df}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( -2x \right)=-2<0$ for any value of $x$.
We have an arbitrary curve Y= f(x). We took two points A and B.
The tangents at those points are valued positive and negative respectively.
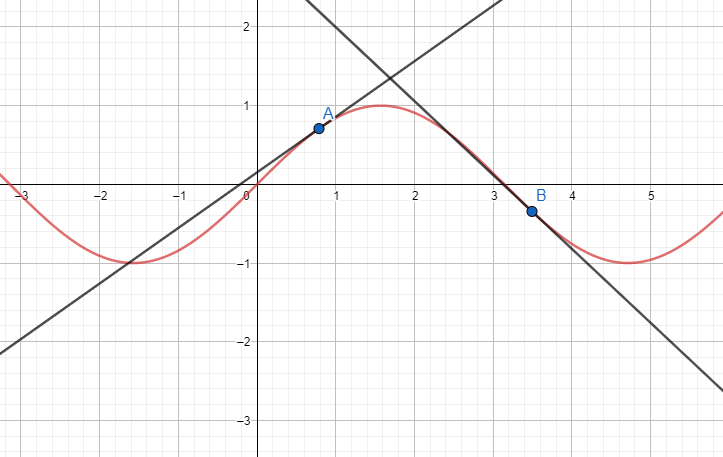
Note: We can also find the value of $x$ for which if we get ${{x}_{1}}>{{x}_{2}}$ and $f\left( {{x}_{1}} \right)>f\left( {{x}_{2}} \right)$, the curve is increasing. If we find ${{x}_{1}}<{{x}_{2}}$ and $f\left( {{x}_{1}} \right)>f\left( {{x}_{2}} \right)$, the curve is decreasing. The change of values is equal to the slope.
Complete step by step answer:
We first try to find the general term of a function where $y=f\left( x \right)$. We express the terms as ${{t}_{n}}$, the ${{n}^{th}}$ term of the series.
We take differentiation of the function and find the slope of the function.
So, $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)$ is the slope of the function.
Now, if the slope at any fixed point is negative which means $\dfrac{df}{dx}<0$ then the function is decreasing and if $\dfrac{df}{dx}>0$ then the function is increasing.
If the changes for the whole curve happens very rapidly then the function is not monotone.
Lets’ take as an example where $f\left( x \right)=2x$.
We find the slope of the function by taking $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)$.
So, $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=2$ as \[\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n{{x}^{n-1}}\].
Now for any value of $x$, the value of $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=2>0$.
The function is monotonically increasing the whole function.
If we change the function from $f\left( x \right)=2x$ to $f\left( x \right)=-2x$, the function becomes monotonically decreasing as $\dfrac{df}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( -2x \right)=-2<0$ for any value of $x$.
We have an arbitrary curve Y= f(x). We took two points A and B.
The tangents at those points are valued positive and negative respectively.

Note: We can also find the value of $x$ for which if we get ${{x}_{1}}>{{x}_{2}}$ and $f\left( {{x}_{1}} \right)>f\left( {{x}_{2}} \right)$, the curve is increasing. If we find ${{x}_{1}}<{{x}_{2}}$ and $f\left( {{x}_{1}} \right)>f\left( {{x}_{2}} \right)$, the curve is decreasing. The change of values is equal to the slope.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




