
Do the following conversions in not more than two steps:
Propanoic acid to 2-hydroxypropanoic acid
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: We know that propanoic acid is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acid contains a carboxyl functional group. We have to know that the carboxyl functional group has a carbonyl functional group and a hydroxyl functional group. The carbonyl functional group is $ - CO$ and the hydroxyl functional group is $ - OH$. The general formula of carboxylic acid is $R - COOH$.
Complete step by step answer:
In the propanoic acid, there would be three atoms of carbon and in carbon first, the carboxyl functional group could be present.
In 2-hydroxypropanoic acid, a hydroxyl group could be present in the carbon second position of the parent carboxylic acid chain.
We can draw the structure of propanoic acid as,
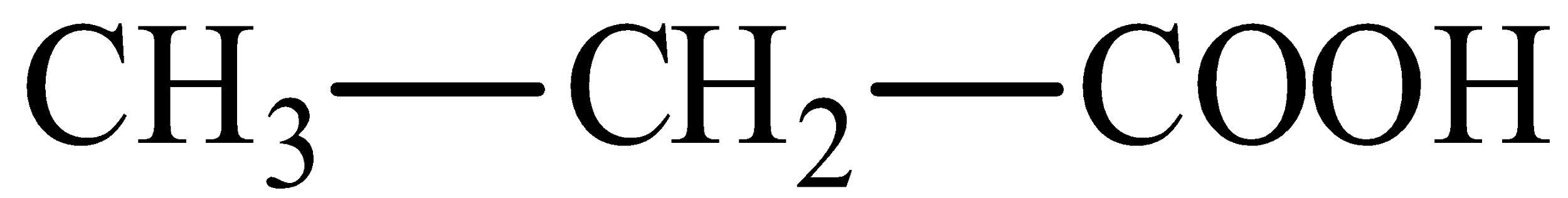
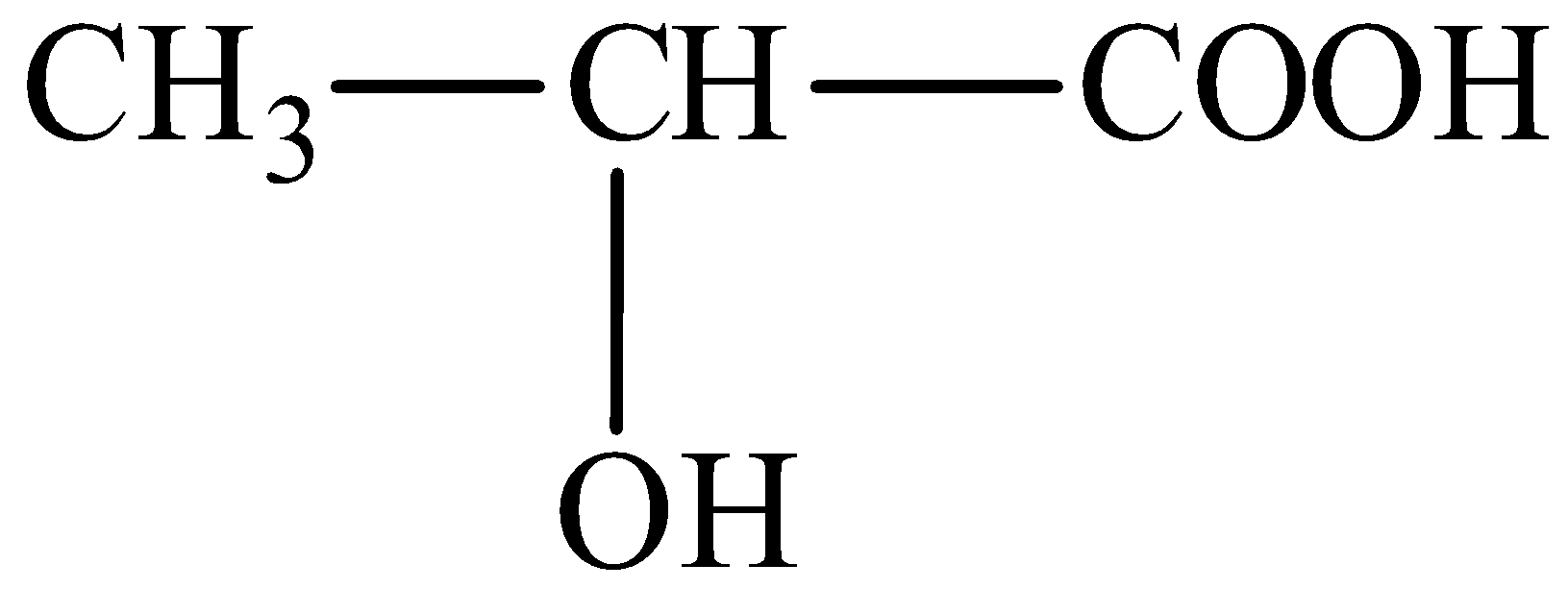
We can draw the structure of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid is,
We can convert propanoic acid to 2-hydroxypropanoic acid by alpha halogenation reaction.
Propanoic acid is reacted with halogen such as chlorine, bromine in the presence of red phosphorus. We obtain alpha-halo carboxylic acid. This reaction is called the Hell Vohlard Zelinsky reaction. This alpha-halo carboxylic acid undergoes hydrolysis to form 2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
In the first step, propanoic acid is reacted with bromine in the presence of red phosphorus to form alpha-bromo carboxylic acid. The formed alpha-bromo carboxylic acid undergoes hydrolysis to form 2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
We can write the first step of this reaction as,
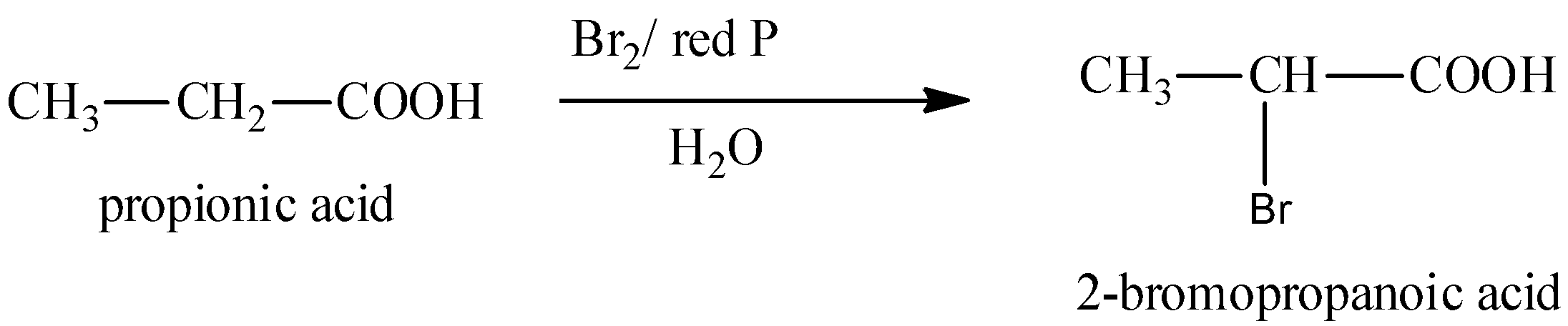
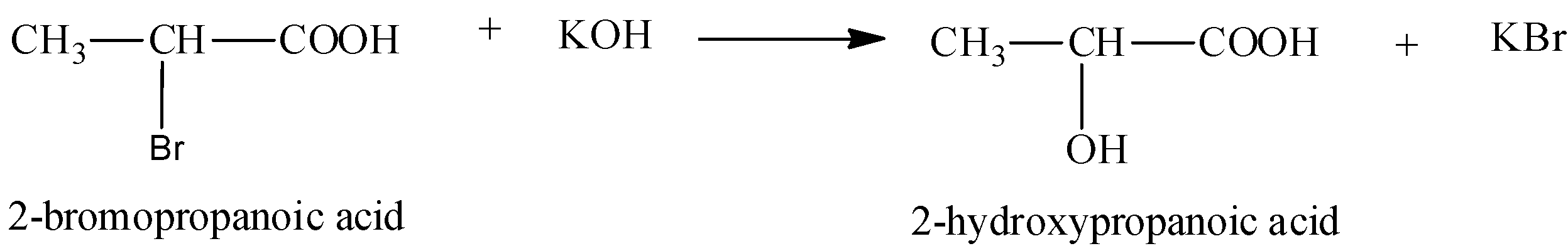
We can write the second step of this reaction as,
Note:
We have to know that the Hell Vohlard Zelinsky reaction is a reaction that is utilized for halogenation of carboxylic acid at the position of alpha carbon. Certain carboxylic acids and derivatives of acid like anhydrides (or) acyl halides could be halogenated during the absence of a catalyst. Iodination and fluorination of carboxylic acids could be accomplished by Hell Vohlard Zelinsky reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
In the propanoic acid, there would be three atoms of carbon and in carbon first, the carboxyl functional group could be present.
In 2-hydroxypropanoic acid, a hydroxyl group could be present in the carbon second position of the parent carboxylic acid chain.
We can draw the structure of propanoic acid as,
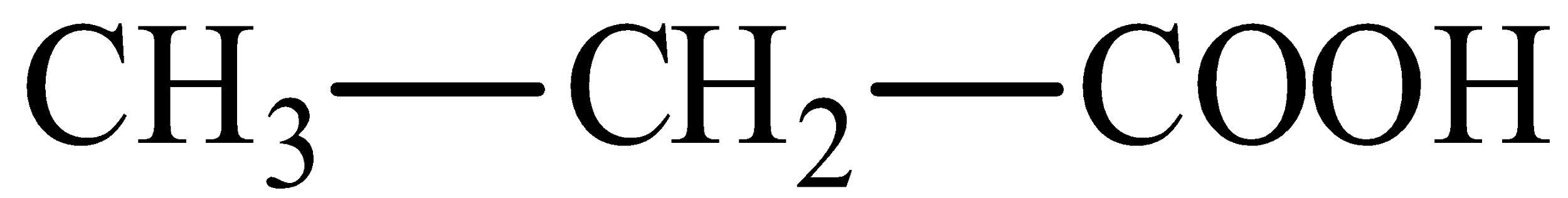
We can draw the structure of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid is,

We can convert propanoic acid to 2-hydroxypropanoic acid by alpha halogenation reaction.
Propanoic acid is reacted with halogen such as chlorine, bromine in the presence of red phosphorus. We obtain alpha-halo carboxylic acid. This reaction is called the Hell Vohlard Zelinsky reaction. This alpha-halo carboxylic acid undergoes hydrolysis to form 2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
In the first step, propanoic acid is reacted with bromine in the presence of red phosphorus to form alpha-bromo carboxylic acid. The formed alpha-bromo carboxylic acid undergoes hydrolysis to form 2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
We can write the first step of this reaction as,

We can write the second step of this reaction as,

Note:
We have to know that the Hell Vohlard Zelinsky reaction is a reaction that is utilized for halogenation of carboxylic acid at the position of alpha carbon. Certain carboxylic acids and derivatives of acid like anhydrides (or) acyl halides could be halogenated during the absence of a catalyst. Iodination and fluorination of carboxylic acids could be accomplished by Hell Vohlard Zelinsky reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




