
DNA replication occurs in which phase of cell cycle?
a) Mitosis
b) Prophase
c) Interphase
d) Metaphase
e) Cytokinesis
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: A complete cell cycle comprises four stages namely G1, S, G2 and M phases. Out of these four stages, G1, S & G2 phases constitute the interphase period after the completion of which the cell enters the mitotic phase i.e., the division phase.
Complete answer:
In general, every cell has two major periods in its life cycle – the interphase or non-division phase and the phase of division (which produce two daughter cells). The Synthetic activities taking place during interphase mainly include the synthesis of DNA, RNA and proteins. The synthesis of RNA and proteins continues throughout the interphase i.e. throughout the G1 (Gap 1) and G2 (Gap 2) phases as well as the S (Synthesis) phase. DNA synthesis however is limited only to the S phase.
The events occurring in Interphase or non-division phase are –
G1 phase: At the end of one cell division, the post mitotic gap phase (G1) occurs. RNA and protein synthesis takes place during this phase.
S phase: S phase or synthesis phase involves DNA synthesis from purine and pyrimidine nucleotides. Replication of chromosomal DNA takes place in this phase and histones are also synthesized.
G2 phase: During the pre-mitotic gap phase (G2) all the metabolic activities related to the growth of cytoplasm and of its constituent organelles and macromolecules are performed. Protein and RNA synthesis takes place in this phase, however, DNA synthesis stops.
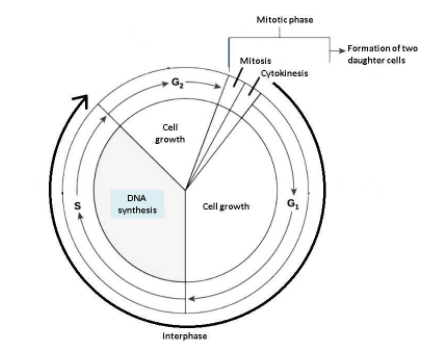
Different stages of Cell cycle
The division phase or mitosis can be explained as –
Mitosis: Mitosis is an equational division in which two daughter cells are formed at the end of the division from one parent cell and both the daughter cells carry the same number of chromosomes that was present in the parent cell. Mitosis includes Karyokinesis (the division of the chromosomes) followed by cytokinesis (the division of the cytoplasm). Karyokinesis is divided into four phases – 1.Prophase, 2. Metaphase, 3. Anaphase and, 4. Telophase.
The options A, i.e., Mitosis; B, i.e., Prophase; D, i.e., Metaphase and E, i.e. Cytokinesis is related to the division phase of cell cycle. The option C, i.e. Interphase includes gap phases (G1 and G2) and S phase.
Thus, the option C, i.e. Interphase is the correct answer.
Note:Replication of DNA molecule (duplication of DNA) occurs during S phase of Interphase. In this way, the genetic material of a cell is doubled before it enters the division phase, where division of genetic material takes place.
Complete answer:
In general, every cell has two major periods in its life cycle – the interphase or non-division phase and the phase of division (which produce two daughter cells). The Synthetic activities taking place during interphase mainly include the synthesis of DNA, RNA and proteins. The synthesis of RNA and proteins continues throughout the interphase i.e. throughout the G1 (Gap 1) and G2 (Gap 2) phases as well as the S (Synthesis) phase. DNA synthesis however is limited only to the S phase.
The events occurring in Interphase or non-division phase are –
G1 phase: At the end of one cell division, the post mitotic gap phase (G1) occurs. RNA and protein synthesis takes place during this phase.
S phase: S phase or synthesis phase involves DNA synthesis from purine and pyrimidine nucleotides. Replication of chromosomal DNA takes place in this phase and histones are also synthesized.
G2 phase: During the pre-mitotic gap phase (G2) all the metabolic activities related to the growth of cytoplasm and of its constituent organelles and macromolecules are performed. Protein and RNA synthesis takes place in this phase, however, DNA synthesis stops.

Different stages of Cell cycle
The division phase or mitosis can be explained as –
Mitosis: Mitosis is an equational division in which two daughter cells are formed at the end of the division from one parent cell and both the daughter cells carry the same number of chromosomes that was present in the parent cell. Mitosis includes Karyokinesis (the division of the chromosomes) followed by cytokinesis (the division of the cytoplasm). Karyokinesis is divided into four phases – 1.Prophase, 2. Metaphase, 3. Anaphase and, 4. Telophase.
The options A, i.e., Mitosis; B, i.e., Prophase; D, i.e., Metaphase and E, i.e. Cytokinesis is related to the division phase of cell cycle. The option C, i.e. Interphase includes gap phases (G1 and G2) and S phase.
Thus, the option C, i.e. Interphase is the correct answer.
Note:Replication of DNA molecule (duplication of DNA) occurs during S phase of Interphase. In this way, the genetic material of a cell is doubled before it enters the division phase, where division of genetic material takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




