
Distinguish between \[{C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}\] and \[{C_6}{H_5}NHC{H_3}\] .
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: The derivatives of amine are formed by substituting the hydrogen atoms that are attached to the nitrogen. This makes the nitrogen either 1 – degree, 2 – degree, or 3 – degree depending on the number of hydrogens that have been substituted. Here, \[{C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}\] is a primary amine or 1-degree amine and \[{C_6}{H_5}NHC{H_3}\] is a secondary amine or 2-degree amine.
Complete step by step answer:
To distinguish one from another use reactions where a change of physical characteristics has happened. For example, change of color of the solution, precipitation takes place, generation of effervescence, generation of different odors, etc.
To distinguish between \[{C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}\] and \[{C_6}{H_5}NHC{H_3}\] . Carbylamine reaction is used.
The Carbylamine test is a method for detecting or determining primary amines given in the present compounds, by heating the given substance with chloroform in a basic solution. The test shows positive results for the presence of a primary amine, by emitting a characteristic foul smell, which is caused by the release of isocyanide.
The reaction is shown below,
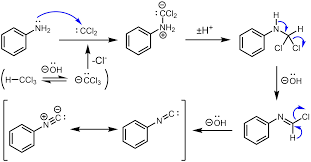
But the secondary amine does not perform this reaction.
Additional information:
To name any amine, the parent compound can be understood by the suffix added at the end of the name of the compound. As we can see, the name of the amine compound ends with the suffix -amine.
Hence, the parent compound is Amine. The structure of amine can be given as:
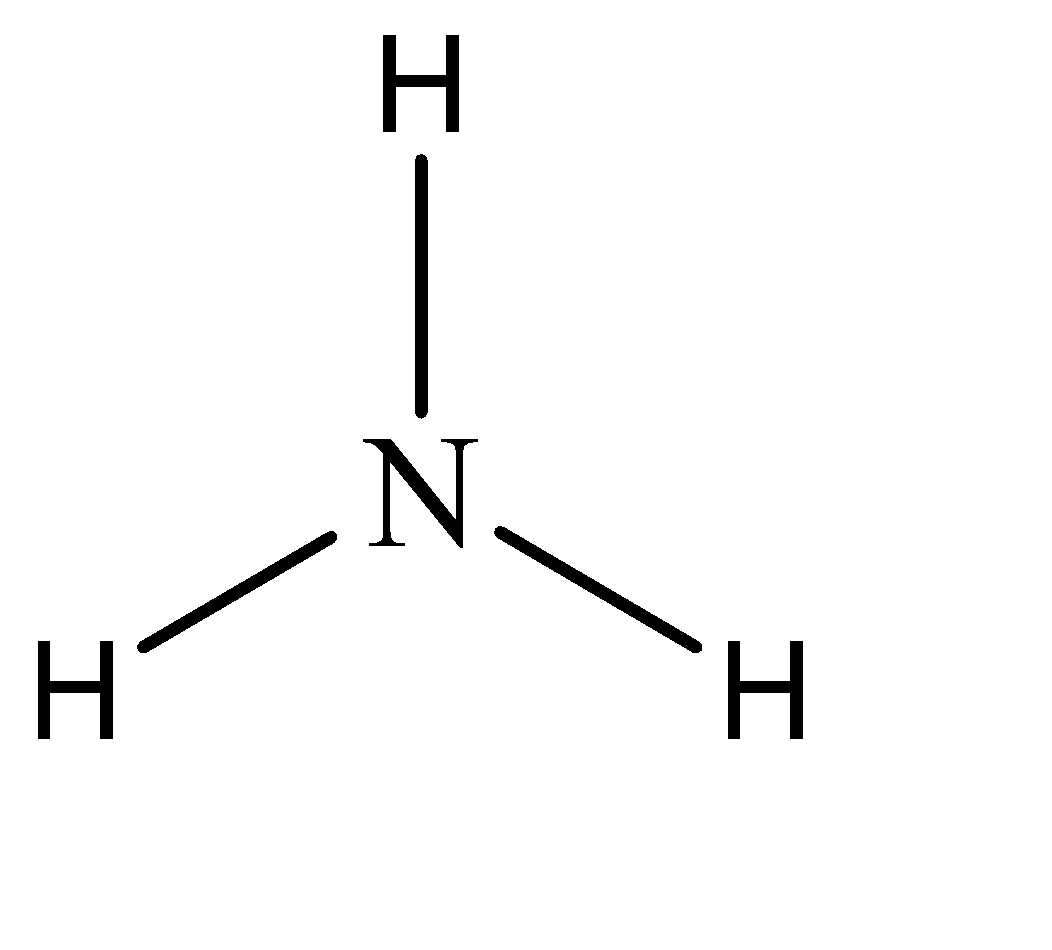
Now, while naming derivative compounds of amine, the rules that are followed include placing the corresponding replacing functional groups in alphabetical order followed by the suffix ‘amine’.
Now for example the amine compound is n – methylethanamine. This means that two of the hydrogen atoms are substituted from amine. The functional groups that have substituted these hydrogen atoms are ethyl and methyl. Hence the structure of n – methylethanamine can be given as:
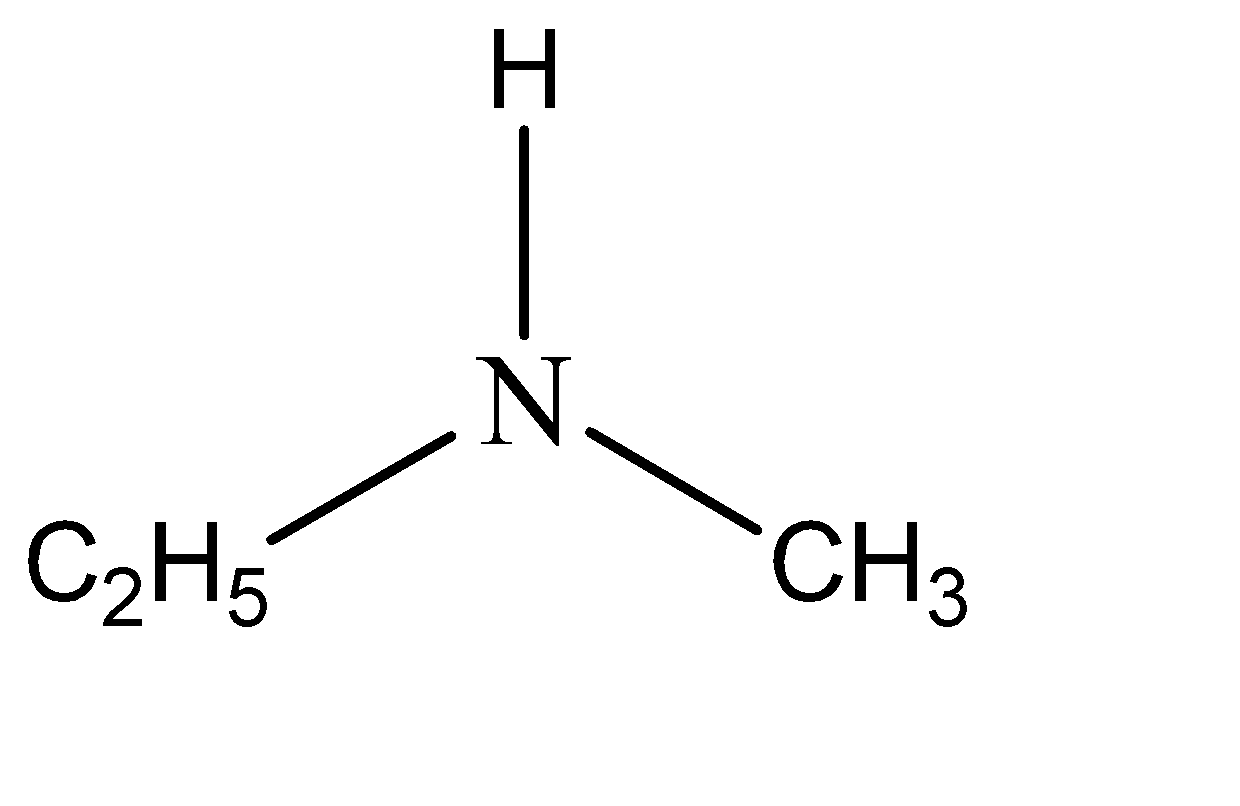
Note:The terms primary, secondary & tertiary are used to classify amines in a completely different manner than they were used for alcohol or alkyl halides. When applied to amines these terms refer to the number of alkyls (or aryl) substituents bonded to the nitrogen atom, whereas in other cases they refer to the nature of an alkyl group.
Complete step by step answer:
To distinguish one from another use reactions where a change of physical characteristics has happened. For example, change of color of the solution, precipitation takes place, generation of effervescence, generation of different odors, etc.
To distinguish between \[{C_6}{H_5}N{H_2}\] and \[{C_6}{H_5}NHC{H_3}\] . Carbylamine reaction is used.
The Carbylamine test is a method for detecting or determining primary amines given in the present compounds, by heating the given substance with chloroform in a basic solution. The test shows positive results for the presence of a primary amine, by emitting a characteristic foul smell, which is caused by the release of isocyanide.
The reaction is shown below,

But the secondary amine does not perform this reaction.
Additional information:
To name any amine, the parent compound can be understood by the suffix added at the end of the name of the compound. As we can see, the name of the amine compound ends with the suffix -amine.
Hence, the parent compound is Amine. The structure of amine can be given as:

Now, while naming derivative compounds of amine, the rules that are followed include placing the corresponding replacing functional groups in alphabetical order followed by the suffix ‘amine’.
Now for example the amine compound is n – methylethanamine. This means that two of the hydrogen atoms are substituted from amine. The functional groups that have substituted these hydrogen atoms are ethyl and methyl. Hence the structure of n – methylethanamine can be given as:

Note:The terms primary, secondary & tertiary are used to classify amines in a completely different manner than they were used for alcohol or alkyl halides. When applied to amines these terms refer to the number of alkyls (or aryl) substituents bonded to the nitrogen atom, whereas in other cases they refer to the nature of an alkyl group.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




