
Discuss the mechanism of the following reactions: (a) Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides.
Answer
549.3k+ views
Hint: On heating alkyl halide with hot conc potassium hydroxide solution, hydrogen halide molecule gets eliminated and there is formation of an alkene.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to know about dehydrohalogenation reactions in case of alkyl halides. Dehydrohalogenation is a reaction where the alkyl halide gets treated with potassium hydroxide solution, which is prepared in a very concentrated solution, and also, the temperature of the solution is kept high. It is done so in order to reach the optimum conditions for the reaction to occur and so that the reaction occurs fast.
On adding this potassium hydroxide solution, elimination of a molecule of hydrogen halide occurs and in order to fill the octet, there is a formation of a double bond, which gives the product as an alkene. Let us see the reaction:
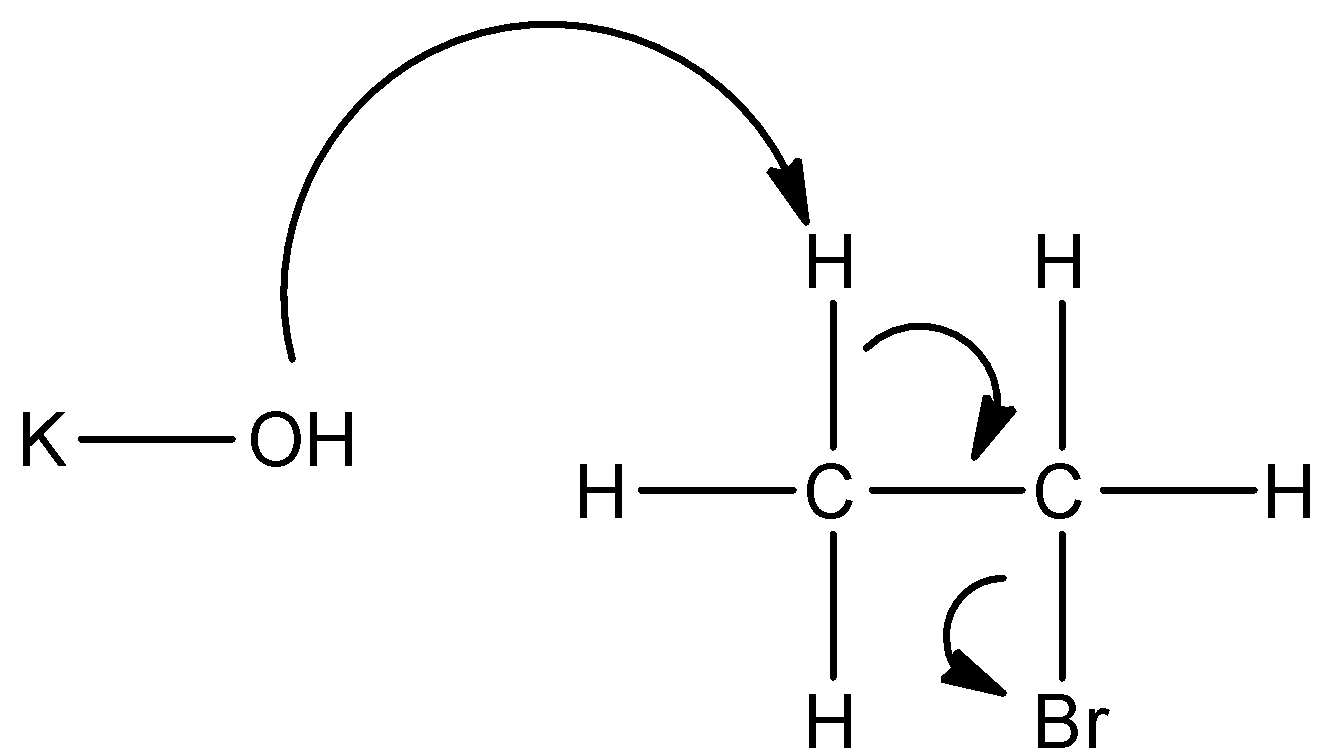
Here, we can see that as potassium hydroxide is a strong base, so the hydrogen gets replaced by $O{{H}^{-}}$. But, on a single carbon atom, two molecules of hydrogen and one molecule of oxygen will get unstable. So, when it is heated, these molecules come out as ${{H}_{2}}O$, which is water. Since one valency is missing it is accompanied by a double bond. So, we get the final compound as ethene.
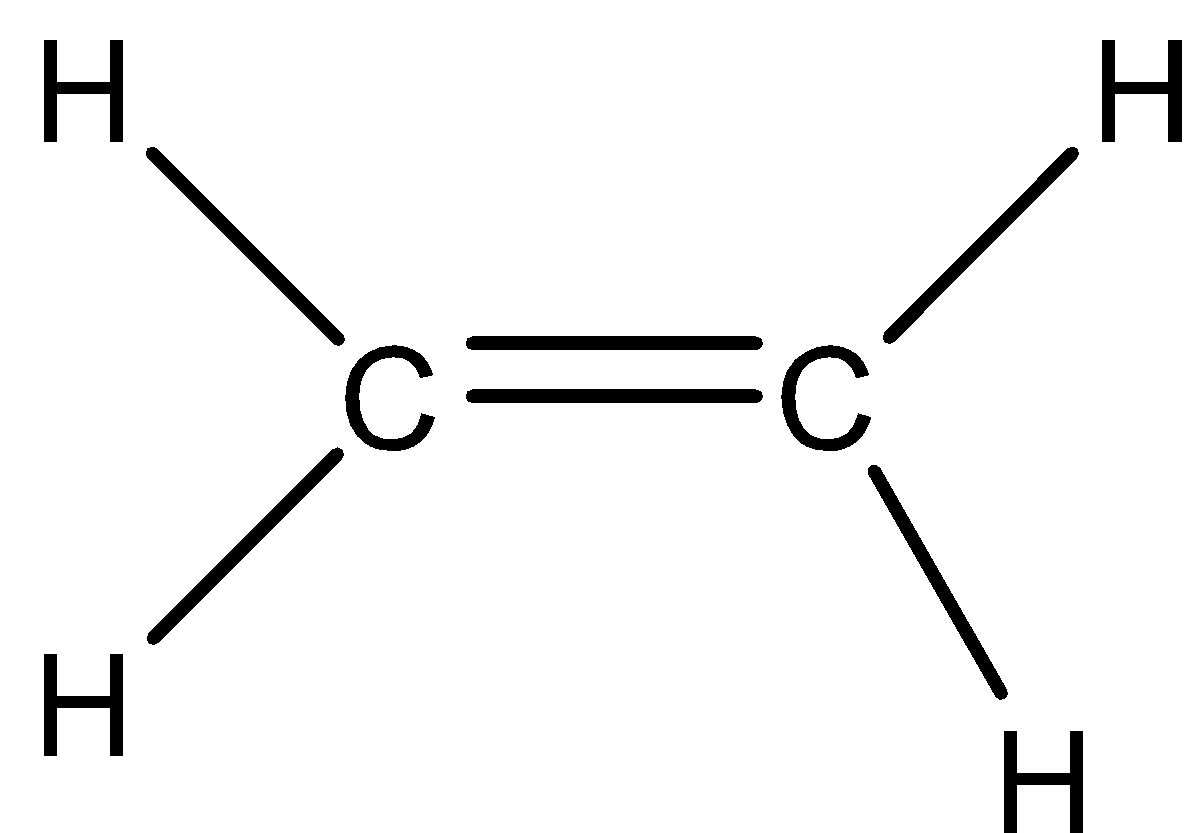
Summing it up, we can write the whole reaction as:
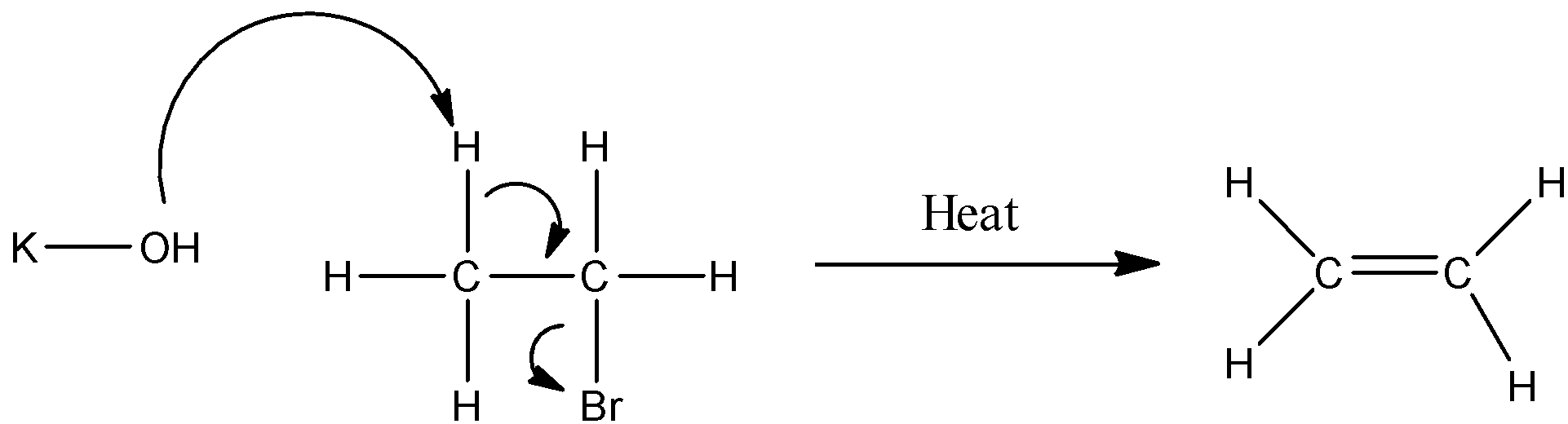
Note:
It is to be noted that apart from water, some amount of $KBr$ is also formed, as the potassium ion reacts with the outgoing bromide ion.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to know about dehydrohalogenation reactions in case of alkyl halides. Dehydrohalogenation is a reaction where the alkyl halide gets treated with potassium hydroxide solution, which is prepared in a very concentrated solution, and also, the temperature of the solution is kept high. It is done so in order to reach the optimum conditions for the reaction to occur and so that the reaction occurs fast.
On adding this potassium hydroxide solution, elimination of a molecule of hydrogen halide occurs and in order to fill the octet, there is a formation of a double bond, which gives the product as an alkene. Let us see the reaction:

Here, we can see that as potassium hydroxide is a strong base, so the hydrogen gets replaced by $O{{H}^{-}}$. But, on a single carbon atom, two molecules of hydrogen and one molecule of oxygen will get unstable. So, when it is heated, these molecules come out as ${{H}_{2}}O$, which is water. Since one valency is missing it is accompanied by a double bond. So, we get the final compound as ethene.

Summing it up, we can write the whole reaction as:

Note:
It is to be noted that apart from water, some amount of $KBr$ is also formed, as the potassium ion reacts with the outgoing bromide ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




