
Differentiate between homozygous and heterozygous
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: Homozygous individuals have the same forms of gene i.e. same alleles. Heterozygous individuals have different forms of a gene.
Complete answer: The differences between homozygous and heterozygous are as follows:
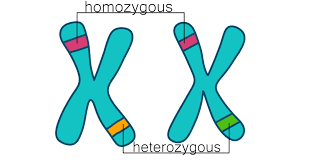
Note: The above lines can be explained easily with an example.
If we consider the T allele for the tall phenotype and t for the short, then a homozygous individual would have a genotype of TT (homozygous dominant) or tt (homozygous recessive)while the heterozygous individual would have Tt (with dominant phenotype).
Complete answer: The differences between homozygous and heterozygous are as follows:
| Homozygous | Heterozygous |
| If both the chromosomes of an individual have the same allele of a particular gene, they are known to be homozygous. | If both the chromosomes of an individual have the same allele of a particular gene, they are known to be homozygous. |
| When homozygous individuals have both the dominant alleles on the chromosomes, then the dominant trait is expressed and they are called homozygous dominant. If both are recessive, they are called homozygous recessive. | When homozygous individuals have one dominant allele and another allele is recessive, then the dominant trait is expressed and they are called heterozygous dominant.It happens because the dominant allele overpowers the recessive. |
| In homozygous condition, the recessive trait will be expressed. Because the dominant allele is absent. | In the heterozygous condition, only the dominant trait is expressed. Because the recessive allele needs another recessive to express itself and heterozygosity does not support that. |

Note: The above lines can be explained easily with an example.
If we consider the T allele for the tall phenotype and t for the short, then a homozygous individual would have a genotype of TT (homozygous dominant) or tt (homozygous recessive)while the heterozygous individual would have Tt (with dominant phenotype).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




