
Differentiate between back cross and test cross.
Answer
536.2k+ views
Hint: The main difference between a test cross and a back cross lies in their role of action.
Complete answer: The major differences between the test cross and back cross are as follows:
Additional Information:
1. Zygosity refers to the proportion of individuals that can be either homozygous or heterozygous. A heterozygous genotype has a dominant and a recessive allele. Whereas a homozygous genotype can have either both dominant or both recessive alleles.
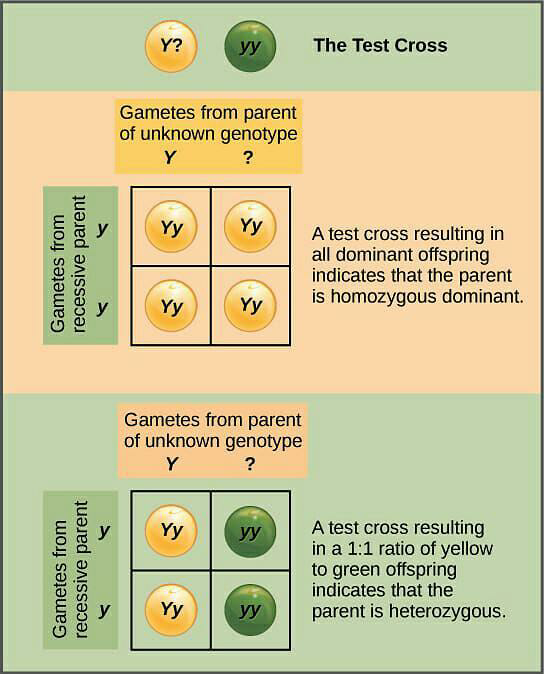
2. If in a test cross, the dominant character (F1) is heterozygous, then crossing it with a recessive parent will also produce a recessive product whereas if the dominant character (F1) is homozygous then it will not produce any recessive product.
Note:
1. In animals, the back cross is also referred to as a ‘top cross'.
2. The back cross and test cross were first discovered by Gregor Mendel during his hybridization experiment on the pea plant.
3. All the crosses can be diagrammatically presented with the help of a square known as Punnett square. Let us understand the test cross with the help of a Punnett square.
Complete answer: The major differences between the test cross and back cross are as follows:
| Test cross | Back cross |
| Breeding of the dominant phenotype with the homozygous recessive phenotype (parent) is known as a test cross. | The breeding of F1 generation with one of its parent plants is known as a back cross. |
| All test crosses are backcrosses. | A backcross can be said as a test cross if the parent is recessive. |
| The F1 hybrid is crossed with a recessive genotype. | An F1 hybrid is crossed with either homozygous dominant or heterozygous genotypes. |
| The test cross helps in the identification of the genotype of the dominant individual. | The back cross helps in the identification of the elite genotype by checking the segregation of genes at the time of gamete formation. |
Additional Information:
1. Zygosity refers to the proportion of individuals that can be either homozygous or heterozygous. A heterozygous genotype has a dominant and a recessive allele. Whereas a homozygous genotype can have either both dominant or both recessive alleles.
2. If in a test cross, the dominant character (F1) is heterozygous, then crossing it with a recessive parent will also produce a recessive product whereas if the dominant character (F1) is homozygous then it will not produce any recessive product.
Note:
1. In animals, the back cross is also referred to as a ‘top cross'.
2. The back cross and test cross were first discovered by Gregor Mendel during his hybridization experiment on the pea plant.
3. All the crosses can be diagrammatically presented with the help of a square known as Punnett square. Let us understand the test cross with the help of a Punnett square.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




