
Differentiate between alternate and whorled phyllotaxy.
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: The mode of arrangement of mature leaves on the stem and its branches. This type of arrangement helps in avoiding shading each other in order that every leaf gets full light.
Complete step by step answer:
Additional Information:
- Phyllotaxy are three basic types of leaf arrangement: Trees with alternate arrangement have one leaf at each node.
- When one leaf arises at each node and leaf of adjacent nodes lie towards the other sides. They're arranged spirally round the nodes and appear to be arranged in vertical rows. This is often called orthostichy.
- In the cyclic sort of phyllotaxy the leaves at each node form a whorl with the leaves placed on a circle during which the angles between adjacent leaves are an equivalent .
- Leaf mosaic the arrangement of foliage in such a pattern exposes the utmost number of leaves to the direct rays of the sun with little loss of intervening space. eg. ivy , sycamore , Oxalis, Indian cress .
- Incision leaf may be a compound leaf that's divided into smaller leaflets. It can either be even or odd, which is that the amount of leaflets contained on the leaf.
- Palmate leaf: may be a leaf that has smaller leaflets attaching to a standard point. the entire structure is "palm- like" and shaped just like the palm of your hand.
- Petiole (Mesopodium) is the cylindrical stalk of a leaf which lifts the lamina above the stem to supply exposure. Leaf having petiole is named petiolate and sessile if petiole is absent.
- Peltate: it's a kind of leaf insertion during which leaf lamina is at right angles to the petiole. Eg. Lotus.
Note:
Venation is that the arrangement of veins & veinlets within the lamina of leaves
Functions:
- Conduction of water through xylem.
- Providing channels for translocation of organic nutrients.
- Conduction of minerals.
- Provide skeletal support to lamina.
Complete step by step answer:
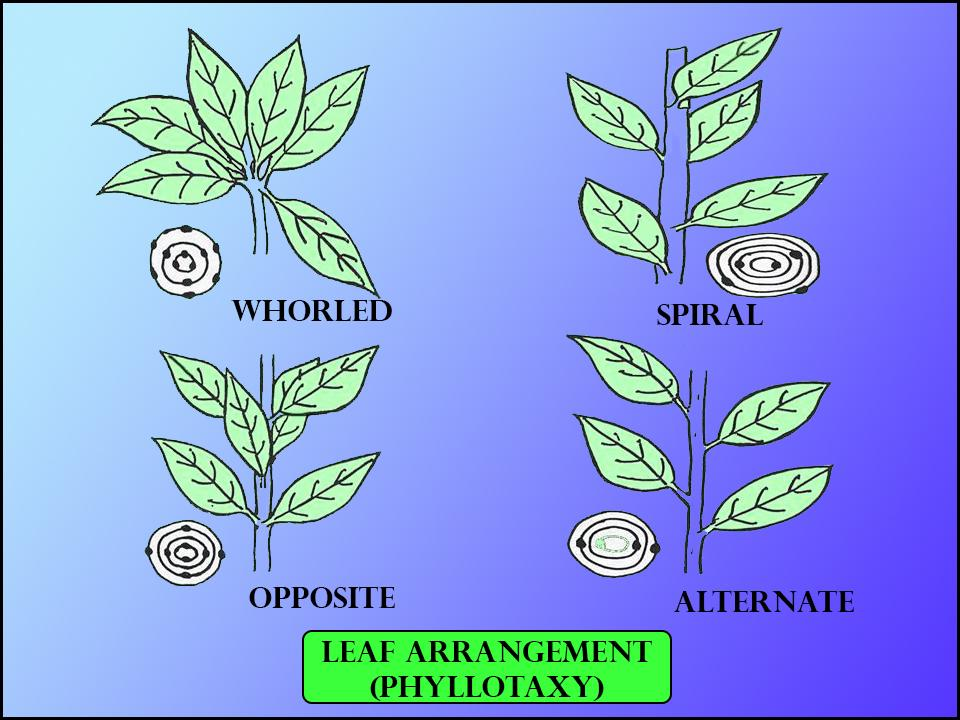
| Whorled phyllotaxy | Alternate and whorled phyllotaxy |
| In this type of phyllotaxy more than two leaves are present at each node, forming a whorl. | In such a case only one leaf is attached at each node. |
| When more than two leaves are arranged in the form of a whorl at each node. | The leaves are arranged that a line drawn on the stem through the leaf bases will take a spiral course. |
| Ex. Oleander, Alstonia etc. | Ex. Hibiscus, Brassica etc. |

Additional Information:
- Phyllotaxy are three basic types of leaf arrangement: Trees with alternate arrangement have one leaf at each node.
- When one leaf arises at each node and leaf of adjacent nodes lie towards the other sides. They're arranged spirally round the nodes and appear to be arranged in vertical rows. This is often called orthostichy.
- In the cyclic sort of phyllotaxy the leaves at each node form a whorl with the leaves placed on a circle during which the angles between adjacent leaves are an equivalent .
- Leaf mosaic the arrangement of foliage in such a pattern exposes the utmost number of leaves to the direct rays of the sun with little loss of intervening space. eg. ivy , sycamore , Oxalis, Indian cress .
- Incision leaf may be a compound leaf that's divided into smaller leaflets. It can either be even or odd, which is that the amount of leaflets contained on the leaf.
- Palmate leaf: may be a leaf that has smaller leaflets attaching to a standard point. the entire structure is "palm- like" and shaped just like the palm of your hand.
- Petiole (Mesopodium) is the cylindrical stalk of a leaf which lifts the lamina above the stem to supply exposure. Leaf having petiole is named petiolate and sessile if petiole is absent.
- Peltate: it's a kind of leaf insertion during which leaf lamina is at right angles to the petiole. Eg. Lotus.
Note:
Venation is that the arrangement of veins & veinlets within the lamina of leaves
Functions:
- Conduction of water through xylem.
- Providing channels for translocation of organic nutrients.
- Conduction of minerals.
- Provide skeletal support to lamina.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




