
Differentiate between acetaldehyde and acetone with suitable reactions.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: The IUPAC name of acetaldehyde and acetone are ethanol and propanone respectively. They have the functional groups of –CHO and =O respectively. These groups are responsible for different characteristics present in the compounds given in the question.
Complete step by step solution:
-Acetaldehyde has 2 carbon chains in it while acetone has 3 carbon chains as suggested by their IUPAC names. Acetaldehyde is an aldehyde and acetone is a ketone and so they show different reactions. Their structures can be shown as
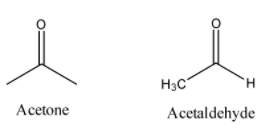
-They form different products on oxidation, reaction with 1 mole of grignard’s reagent, reaction with Tollen’s reagent, reaction of Benedict’s solution and many more reactions.
Acetaldehyde gives black silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent $\left( AgN{{O}_{3}}+N{{H}_{4}}OH \right)$ and red precipitate with Fehling’s solution while acetone does not give this test. The reactions can be given as
\[\text{(Tex translation failed)}\]
-Acetaldehyde reacts with grignard’s reagent to form second degree alcohol while acetone forms three degree alcohol with Grignard reagent. Reaction can be shown as
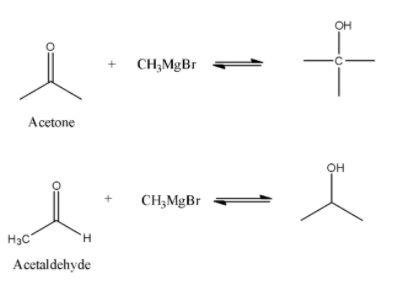
Additional information:
Some of the functional groups used in organic chemistry can be shown as:
Note: Both aldehyde and ketone are pure carbonyl compounds and so they undergo nucleophilic addition reactions to form the compounds. So all the reactions of acetaldehyde and acetone are nucleophilic addition reactions only. Both are colourless compounds but can be easily distinguished by the above reactions.
Complete step by step solution:
-Acetaldehyde has 2 carbon chains in it while acetone has 3 carbon chains as suggested by their IUPAC names. Acetaldehyde is an aldehyde and acetone is a ketone and so they show different reactions. Their structures can be shown as

-They form different products on oxidation, reaction with 1 mole of grignard’s reagent, reaction with Tollen’s reagent, reaction of Benedict’s solution and many more reactions.
Acetaldehyde gives black silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent $\left( AgN{{O}_{3}}+N{{H}_{4}}OH \right)$ and red precipitate with Fehling’s solution while acetone does not give this test. The reactions can be given as
\[\text{(Tex translation failed)}\]
-Acetaldehyde reacts with grignard’s reagent to form second degree alcohol while acetone forms three degree alcohol with Grignard reagent. Reaction can be shown as

Additional information:
Some of the functional groups used in organic chemistry can be shown as:
| CLASS | NAME | SUFFIX | PREFIX |
| R-COOH | Alkanoic acid | Oic acid | Carboxy |
| $R-S{{O}_{3}}H$ | Alkane sulfonic acid | Sulfonic acid | Sulfo |
| R-(CO)-O-(CO)-R | Alkanoic anhydride | Oic anhydride | ----- |
| R-COOR | Alkyl alkanoate | oate | Alkoxy carbonyl |
| R-(CO)-X | Alkanoyl halide | Oyl-halide | Halo Carbonyl |
| $R-\left( CO \right)-N{{H}_{2}}$ | Alkanamide | Amide | Carbamoyl |
| R-CN | Alkane nitrile | Nitrile | Cyano |
| R-CHO | Alkanal | -al | Oxo |
| R-CO-R | Alkanone | -one | oxo |
| R-OH | Alkanol | -ol | Hydroxy |
| R-SH | Alkanethiol | -thiol | mercapto |
| $R-N{{H}_{2}}$ | alkanamide | -amine | amino |
Note: Both aldehyde and ketone are pure carbonyl compounds and so they undergo nucleophilic addition reactions to form the compounds. So all the reactions of acetaldehyde and acetone are nucleophilic addition reactions only. Both are colourless compounds but can be easily distinguished by the above reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




