
How many different types of gametes are produced by genotype AaVv?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 4
d) 6
e) 8
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: A heterozygous organism is one that possesses two distinct alleles at the same genetic location, or locus. A dihybrid is an individual that is heterozygous at two genes. At the time of gamete formation, each gamete receives only one copy of the gene, which is selected randomly. This is known as law of segregation
Complete answer:
The number of sets of chromosomes in a cell or an organism is defined as ploidy. For example, haploid means one set of chromosomes and diploid means two sets of chromosomes. Most eukaryotes (plants and animals) have two copies of each chromosome, known as homologous pairs. A homologous chromosome pair is made up of chromosomes with similar lengths, gene positions, and centromere positions. Meiosis is the mechanism of gamete formation that involves a two-stage division process. During the first meiotic division, homologous chromosomes divide, and the sister chromatids that arise separate during the second division resulting in four daughter cells at the end of meiosis. Each of these is haploid, meaning each gamete only has half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. The chromosomes in each gamete have the right sequence of genes but various gene alleles.
In the given question, the person is heterozygous (both alleles are present) for two different traits.
Types of gametes produced by an organism= \[{2^n}\]
where n= number of genes for which the organism is heterozygous.
The given genotype "AaVv" is heterozygous for $2$ genes;
Therefore total number of types of gametes formed by an organisms is ${2^2} = 4$
Total types of gamete produced by it= \[22 = {\text{ }}4\] (AV, Av, aV and av)
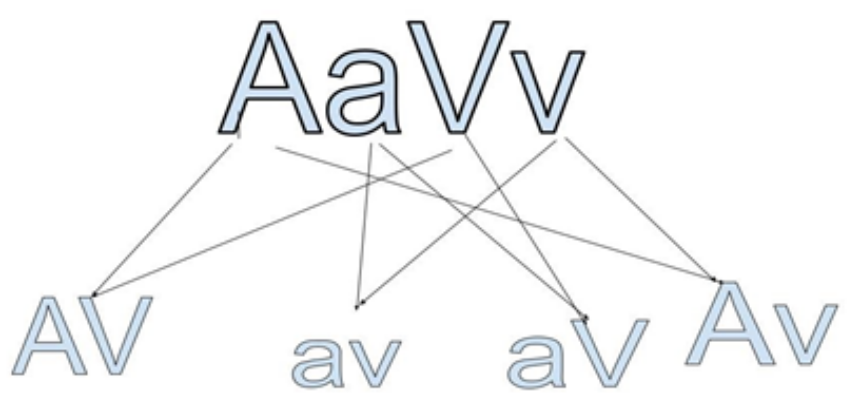
Hence, Option C is the correct answer.
Additional information:
The term 'genotype' was introduced by a Danish Botanist named Wilhelm Johannsen. Before Gregor Mendel who was known as the father of genetics, the theories were based on logic and speculation but not on experiments. In his monastery garden, Mendel carried out a number of cross-pollination experiments. These experiments were between variants of garden pea. The Principle of Segregation describes how pairs of gene variants are separated into reproductive cells. In 1865, Gregor Mendel first observed the segregation of gene variants, called alleles, and their corresponding traits. The Principle of Independent Assortment describes how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop.
Note:
Meiosis is the mechanism of gamete formation that involves a two-stage division process. During the first meiotic division, homologous chromosomes divide, and the sister chromatids that arise separate during the second division resulting in four daughter cells at the end of meiosis. Each of these is haploid, meaning each gamete only has half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. The chromosomes in each gamete have the right sequence of genes but various gene alleles.
Complete answer:
The number of sets of chromosomes in a cell or an organism is defined as ploidy. For example, haploid means one set of chromosomes and diploid means two sets of chromosomes. Most eukaryotes (plants and animals) have two copies of each chromosome, known as homologous pairs. A homologous chromosome pair is made up of chromosomes with similar lengths, gene positions, and centromere positions. Meiosis is the mechanism of gamete formation that involves a two-stage division process. During the first meiotic division, homologous chromosomes divide, and the sister chromatids that arise separate during the second division resulting in four daughter cells at the end of meiosis. Each of these is haploid, meaning each gamete only has half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. The chromosomes in each gamete have the right sequence of genes but various gene alleles.
In the given question, the person is heterozygous (both alleles are present) for two different traits.
Types of gametes produced by an organism= \[{2^n}\]
where n= number of genes for which the organism is heterozygous.
The given genotype "AaVv" is heterozygous for $2$ genes;
Therefore total number of types of gametes formed by an organisms is ${2^2} = 4$
Total types of gamete produced by it= \[22 = {\text{ }}4\] (AV, Av, aV and av)

Hence, Option C is the correct answer.
Additional information:
The term 'genotype' was introduced by a Danish Botanist named Wilhelm Johannsen. Before Gregor Mendel who was known as the father of genetics, the theories were based on logic and speculation but not on experiments. In his monastery garden, Mendel carried out a number of cross-pollination experiments. These experiments were between variants of garden pea. The Principle of Segregation describes how pairs of gene variants are separated into reproductive cells. In 1865, Gregor Mendel first observed the segregation of gene variants, called alleles, and their corresponding traits. The Principle of Independent Assortment describes how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop.
Note:
Meiosis is the mechanism of gamete formation that involves a two-stage division process. During the first meiotic division, homologous chromosomes divide, and the sister chromatids that arise separate during the second division resulting in four daughter cells at the end of meiosis. Each of these is haploid, meaning each gamete only has half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. The chromosomes in each gamete have the right sequence of genes but various gene alleles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




