
How many different acyclic isomers of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{8}}$ on catalytic hydrogenation give the same n-pentane?
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: Acyclic isomers do not include the ring isomers. To find the isomers, always try to draw the structure of the compound. After drawing the main structure, assign different positions to the functional groups present in the compound. That makes different compounds. Also before drawing the compound, find the DBE to know the presence of multiple bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
-Isomers are the compounds that have the same molecular formula of the compound but they differ in the properties and characteristics due to the difference in the structure of the compounds so formed.
-Organic compounds show mainly 2 types of isomerism namely structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. Structural isomers have different structures of the compounds and are subdivided into chain, position, ring and functional isomers.
-Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula also and same structure also. They differ in their orientation along the three dimensions and are classified as geometrical isomers and optical isomers. All of the isomers are counted as different compounds.
-To find the isomers, we first need to find the DBE which is called the double bond equivalent of a compound. It suggests the presence of a ring, double bond or triple bond. Its formula is
DBE = C+1-$\dfrac{\left( H+X-N \right)}{2}$
Where C=no. of carbon atoms
H=no. of hydrogen atoms
X=no. of monovalent atoms
N= no. of trivalent atoms
-DBE=1 suggests the presence of a ring or a double bond. Here we have to find the acyclic isomers. So we find the DBE of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{8}}$
-According to the formula, DBE will be equal to 5+1-4=2. This suggests the presence of either 1 triple bond or 2 double bonds. We only need to find the acyclic isomers and so we do not consider the rings that can be formed in the compounds with the same molecular formula.
-Both the triple bond and the double bond can give n-pentane on hydrogenation. So we need to find different structural isomers of the compound with the molecular formula ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{8}}$. There can be 7 such isomers. They can be shown as
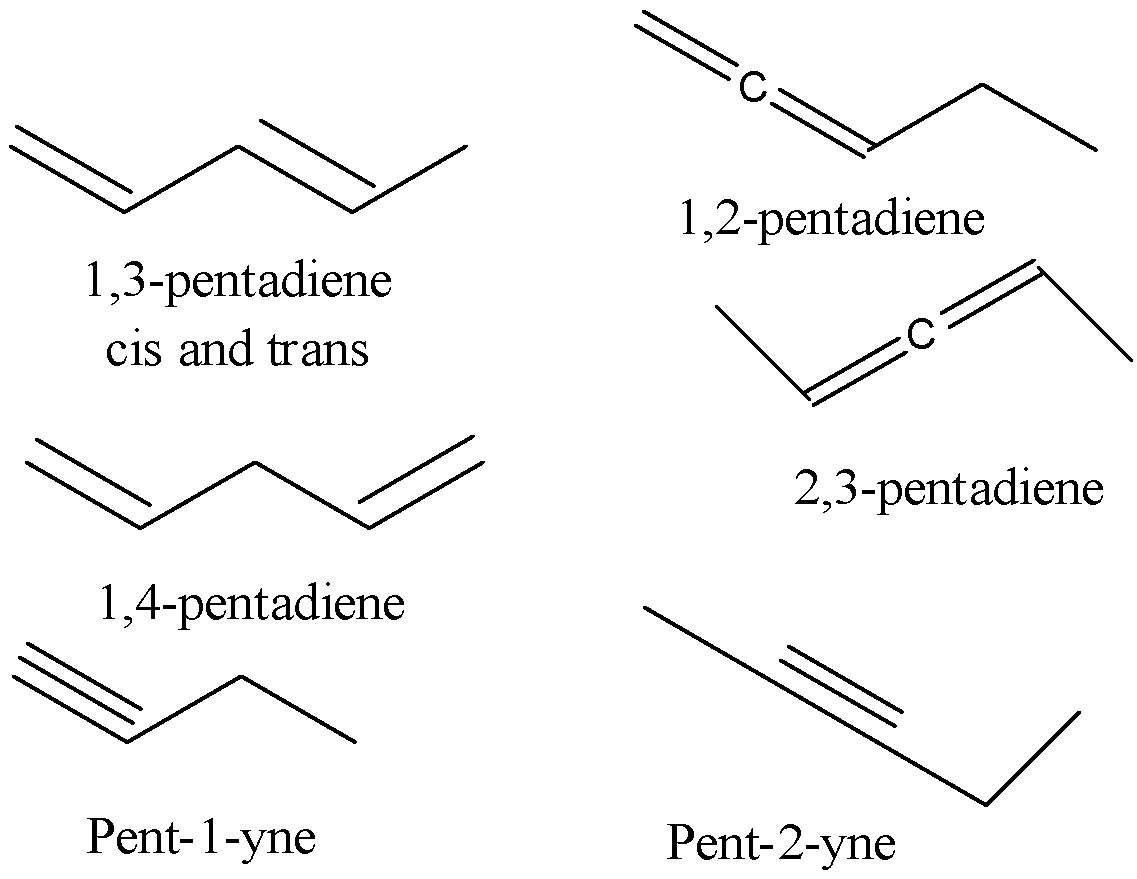
Therefore there are 7 different acyclic isomers of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{8}}$ on catalytic hydrogenation that give the same n-pentane.
Note: In finding the different structures, always ensure that both structural and stereoisomers are being counted. First, draw the structural isomers and then find the presence of stereoisomers. Also, there can be only 1 structural isomer of a compound, not more than 1. If multiple such isomers are present, then priority rule is applied. The priority order is
1. functional isomer
2. metamers
3. chain isomers
4. position isomers
Complete step by step solution:
-Isomers are the compounds that have the same molecular formula of the compound but they differ in the properties and characteristics due to the difference in the structure of the compounds so formed.
-Organic compounds show mainly 2 types of isomerism namely structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. Structural isomers have different structures of the compounds and are subdivided into chain, position, ring and functional isomers.
-Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula also and same structure also. They differ in their orientation along the three dimensions and are classified as geometrical isomers and optical isomers. All of the isomers are counted as different compounds.
-To find the isomers, we first need to find the DBE which is called the double bond equivalent of a compound. It suggests the presence of a ring, double bond or triple bond. Its formula is
DBE = C+1-$\dfrac{\left( H+X-N \right)}{2}$
Where C=no. of carbon atoms
H=no. of hydrogen atoms
X=no. of monovalent atoms
N= no. of trivalent atoms
-DBE=1 suggests the presence of a ring or a double bond. Here we have to find the acyclic isomers. So we find the DBE of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{8}}$
-According to the formula, DBE will be equal to 5+1-4=2. This suggests the presence of either 1 triple bond or 2 double bonds. We only need to find the acyclic isomers and so we do not consider the rings that can be formed in the compounds with the same molecular formula.
-Both the triple bond and the double bond can give n-pentane on hydrogenation. So we need to find different structural isomers of the compound with the molecular formula ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{8}}$. There can be 7 such isomers. They can be shown as

Therefore there are 7 different acyclic isomers of ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{8}}$ on catalytic hydrogenation that give the same n-pentane.
Note: In finding the different structures, always ensure that both structural and stereoisomers are being counted. First, draw the structural isomers and then find the presence of stereoisomers. Also, there can be only 1 structural isomer of a compound, not more than 1. If multiple such isomers are present, then priority rule is applied. The priority order is
1. functional isomer
2. metamers
3. chain isomers
4. position isomers
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




