
What is the difference in oxidation number of the two types of sulfur atoms in ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}$?
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: To find the oxidation number we draw the structure and have knowledge about the charge contained by the ligand. Whether the compound has ionic bonds, covalent bonds or both of them. Then according to their charge we will calculate the oxidation state of sulfur.
Complete step by step answer:
First we will see what type of bonds it has
${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ 2N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}^{{\text{2 - }}}$
This shows that the sodium was attached through ionic bonds and the rest of the anion has only covalent bonds.
Now we will see the structure of the anion
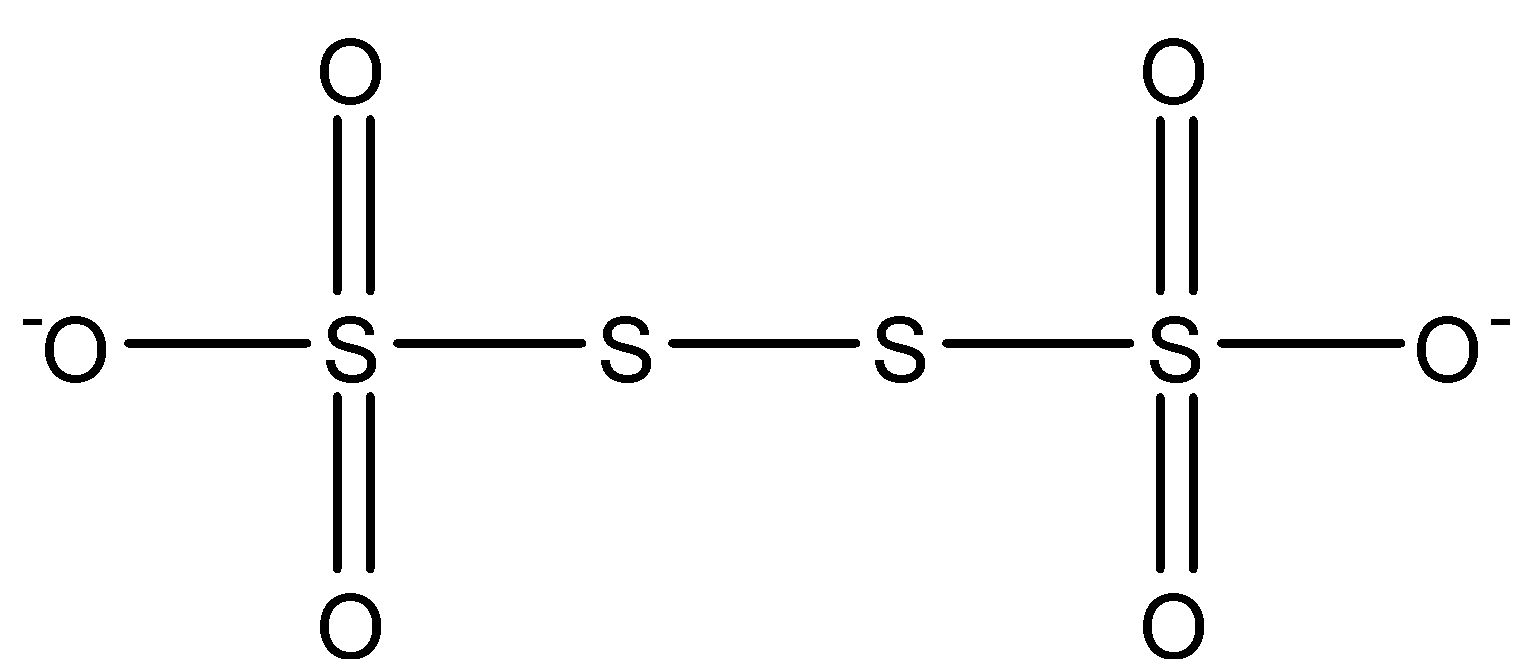
On seeing the structure above, we see four oxygen connected with a double bond and rest two oxygen with a single bond. The middle two sulfur are connected by only a single bond.
Oxidation state of double bond oxygen = ${\text{ - 2}}$
Oxidation state of single bond oxygen = ${\text{ - 1}}$
We know the minimum valency of sulfur is ${\text{0}}$ when it is connected with neutral ligands. Here the two sulfur in between connected with neutral sulfur have oxidation state ${\text{0}}$.
The Sulfur atoms connected with two double bond oxygen and single bond oxygen is having
${\text{2}}\left( {{\text{ - 2}}} \right){\text{ + 1}}\left( {{\text{ - 1}}} \right){\text{ + x = 0}}$
${\text{x = + 5}}$
Additional information:
The name of ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}$ is sodium tetrathionate. The salt contains two molecules of water of crystallization means it is a hydrate salt. It is colorless and soluble in water. It is made by oxidizing sodium thiosulfate by iodine.
Note: The difference in the same sulfur atom in a compound occurred because of the substituent groups. The substituent or attached groups decide the oxidation state of the element. So we can calculate the oxidation state of an element if we know the charge on the attached group.
Complete step by step answer:
First we will see what type of bonds it has
${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ 2N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}^{{\text{2 - }}}$
This shows that the sodium was attached through ionic bonds and the rest of the anion has only covalent bonds.
Now we will see the structure of the anion

On seeing the structure above, we see four oxygen connected with a double bond and rest two oxygen with a single bond. The middle two sulfur are connected by only a single bond.
Oxidation state of double bond oxygen = ${\text{ - 2}}$
Oxidation state of single bond oxygen = ${\text{ - 1}}$
We know the minimum valency of sulfur is ${\text{0}}$ when it is connected with neutral ligands. Here the two sulfur in between connected with neutral sulfur have oxidation state ${\text{0}}$.
The Sulfur atoms connected with two double bond oxygen and single bond oxygen is having
${\text{2}}\left( {{\text{ - 2}}} \right){\text{ + 1}}\left( {{\text{ - 1}}} \right){\text{ + x = 0}}$
${\text{x = + 5}}$
Additional information:
The name of ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}$ is sodium tetrathionate. The salt contains two molecules of water of crystallization means it is a hydrate salt. It is colorless and soluble in water. It is made by oxidizing sodium thiosulfate by iodine.
Note: The difference in the same sulfur atom in a compound occurred because of the substituent groups. The substituent or attached groups decide the oxidation state of the element. So we can calculate the oxidation state of an element if we know the charge on the attached group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




