
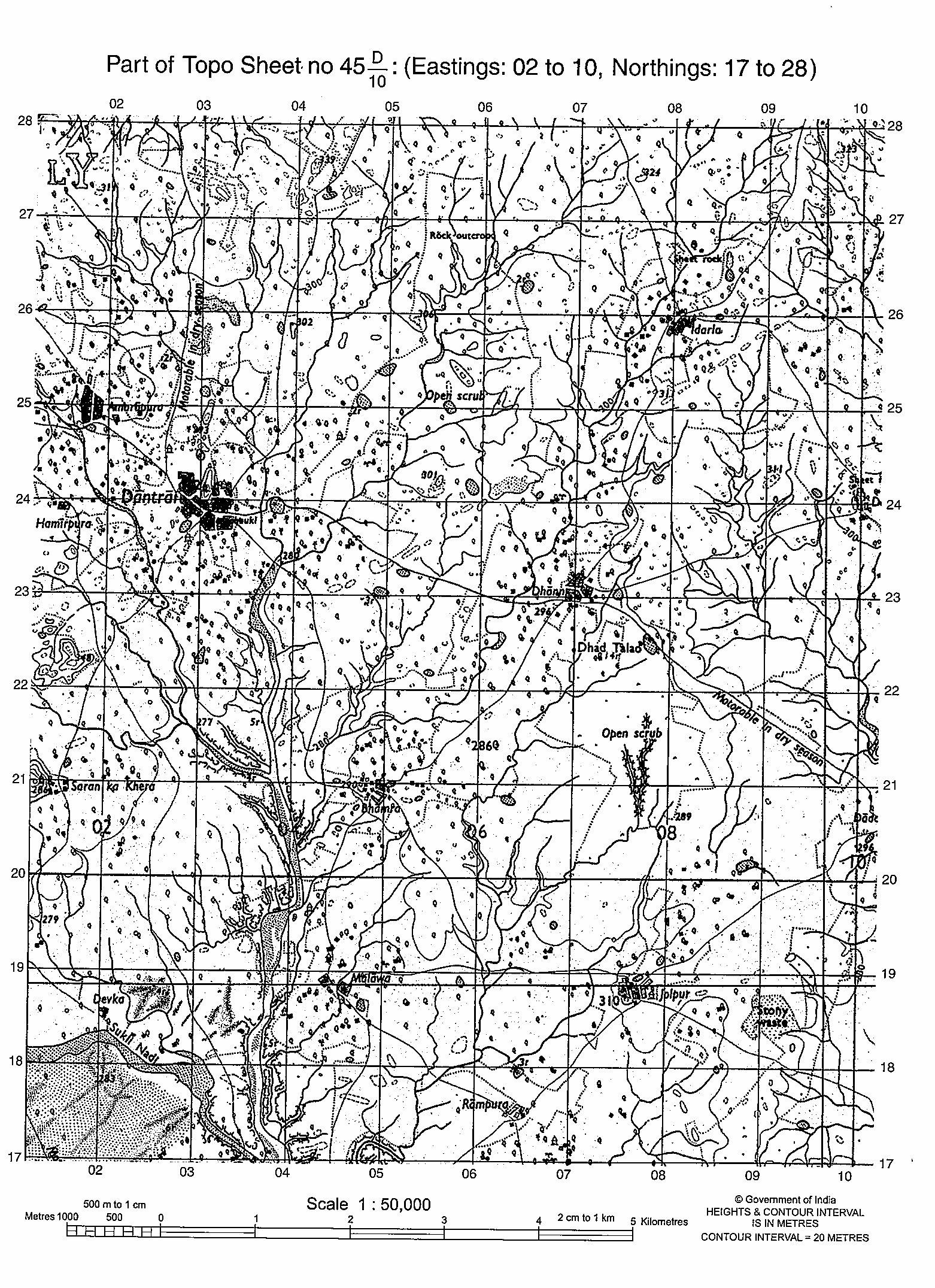
What is the difference between the drainage pattern of the streams in 0624 and those in 0824?

Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint:
In geomorphology, drainage systems otherwise called river systems, are the examples shaped by the streams, waterways, and lakes in a specific waste bowl. They are represented by the geography of the land, regardless of whether a specific area is overwhelmed by hard or delicate rocks and the slope of the land. Geomorphologists and hydrologists frequently see streams as a feature of seepage bowls (and sub-bowls).
Complete solution:
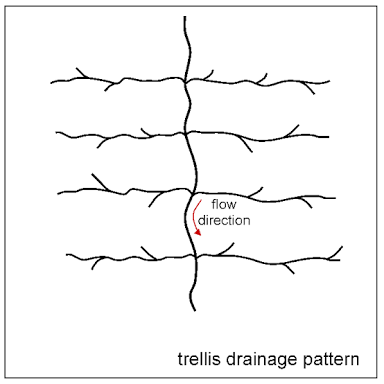
•Waste example in 0624-Trellis.
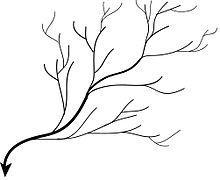
•Waste example in 0824-Dendritic.
Trellis system: The geometry of a trellis seepage framework is like that of a typical nursery lattice. Along a strike valley, more modest feeders feed into from the lofty slants of mountainsides. These feeders enter the principle waterway about the opposite, causing a lattice-like appearance of the framework. The structure where hard and delicate developments exist on the two banks of the principal waterway and are intelligent of stature, complemented by disintegration. Lattice waste is normal for collapsed mountains, for example, the Appalachian Mountains in North America and in the north piece of Trinidad.
Dendritic system: Dendritic waste frameworks (from Greek dendrites, “of or like a tree”) are not straight and are the most well-known type of seepage framework. In this, there are many sub-feeders (closely resembling the twigs of a tree), which converge into feeders of the primary waterway (the branches and the storage compartment of the tree, separately). They are believed to take care of a waterway channel that matches and is unequivocally agreeing to the abrogating inclination of the land. Genuinely dendritic frameworks structure in V-formed valleys; thus, the stone kinds must be very impenetrable and non-permeable.
Hence, the correct answer is option .
Note:
This is the geological area from which a stream gets overflow, throughflow, and its soaked same, groundwater stream. The number, size, and state of the seepage bowls differ and the bigger and more itemized the geographical guide.
In geomorphology, drainage systems otherwise called river systems, are the examples shaped by the streams, waterways, and lakes in a specific waste bowl. They are represented by the geography of the land, regardless of whether a specific area is overwhelmed by hard or delicate rocks and the slope of the land. Geomorphologists and hydrologists frequently see streams as a feature of seepage bowls (and sub-bowls).
Complete solution:
•Waste example in 0624-Trellis.
•Waste example in 0824-Dendritic.
Trellis system: The geometry of a trellis seepage framework is like that of a typical nursery lattice. Along a strike valley, more modest feeders feed into from the lofty slants of mountainsides. These feeders enter the principle waterway about the opposite, causing a lattice-like appearance of the framework. The structure where hard and delicate developments exist on the two banks of the principal waterway and are intelligent of stature, complemented by disintegration. Lattice waste is normal for collapsed mountains, for example, the Appalachian Mountains in North America and in the north piece of Trinidad.

Dendritic system: Dendritic waste frameworks (from Greek dendrites, “of or like a tree”) are not straight and are the most well-known type of seepage framework. In this, there are many sub-feeders (closely resembling the twigs of a tree), which converge into feeders of the primary waterway (the branches and the storage compartment of the tree, separately). They are believed to take care of a waterway channel that matches and is unequivocally agreeing to the abrogating inclination of the land. Genuinely dendritic frameworks structure in V-formed valleys; thus, the stone kinds must be very impenetrable and non-permeable.

Hence, the correct answer is option .
Note:
This is the geological area from which a stream gets overflow, throughflow, and its soaked same, groundwater stream. The number, size, and state of the seepage bowls differ and the bigger and more itemized the geographical guide.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




