
What is the difference between oxidation and reduction?
A. Oxidation is a reaction that removes an electron from a substance, reduction is a reaction that adds electrons to a substance.
B. Reduction is when the total number of electrons increases in a reaction, oxidation is when the total number of electrons decreases in a reaction.
C. Reduction is a reaction that removes an electron from a substance, oxidation is a reaction that adds electrons to a substance.
D. They are both halves of the same reaction.
E. Oxidation is when the total number of electrons increases in a reaction, reduction is when the total number of electrons decreases in a reaction.
Answer
534.4k+ views
Hint: We should have an idea about the occurrence of oxidation and reduction reactions. It is never possible for oxidation and reduction to occur separately. In any reaction, oxidation and reduction always work simultaneously.
Complete answer:
Oxidation is defined as the process when an atom, molecule, or an ion loses one or more number of electrons in a chemical reaction. When oxidation occurs, the state of the chemical species increases. Oxidation does not necessarily have to involve oxygen.
Reduction is defined as the process when an atom, molecule, or an ion gains one or more electrons in a chemical reaction. When reduction occurs, the state of the chemical species decreases. Reduction does not necessarily have to involve hydrogen.
Let us examine the process of Oxidation and Reduction with an example:
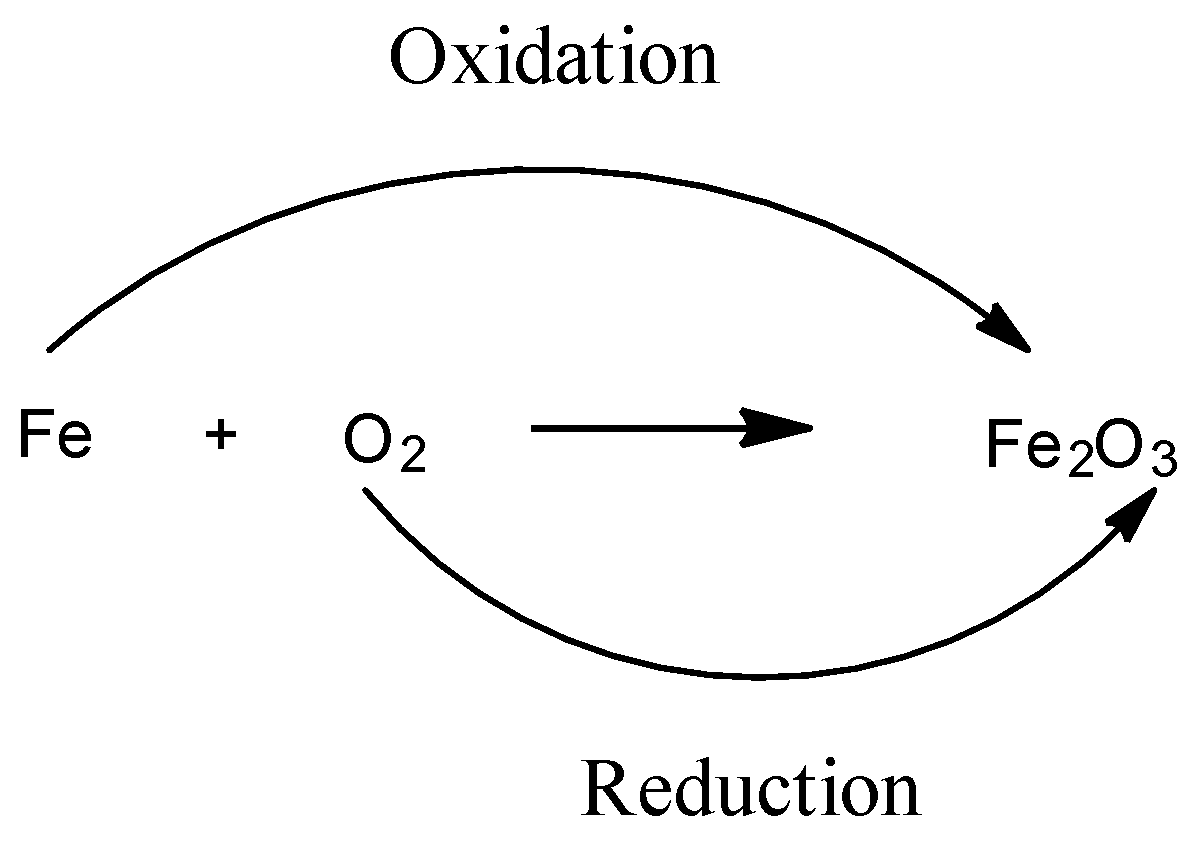
This reaction occurs in the presence of ${{H}_{2}}O$. Here we can see that originally, the oxidation numbers of both $Fe$ and $O$ atoms are 0. After the reaction the oxidation state of $Fe$ goes from 0 to +3 and the oxidation state of $O$ goes from 0 to -2. Thus, iron is losing electrons and oxygen is gaining electrons. Hence, iron is undergoing oxidation and oxygen is undergoing reduction.
So, among the above options, we can see that the option A satisfies the criteria of the oxidation and reduction.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: An oxidizing agent or oxidant causes the other agent to be oxidized or lose electrons. It makes the other agent lose electrons by gaining electrons itself. Thus, an oxidizing agent is itself reduced while oxidizing the other substance. In the example given above iron is the reducing agent and oxygen is the oxidizing agent.
Remember the acronym ‘OIL RIG’ to memorize what happens during a redox reaction. It denotes ‘Oxygen Is Losing (electrons), Reduction Is Gaining (electrons)’
Complete answer:
Oxidation is defined as the process when an atom, molecule, or an ion loses one or more number of electrons in a chemical reaction. When oxidation occurs, the state of the chemical species increases. Oxidation does not necessarily have to involve oxygen.
Reduction is defined as the process when an atom, molecule, or an ion gains one or more electrons in a chemical reaction. When reduction occurs, the state of the chemical species decreases. Reduction does not necessarily have to involve hydrogen.
Let us examine the process of Oxidation and Reduction with an example:

This reaction occurs in the presence of ${{H}_{2}}O$. Here we can see that originally, the oxidation numbers of both $Fe$ and $O$ atoms are 0. After the reaction the oxidation state of $Fe$ goes from 0 to +3 and the oxidation state of $O$ goes from 0 to -2. Thus, iron is losing electrons and oxygen is gaining electrons. Hence, iron is undergoing oxidation and oxygen is undergoing reduction.
So, among the above options, we can see that the option A satisfies the criteria of the oxidation and reduction.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: An oxidizing agent or oxidant causes the other agent to be oxidized or lose electrons. It makes the other agent lose electrons by gaining electrons itself. Thus, an oxidizing agent is itself reduced while oxidizing the other substance. In the example given above iron is the reducing agent and oxygen is the oxidizing agent.
Remember the acronym ‘OIL RIG’ to memorize what happens during a redox reaction. It denotes ‘Oxygen Is Losing (electrons), Reduction Is Gaining (electrons)’
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




