
What is the difference between E $ \& $ Z isomerism and cis – trans isomerism $ ? $
Answer
529.2k+ views
Hint :Molecules that have the same molecular formula i.e., have the same number of atoms but differ in structural formula are called isomers and this phenomenon is known as isomerism. E $ \& $ Z isomers and cis- trans isomers are stereoisomers where the molecules have the same connectivity. They differ in the spatial arrangement of the bonds in $ 2D $ or $ 3D $ space.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
From the hint given, we understood what an isomer is. Isomers differ in physical and chemical properties. It can be broadly divided into constitutional (structural) and stereoisomers (spatial) which can later be divided into different isomers. Here, we discuss two major classes of stereoisomers. Stereoisomers have the same kind of bond but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms.
Cis- trans isomerism: It is also known as geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism. When a pair of molecules have the same molecular formula, but the functional groups present in them differ inside due to restricted rotation around a double bond and have a different orientation in space. Cis indicates similar groups present on the same side and trans indicates the presence of similar groups on opposite sides of a double bond.
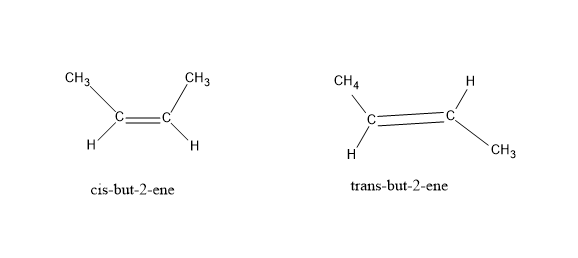
E $ \& $ Z isomerism : Like the cis – trans isomerism these are also stereoisomers but a special case of cis-trans isomerism. Here, E stands for opposite side (trans) and Z stands for same side (cis). It can be and when cis- trans isomerism fails. When there are no similar functional groups and double bond has two or more substituents. A priority is set among the substituents of the same carbon atom based on atomic number. If the two substituents with highest priority come on the same side of the double bond , it is Z isomer and if they are on opposite sides, then E.
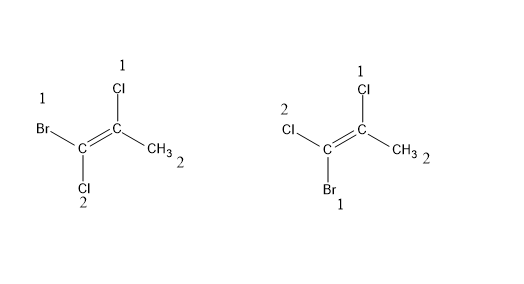
(Z)-1-Bromo-1,2-dichloropropane (E)-1-Bromo-1,2-dichloropropane
Note :
Cis-trans isomerism is based on relative stereochemistry whereas E-Z isomerism is based on absolute stereochemistry of the double bond. These can be applied in the nomenclature of cycloalkanes also. The former has applications in inorganic chemistry as well as in coordination complexes.
Stereoisomers are again divided into geometrical and optical isomers.
Conformational isomerism is molecules having the same structural formula but different shape or orientation due to rotation around bonds. In stereoisomers there is restricted rotation around bonds.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
From the hint given, we understood what an isomer is. Isomers differ in physical and chemical properties. It can be broadly divided into constitutional (structural) and stereoisomers (spatial) which can later be divided into different isomers. Here, we discuss two major classes of stereoisomers. Stereoisomers have the same kind of bond but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms.
Cis- trans isomerism: It is also known as geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism. When a pair of molecules have the same molecular formula, but the functional groups present in them differ inside due to restricted rotation around a double bond and have a different orientation in space. Cis indicates similar groups present on the same side and trans indicates the presence of similar groups on opposite sides of a double bond.

E $ \& $ Z isomerism : Like the cis – trans isomerism these are also stereoisomers but a special case of cis-trans isomerism. Here, E stands for opposite side (trans) and Z stands for same side (cis). It can be and when cis- trans isomerism fails. When there are no similar functional groups and double bond has two or more substituents. A priority is set among the substituents of the same carbon atom based on atomic number. If the two substituents with highest priority come on the same side of the double bond , it is Z isomer and if they are on opposite sides, then E.

(Z)-1-Bromo-1,2-dichloropropane (E)-1-Bromo-1,2-dichloropropane
Note :
Cis-trans isomerism is based on relative stereochemistry whereas E-Z isomerism is based on absolute stereochemistry of the double bond. These can be applied in the nomenclature of cycloalkanes also. The former has applications in inorganic chemistry as well as in coordination complexes.
Stereoisomers are again divided into geometrical and optical isomers.
Conformational isomerism is molecules having the same structural formula but different shape or orientation due to rotation around bonds. In stereoisomers there is restricted rotation around bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




