
What is the difference between cell membrane and cytoplasm in an animal cell?
Answer
528.3k+ views
Hint: The cell membrane is a biological membrane which separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. It is composed of bilayer of phospholipids with their hydrophobic, fatty acid tails in contact with each other. Cytoplasm, on the other hand, is the gelatinous liquid inside a cell. It is composed of water, salts, and various organic molecules. Organelles like mitochondria and nucleus are separated from the cytoplasm by their own membrane.
Complete step by step answer:
The cell membrane surrounds the cytoplasm. The cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer that is only 7 nm thick. It is responsible for controlling what can enter and exit the cell. The cytoplasm, however, is a jelly-like material. Cytoplasm is where all the metabolic reactions of the cell take place in organelles, e.g. respiration takes place in the mitochondria (an organelle in the cytoplasm). Basically, the cell membrane protects the cell's contents, which is basically the cytoplasm.
Note:
The cytoplasm is divided into two primary parts: the endoplasm (endo-,-plasm) and ectoplasm (ecto-,-plasm). The endoplasm is the central area of the cytoplasm that contains the organelles. The ectoplasm is the gel-like peripheral portion of the cytoplasm of a cell. The major components of a cell membrane are phospholipids, glycolipids, proteins and cholesterol. Both the cell membrane and cytoplasm function as the protective shields of a cell.
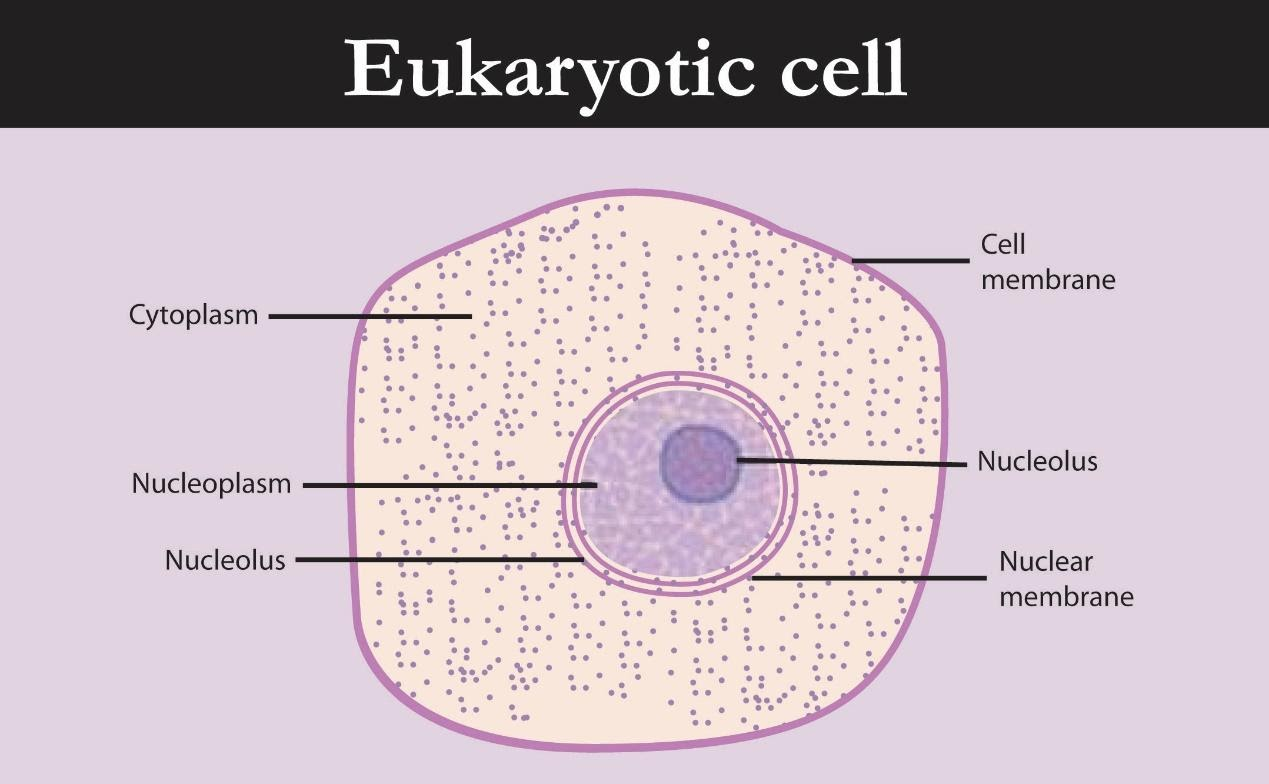
Figure 1: Typical Cytoplasm
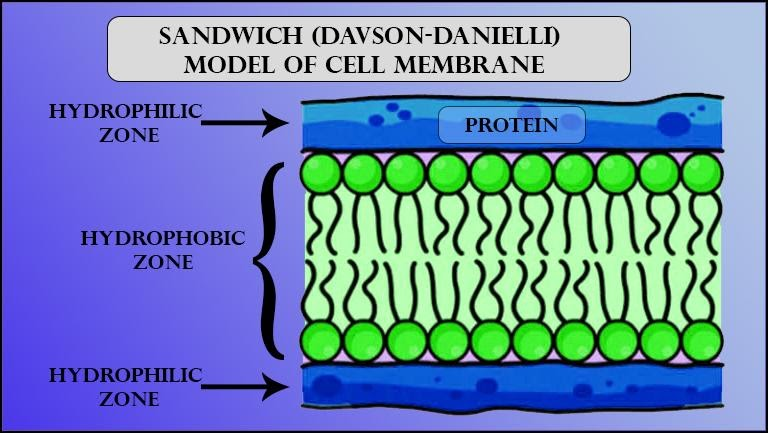
Figure 2: Cell membrane
Complete step by step answer:
The cell membrane surrounds the cytoplasm. The cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer that is only 7 nm thick. It is responsible for controlling what can enter and exit the cell. The cytoplasm, however, is a jelly-like material. Cytoplasm is where all the metabolic reactions of the cell take place in organelles, e.g. respiration takes place in the mitochondria (an organelle in the cytoplasm). Basically, the cell membrane protects the cell's contents, which is basically the cytoplasm.
| Sl. No. | Cell membrane | Cytoplasm |
| 1. | It is the membrane that is the boundary of a cell. | Cytoplasm is the gelatinous liquid inside the cell. |
| 2. | The cell membrane determines what enters and exits the cell, basically acting as a gate. | The main function of cytoplasm is to protect the organelles inside the cell. |
| 3. | The cell membrane is made of phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins which are 7nm thick. | Cytoplasm is composed of water, salts and various organelles. |
| 4. | Cell membrane is also called plasma membrane. | Cytoplasm is vaguely referred to as cytosol. |
| 5. | Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling. They also serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, the carbohydrate layer called the glycocalyx and the intracellular network of protein fibers called the cytoskeleton. | The cytoplasm supports and suspends organelles and cellular molecules. Many cellular processes occur in the cytoplasm, such as protein synthesis, the first stage of cellular respiration (known as glycolysis), mitosis, and meiosis.The cytoplasm helps to move materials, such as hormones, around the cell and also dissolves cellular waste. |
Note:
The cytoplasm is divided into two primary parts: the endoplasm (endo-,-plasm) and ectoplasm (ecto-,-plasm). The endoplasm is the central area of the cytoplasm that contains the organelles. The ectoplasm is the gel-like peripheral portion of the cytoplasm of a cell. The major components of a cell membrane are phospholipids, glycolipids, proteins and cholesterol. Both the cell membrane and cytoplasm function as the protective shields of a cell.

Figure 1: Typical Cytoplasm

Figure 2: Cell membrane
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




