
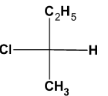
How many dichlorinated products, including stereoisomers, can be isolated when (S)-2- chlorobutane reacts with ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}/{\text{h}}\nu $?
A.1
B.2
C.3
D.5

Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must be familiar with the types of isomerism shown by organic compounds. Organic compounds show broadly two types of isomerism, namely structural or constitutional isomerism or stereoisomerism.
Complete step-by-step answer:Structural isomers are those isomers which have the same molecular formula but different linkage of atoms inside the molecule, i.e., they differ in their structures. Stereoisomers are those isomers which possess the same molecular and structural formula but differ due to the variation in arrangement in space of their atoms in a molecule.
The given compound (S)-2- chlorobutane has four carbon atoms with a replaceable hydrogen atom. So on chlorination, the chlorine atom can replace hydrogen atom from any of the four carbon atoms and thus four structural isomers of the dichlorinated product will be formed. They can be drawn as:
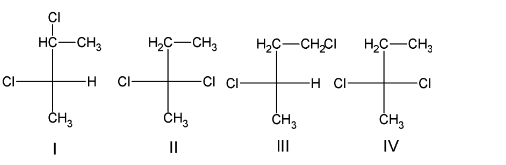
Of the given structural isomers, the structure I additionally shows stereoisomerism. It can exist in two configuration, either as the R- configuration or as the S- configuration. The stereoisomers formed can be drawn as
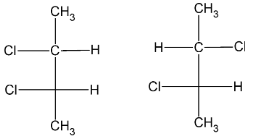
Thus, the total number of isomers of the dichloro- substituted product formed including stereoisomers are 5.
The correct answer is D.
Note: Stereoisomerism can be further divided into configurational isomerism, conformational isomerism and geometrical isomerism. Conformational isomers are interconvertible forms of the same molecule derived from the rotation about the carbon- carbon $\sigma $ bond. Configurational isomers are those stereoisomers which cannot be converted to each other by rotation about carbon- carbon $\sigma $ bond. Geometrical isomers are non- interconvertible stereoisomers due to the restricted rotation about carbon- carbon $\pi $ bond.
Complete step-by-step answer:Structural isomers are those isomers which have the same molecular formula but different linkage of atoms inside the molecule, i.e., they differ in their structures. Stereoisomers are those isomers which possess the same molecular and structural formula but differ due to the variation in arrangement in space of their atoms in a molecule.
The given compound (S)-2- chlorobutane has four carbon atoms with a replaceable hydrogen atom. So on chlorination, the chlorine atom can replace hydrogen atom from any of the four carbon atoms and thus four structural isomers of the dichlorinated product will be formed. They can be drawn as:

Of the given structural isomers, the structure I additionally shows stereoisomerism. It can exist in two configuration, either as the R- configuration or as the S- configuration. The stereoisomers formed can be drawn as

Thus, the total number of isomers of the dichloro- substituted product formed including stereoisomers are 5.
The correct answer is D.
Note: Stereoisomerism can be further divided into configurational isomerism, conformational isomerism and geometrical isomerism. Conformational isomers are interconvertible forms of the same molecule derived from the rotation about the carbon- carbon $\sigma $ bond. Configurational isomers are those stereoisomers which cannot be converted to each other by rotation about carbon- carbon $\sigma $ bond. Geometrical isomers are non- interconvertible stereoisomers due to the restricted rotation about carbon- carbon $\pi $ bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




