
What is diamond? Of what substance is diamond made?
Describe the structure of diamond. Draw a simple diagram to show the arrangement of carbon atoms in it.
Explain why diamonds have a high melting point.
State any two uses of diamond.
Answer
476.1k+ views
Hint: Diamond gets its name from the German word “Adamas”, which means "unconquerable." It is the hardest of all known minerals and is a form of pure carbon that occurs naturally as a transparent crystal. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at ambient temperature and pressure, but diamond almost never transforms to it. A natural material with the maximum hardness and thermal conductivity is diamond.
Complete answer:
In chemistry, a diamond is an allotrope of the element carbon, solid in nature, in which the carbon atoms are arranged in a cubic crystal lattice.
An allotrope means it's only one of several distinct forms of an element, which simply means a diamond is made completely of one element and that element can take on several different forms. Diamond is made up of repeated units of carbon atoms connected by the strongest chemical linkage, covalent bonds, to four other carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is surrounded by a stiff tetrahedral network in which it is equidistant from its neighbours. Diamond is made up of eight atoms that are basically arranged in a square.
Each of the carbon atoms in the diamond's structure is connected to the other four carbon atoms in a regular tetrahedral manner.
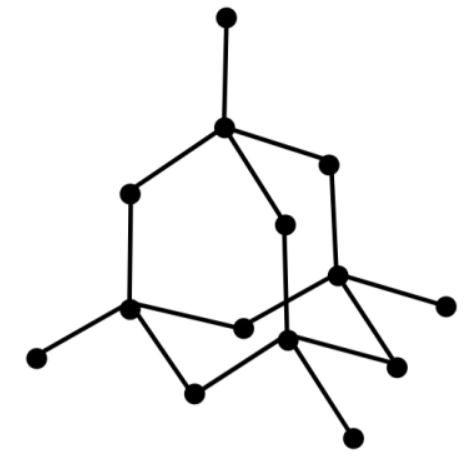
These carbon atoms form a solid three-dimensional structure when they are joined with the other four carbon atoms in a regular tetrahedral structure. As a result, diamond has a three-dimensional structure. Each carbon atom in a diamond is a covalent bond to the four surrounding carbon atoms (2) & (4).
Because a considerable amount of energy is required to overcome the many strong covalent bonds, diamond has a very high melting point. Diamond does not conduct electricity because it contains no free-moving electrons or other charged particles.
Two uses of diamond can be stated as follows:
Diamonds are used in jewellery in a variety of ways. Because of their lustrous lustre and durability, they are utilised in jewellery (e.g., earrings, nose rings, engagement rings, pendants, etc.). Because of their durability and shine, they are used to make jewellery.
Diamonds are utilised in the manufacturing industry. Its hardness makes it helpful for drilling, grinding, and cutting materials. As a result, diamonds were employed in several cutting blades and drills in the industry. They are tiny and can be found on the margins and tips.
Note:
We must note that a diamond's crystal structure is a face-centered cubic (FCC) lattice. Diamond crystals can take on a variety of shapes, known as 'crystal habits,' because of their cubic geometry and highly symmetrical atom arrangement. The eight-sided octahedron or diamond form is the most frequent crystal habit. Cubes, dodecahedra, and combinations of these shapes can be formed using diamond crystals.
Complete answer:
In chemistry, a diamond is an allotrope of the element carbon, solid in nature, in which the carbon atoms are arranged in a cubic crystal lattice.
An allotrope means it's only one of several distinct forms of an element, which simply means a diamond is made completely of one element and that element can take on several different forms. Diamond is made up of repeated units of carbon atoms connected by the strongest chemical linkage, covalent bonds, to four other carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is surrounded by a stiff tetrahedral network in which it is equidistant from its neighbours. Diamond is made up of eight atoms that are basically arranged in a square.
Each of the carbon atoms in the diamond's structure is connected to the other four carbon atoms in a regular tetrahedral manner.

These carbon atoms form a solid three-dimensional structure when they are joined with the other four carbon atoms in a regular tetrahedral structure. As a result, diamond has a three-dimensional structure. Each carbon atom in a diamond is a covalent bond to the four surrounding carbon atoms (2) & (4).
Because a considerable amount of energy is required to overcome the many strong covalent bonds, diamond has a very high melting point. Diamond does not conduct electricity because it contains no free-moving electrons or other charged particles.
Two uses of diamond can be stated as follows:
Diamonds are used in jewellery in a variety of ways. Because of their lustrous lustre and durability, they are utilised in jewellery (e.g., earrings, nose rings, engagement rings, pendants, etc.). Because of their durability and shine, they are used to make jewellery.
Diamonds are utilised in the manufacturing industry. Its hardness makes it helpful for drilling, grinding, and cutting materials. As a result, diamonds were employed in several cutting blades and drills in the industry. They are tiny and can be found on the margins and tips.
Note:
We must note that a diamond's crystal structure is a face-centered cubic (FCC) lattice. Diamond crystals can take on a variety of shapes, known as 'crystal habits,' because of their cubic geometry and highly symmetrical atom arrangement. The eight-sided octahedron or diamond form is the most frequent crystal habit. Cubes, dodecahedra, and combinations of these shapes can be formed using diamond crystals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




