
Why is D-glucose the most common aldohexose in nature?
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: The monosaccharides which contain the aldehyde group in their structure as a main functional moiety are known as aldose. Glucose is considered an aldohexose sugar because it contains an aldehyde group and has a total six carbon in structure.
Complete answer:
Depending upon the type of configuration of sugar they are categorized as $ D - $ family and $ L - $ family. The glucose in which the hydroxyl group next to the aldehyde group is towards the right side is known as $ D - $ glucose while if the hydroxyl group next to the aldehyde group is towards the left side is known as $ L - $ glucose.
Glucose molecule has more than one hydroxyl group which undergoes the intermolecular reaction with the aldehyde group to form a cyclic structure. Hydroxyl groups of glucose generally combine with $ {C_5} $ or $ {C_4} $ carbon.

When the aldehyde group of glucose molecules react with the hydroxyl group at $ {C_5} $ position, cyclization of the molecule takes place which further results in formation of an asymmetric center at $ {C_1} $ .
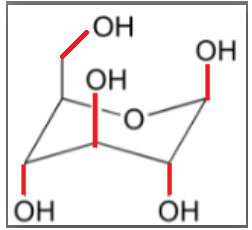
In the above structure of glucose all the bonds shown by red colour show the bonds which are out of the plane.
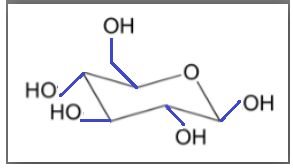
But when a glucose molecule acquires chair conformation during cyclization all the bonds are arranged in the equatorial plane as shown by the blue bond in the diagram.
Cyclization of glucose molecules provides extra stability to the glucose molecule towards chemical reaction because all the substituents attached to the main glucose structure lie in the same equatorial plane.
As we know, the form of any particular compound which is stable in nature is found in maximum amounts and becomes its common form of existence.
Cyclic structure of $ D - $ glucose has higher stability than other monosaccharides therefore $ D -$ glucose is the commonest aldohexose glucose in nature.
D-glucose has the tendency to exist as $ \alpha - $ $ D $ glucose and $ \beta - $ $ D $ glucose.
Note:
Glucose has the capability to crystallize in absolute alcohol in its anhydrous form. Glucose is the main source of energy and is the simplest carbohydrate which is highly soluble in water as well as in alcohol. Glucose forms an optical anomer by having variation only at its one carbon atom.
Complete answer:
Depending upon the type of configuration of sugar they are categorized as $ D - $ family and $ L - $ family. The glucose in which the hydroxyl group next to the aldehyde group is towards the right side is known as $ D - $ glucose while if the hydroxyl group next to the aldehyde group is towards the left side is known as $ L - $ glucose.
Glucose molecule has more than one hydroxyl group which undergoes the intermolecular reaction with the aldehyde group to form a cyclic structure. Hydroxyl groups of glucose generally combine with $ {C_5} $ or $ {C_4} $ carbon.

When the aldehyde group of glucose molecules react with the hydroxyl group at $ {C_5} $ position, cyclization of the molecule takes place which further results in formation of an asymmetric center at $ {C_1} $ .

In the above structure of glucose all the bonds shown by red colour show the bonds which are out of the plane.

But when a glucose molecule acquires chair conformation during cyclization all the bonds are arranged in the equatorial plane as shown by the blue bond in the diagram.
Cyclization of glucose molecules provides extra stability to the glucose molecule towards chemical reaction because all the substituents attached to the main glucose structure lie in the same equatorial plane.
As we know, the form of any particular compound which is stable in nature is found in maximum amounts and becomes its common form of existence.
Cyclic structure of $ D - $ glucose has higher stability than other monosaccharides therefore $ D -$ glucose is the commonest aldohexose glucose in nature.
D-glucose has the tendency to exist as $ \alpha - $ $ D $ glucose and $ \beta - $ $ D $ glucose.
Note:
Glucose has the capability to crystallize in absolute alcohol in its anhydrous form. Glucose is the main source of energy and is the simplest carbohydrate which is highly soluble in water as well as in alcohol. Glucose forms an optical anomer by having variation only at its one carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




