
How do you determine the linear function whose graph is a line that contains the points $\left( { - 1, - 8} \right)$ and $\left( {2,10} \right)$ ?
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: The equation of a line that passes through two points can be calculated by using the two-point form of the equation of a line. We will substitute the given two points into the two-point form of a line. Then after simplifying we can determine the required linear function.
Formula used:
The two-point form of a line passing through the points $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ is given by $\dfrac{{y - {y_1}}}{{x - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know we can determine the equation of a line that passes through two points by using the two-point form of a line.
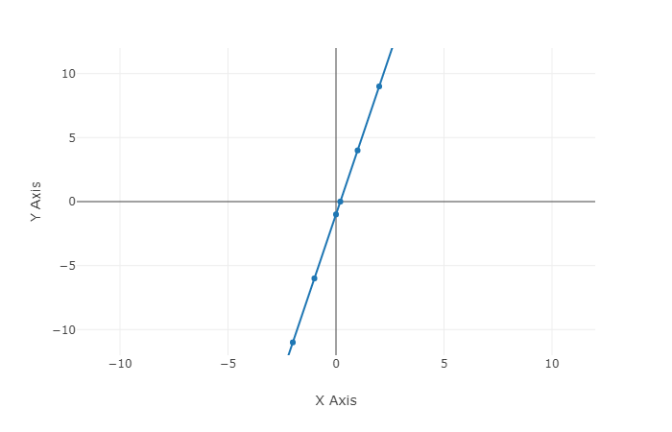
Now, the two given points are
$A = \left( { - 1, - 8} \right)$ and $B = \left( {2,10} \right)$ .
Now, we know that the first coordinate is the x-coordinate and the second coordinate is the y-coordinate.
Here,
For point $A$, ${x_1} = - 1$ and ${y_1} = - 8$
For point $B$, ${x_2} = 2$ and ${y_2} = 10$
Now, as we know that, the two-point form of a line is
$\dfrac{{y - {y_1}}}{{x - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ .
Now, we can determine the linear function by substituting the ${x_1} = - 1$ , ${x_2} = 2$ , ${y_1} = - 8$ and ${y_2} = 10$ in the two-point form of the equation of a line.
After substituting the values, we get
$\dfrac{{y - ( - 8)}}{{x - ( - 1)}} = \dfrac{{10 - ( - 8)}}{{2 - ( - 1)}}$
Now, after opening the brackets of numerators as well as denominators on both sides, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{{10 + 8}}{{2 + 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{{18}}{3}$
On Right-hand side, simplifying by dividing $18\;$ by $3$ , we have
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{6}{1}$
Now, by cross multiplying, we get
$1(y + 8) = 6(x + 1)$
$ \Rightarrow y + 8 = 6x + 6$
Now, by subtracting $8$ on both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$$y + 8 - 8 = 6x + 6 - 8$
$ \Rightarrow y = 6x - 2$
∴ $y = 6x - 2$ is the required linear function whose graph is a line that passes through the points $( - 1, - 8)$ and $(2,10)$.
Note:
There is an alternate way to prove the two points form of the equation of a straight line. Consider the point-slope form of the equation of a line,
we have, $y - {y_1} = m(x - {x_1})$ - - - - - - $(1.)$
Since the line is passing through the point $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ in $\left( {1.} \right)$ and the slope of the line is $m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ . So, $(1.)$ becomes $y - {y_1} = \left( {\dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}} \right)\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)$.
Formula used:
The two-point form of a line passing through the points $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ is given by $\dfrac{{y - {y_1}}}{{x - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know we can determine the equation of a line that passes through two points by using the two-point form of a line.

Now, the two given points are
$A = \left( { - 1, - 8} \right)$ and $B = \left( {2,10} \right)$ .
Now, we know that the first coordinate is the x-coordinate and the second coordinate is the y-coordinate.
Here,
For point $A$, ${x_1} = - 1$ and ${y_1} = - 8$
For point $B$, ${x_2} = 2$ and ${y_2} = 10$
Now, as we know that, the two-point form of a line is
$\dfrac{{y - {y_1}}}{{x - {x_1}}} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ .
Now, we can determine the linear function by substituting the ${x_1} = - 1$ , ${x_2} = 2$ , ${y_1} = - 8$ and ${y_2} = 10$ in the two-point form of the equation of a line.
After substituting the values, we get
$\dfrac{{y - ( - 8)}}{{x - ( - 1)}} = \dfrac{{10 - ( - 8)}}{{2 - ( - 1)}}$
Now, after opening the brackets of numerators as well as denominators on both sides, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{{10 + 8}}{{2 + 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{{18}}{3}$
On Right-hand side, simplifying by dividing $18\;$ by $3$ , we have
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{y + 8}}{{x + 1}} = \dfrac{6}{1}$
Now, by cross multiplying, we get
$1(y + 8) = 6(x + 1)$
$ \Rightarrow y + 8 = 6x + 6$
Now, by subtracting $8$ on both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow$$y + 8 - 8 = 6x + 6 - 8$
$ \Rightarrow y = 6x - 2$
∴ $y = 6x - 2$ is the required linear function whose graph is a line that passes through the points $( - 1, - 8)$ and $(2,10)$.
Note:
There is an alternate way to prove the two points form of the equation of a straight line. Consider the point-slope form of the equation of a line,
we have, $y - {y_1} = m(x - {x_1})$ - - - - - - $(1.)$
Since the line is passing through the point $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ in $\left( {1.} \right)$ and the slope of the line is $m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ . So, $(1.)$ becomes $y - {y_1} = \left( {\dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}} \right)\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




