
Describe with the help of a diagram, the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint:Draw the ray diagram of the object placed beyond the centre of curvature of the mirror. To draw the ray diagram take two rays from the top of the object placed at the principal axis beyond the radius of curvature, and pass it through the centre of curvature and pass another ray through the focus of the concave mirror for parallel incidence.
Complete answer:
We have been given here to find the properties of the image when the object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. Now, to know the properties of the image, let’s draw the ray diagram of the object when it is placed in front of the mirror on the principal axis, beyond the radius of the curvature.
To draw the diagram we have to take two rays emitting from the head of the object and take the first ray and pass it directly through the centre of the curvature, it will reflect along the same line since, angle of incidence is zero. Take another ray parallel to the principal axis upon reflection; it will pass through the focus of the mirror since the normal is along the centre of curvature at that point so angle of reflection will always pass through the focus of the mirror.
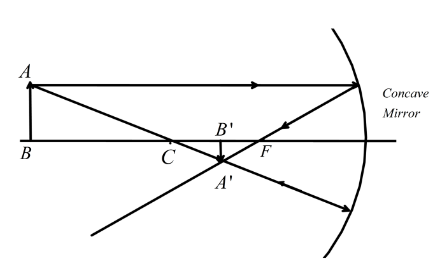
In the diagram we have\[AB\] is the object and \[A'B'\] is the image of the object when it is placed beyond radius of curvature \[C\] and \[F\ is the focus of the mirror. So, from the ray diagram of the object, we can see that the image will be, (i) inverted, (ii) diminished and (iii) real, since it is on the same side as the object in front of the mirror and the object here is real.
Note: The magnification of the object is less than one when it is placed beyond the radius of the curvature.When a ray comes parallel to the principal axis, whether incident on a mirror or a lens the refracted or reflected ray always passes through the focus of the lens or the mirror.
Complete answer:
We have been given here to find the properties of the image when the object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. Now, to know the properties of the image, let’s draw the ray diagram of the object when it is placed in front of the mirror on the principal axis, beyond the radius of the curvature.
To draw the diagram we have to take two rays emitting from the head of the object and take the first ray and pass it directly through the centre of the curvature, it will reflect along the same line since, angle of incidence is zero. Take another ray parallel to the principal axis upon reflection; it will pass through the focus of the mirror since the normal is along the centre of curvature at that point so angle of reflection will always pass through the focus of the mirror.

In the diagram we have\[AB\] is the object and \[A'B'\] is the image of the object when it is placed beyond radius of curvature \[C\] and \[F\ is the focus of the mirror. So, from the ray diagram of the object, we can see that the image will be, (i) inverted, (ii) diminished and (iii) real, since it is on the same side as the object in front of the mirror and the object here is real.
Note: The magnification of the object is less than one when it is placed beyond the radius of the curvature.When a ray comes parallel to the principal axis, whether incident on a mirror or a lens the refracted or reflected ray always passes through the focus of the lens or the mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




