
Describe three kinds of Nerves, giving examples of each.
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: Nerves are a region of the nervous system. they're primarily involved in control and therefore the coordination of all the parts of the body. The nervous system not only sends and receives messages but also processes them into chemical signals called impulses within our body.
Complete answer:
Nerves are a set of neurons, which are the individual nerve cells. Our nerves are located throughout our bodies, that is from our skin, through and around our organs and towards their centre, the brain. There are three types of nerves: motor, sensory and mixed.
Sensory nerves also referred to as afferent nerves, carry impulses from sensory receptors towards the brain. Example: These nerves carry the impulses from the sense organs to the brain or to the spinal cord as the optic nerve of the eye.
Motor nerves also referred to as efferent nerves, carry impulses far from the brain to muscles and glands. Example: These nerves have only motor fibres as nerves to the muscles of the eyeball.
Mixed nerves are composed of motor and sensory fibres, and transmit messages in both directions at once. Example: The nerve going to the tongue.
Additional Information: In biology, the nervous system is split into the central nervous system, which incorporates the nerves of the brain and therefore the spine, and therefore the peripheral nervous system which incorporates the remainder of the nerves. The peripheral nervous system encompasses, as a subcategory, the autonomic nervous system which helps the body to regulate involuntary functions including the movements of our heart, stomach, intestines, bladder and sweating.
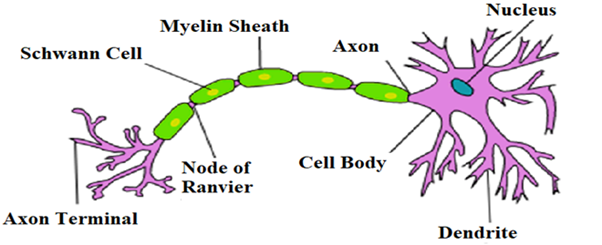
Note: A nerve cell (neuron) consists of a large cell body and nerve fibres one elongated extension (axon) for sending impulses and frequently many branches (dendrites) for receiving impulses. Each large axon is surrounded by oligodendrocytes within the brain and spinal cord and by Schwann cells within the peripheral nervous system.
Complete answer:
Nerves are a set of neurons, which are the individual nerve cells. Our nerves are located throughout our bodies, that is from our skin, through and around our organs and towards their centre, the brain. There are three types of nerves: motor, sensory and mixed.
Sensory nerves also referred to as afferent nerves, carry impulses from sensory receptors towards the brain. Example: These nerves carry the impulses from the sense organs to the brain or to the spinal cord as the optic nerve of the eye.
Motor nerves also referred to as efferent nerves, carry impulses far from the brain to muscles and glands. Example: These nerves have only motor fibres as nerves to the muscles of the eyeball.
Mixed nerves are composed of motor and sensory fibres, and transmit messages in both directions at once. Example: The nerve going to the tongue.
Additional Information: In biology, the nervous system is split into the central nervous system, which incorporates the nerves of the brain and therefore the spine, and therefore the peripheral nervous system which incorporates the remainder of the nerves. The peripheral nervous system encompasses, as a subcategory, the autonomic nervous system which helps the body to regulate involuntary functions including the movements of our heart, stomach, intestines, bladder and sweating.

Note: A nerve cell (neuron) consists of a large cell body and nerve fibres one elongated extension (axon) for sending impulses and frequently many branches (dendrites) for receiving impulses. Each large axon is surrounded by oligodendrocytes within the brain and spinal cord and by Schwann cells within the peripheral nervous system.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




