
Describe the vascular tissue system with the help of diagrams.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Vascular tissue is a complex system of conducting tissues found in plants. All the different types of vascular tissue within a particular plant constitute the vascular tissue system of the plant.
Complete answer:
To solve this question, we have to understand the tissue system of plants. We know that the plants prepare their own food in the leaf by using the water, minerals from the soil and the roots of plants need nutrients to grow and provide support to the plants. So, there must be some kind of connection which helps the passage of water, minerals and nutrients within the different parts of the plants.
Vascular tissues are groups of tissues that transport or conduct the passage of fluid and nutrients. They are arranged in such a way that the passage of transporting materials can be transported easily. The cells in vascular tissues are typically long and slender. Vascular tissue is made up of more than one cell type, found in most of the vascular plants.
The vascular tissue system consists primarily of two types of cells which are xylem and phloem. Both the cells are responsible for the conduction of water, minerals and nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem cells help to transport water and nutrients from roots to stem and are long cells, consisting of two other types of cells known as parenchyma and fibres. Phloem is responsible for transporting sugars and other organic molecules.
Vascular tissues are arranged in the form of long distinct strands which are known as vascular bundles. In addition to the xylem and phloem, the vascular bundles also include other supporting and protecting cells. In between the xylem and phloem, there exists a meristem which is known as vascular cambium.
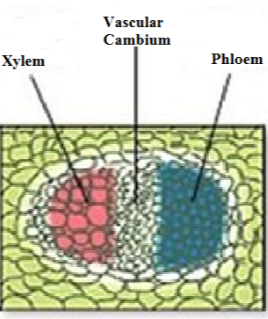
Vascular Bundles
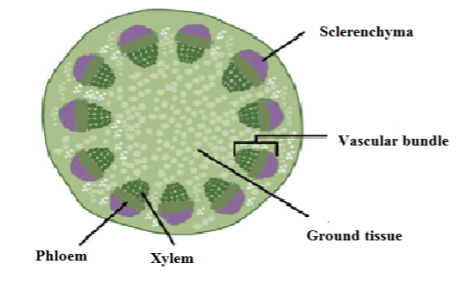
Vascular tissue system in dicot stem
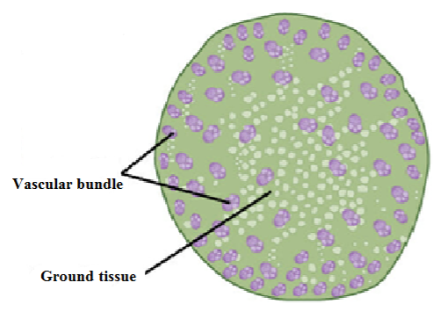
Vascular bundle in monocot stem
Note: The Vascular system acts as the primary conducting system of plants and helps in movement and transportation of water, minerals and nutrients to different parts of the plant. It includes xylem and phloem.
Complete answer:
To solve this question, we have to understand the tissue system of plants. We know that the plants prepare their own food in the leaf by using the water, minerals from the soil and the roots of plants need nutrients to grow and provide support to the plants. So, there must be some kind of connection which helps the passage of water, minerals and nutrients within the different parts of the plants.
Vascular tissues are groups of tissues that transport or conduct the passage of fluid and nutrients. They are arranged in such a way that the passage of transporting materials can be transported easily. The cells in vascular tissues are typically long and slender. Vascular tissue is made up of more than one cell type, found in most of the vascular plants.
The vascular tissue system consists primarily of two types of cells which are xylem and phloem. Both the cells are responsible for the conduction of water, minerals and nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem cells help to transport water and nutrients from roots to stem and are long cells, consisting of two other types of cells known as parenchyma and fibres. Phloem is responsible for transporting sugars and other organic molecules.
Vascular tissues are arranged in the form of long distinct strands which are known as vascular bundles. In addition to the xylem and phloem, the vascular bundles also include other supporting and protecting cells. In between the xylem and phloem, there exists a meristem which is known as vascular cambium.

Vascular Bundles

Vascular tissue system in dicot stem

Vascular bundle in monocot stem
Note: The Vascular system acts as the primary conducting system of plants and helps in movement and transportation of water, minerals and nutrients to different parts of the plant. It includes xylem and phloem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




